univERsity oF copEnhAGEn
... arching, and no buttresses. The bark is reddish and smooth. The imparipinnate leaves are very variable in size, up to 1.5 m long, and mostly clustered at the end of branchlets, with a terminal dormant glandular leaflet. It has 6-18 pairs of opposite or subopposite leaflets, usually oblong-elliptic o ...
... arching, and no buttresses. The bark is reddish and smooth. The imparipinnate leaves are very variable in size, up to 1.5 m long, and mostly clustered at the end of branchlets, with a terminal dormant glandular leaflet. It has 6-18 pairs of opposite or subopposite leaflets, usually oblong-elliptic o ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... plastic bag w/ your name on it. that we will observe in class: Best to bring a Lilly Next best is to bring a large flower where you can see the pistil and stamen. You can go to a florist and ask them of any old flower that they are going to throw away 5 Points ...
... plastic bag w/ your name on it. that we will observe in class: Best to bring a Lilly Next best is to bring a large flower where you can see the pistil and stamen. You can go to a florist and ask them of any old flower that they are going to throw away 5 Points ...
Angiosperms
... o Ex. bees remember the color, shape and odor of a flower it finds food on very clearly • the bee will continue to look for those flowers • on its way to the food (pollen) the bee might pollinate the flower with pollen from the last flower it visited this ensures the survival of the plant o Ex. flow ...
... o Ex. bees remember the color, shape and odor of a flower it finds food on very clearly • the bee will continue to look for those flowers • on its way to the food (pollen) the bee might pollinate the flower with pollen from the last flower it visited this ensures the survival of the plant o Ex. flow ...
seed dispersal
... Cross pollination pollination is transferred from the male part of one plant to the female part of another plant. ...
... Cross pollination pollination is transferred from the male part of one plant to the female part of another plant. ...
invasive species
... massive size of each pampasgrass plant with its accumulated litter reduces wildlife habitat, limits recreational opportunities in conservation areas, and creates a serious fire hazard. ...
... massive size of each pampasgrass plant with its accumulated litter reduces wildlife habitat, limits recreational opportunities in conservation areas, and creates a serious fire hazard. ...
2005 Accomplishments Evaluation of Native Forb and Grass Seed for Areas
... damage, predation, and moisture content. Viability was tested in partnership with Oregon State University Seed Laboratory. In autumn 2004, 18 species were seeded in 20 plots within the burn for on site germination evaluation the remainder were cold stored. In early spring 2005 we germination tested ...
... damage, predation, and moisture content. Viability was tested in partnership with Oregon State University Seed Laboratory. In autumn 2004, 18 species were seeded in 20 plots within the burn for on site germination evaluation the remainder were cold stored. In early spring 2005 we germination tested ...
General Biology 101
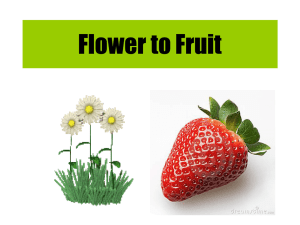
... Endosperm is the nutritious tissue surrounding the embryonic sporophyte in seeds of flowering plants. Fruits are mature ovaries derived from flowers. Their purpose is to help disperse embryonic plants inside the seeds to new destinations (away from the parent plant). Fruits are mature ovaries derive ...
... Endosperm is the nutritious tissue surrounding the embryonic sporophyte in seeds of flowering plants. Fruits are mature ovaries derived from flowers. Their purpose is to help disperse embryonic plants inside the seeds to new destinations (away from the parent plant). Fruits are mature ovaries derive ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
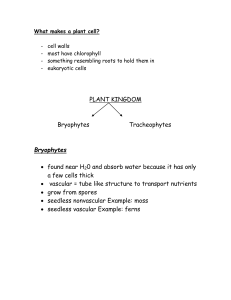
... What are the characteristics of Nonvascular Plants? • Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts • Low growing • Can pass materials only from one cell to the next • Cell walls provide support • They get water directly from their surroundings. ...
... What are the characteristics of Nonvascular Plants? • Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts • Low growing • Can pass materials only from one cell to the next • Cell walls provide support • They get water directly from their surroundings. ...
Mile-a-minute Weed Mile-a-minute Weed
... Common in all three counties. Trailing vine that vigorously climbs into canopy. Inconspicuous white flowers bloom early July to fall. Spherical peasized, blue fruit containing several seeds ripen from early August to fall. Does not tolerate shading. Colonizes open and disturbed areas along the edges ...
... Common in all three counties. Trailing vine that vigorously climbs into canopy. Inconspicuous white flowers bloom early July to fall. Spherical peasized, blue fruit containing several seeds ripen from early August to fall. Does not tolerate shading. Colonizes open and disturbed areas along the edges ...
Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Study Guide List five
... Heterospory indicates that the plant produces two kinds of spores: megaspores and microspores. Explain what each type of spore forms as it develops. ...
... Heterospory indicates that the plant produces two kinds of spores: megaspores and microspores. Explain what each type of spore forms as it develops. ...
Seed Plants
... • Many produce fruit = a wall of tissue surrounding a seed • The seed leaves of plant embryos are called cotyledons • Flowers that complete an entire life cycle within one growing season are called –annuals ...
... • Many produce fruit = a wall of tissue surrounding a seed • The seed leaves of plant embryos are called cotyledons • Flowers that complete an entire life cycle within one growing season are called –annuals ...
Lecture 10, Angiosperms - Cal State LA
... The seeds of many plants cannot develop until they have passed through an animal’s digestive system! ...
... The seeds of many plants cannot develop until they have passed through an animal’s digestive system! ...
Dandelion life from NatureBridge
... • Flowers are expensive for a plant to make. Why bother? (Oddly enough, people used to think plants make flowers for the enjoyment of humans!) • Why do plants get pollinated? (Pollination is plant s ...
... • Flowers are expensive for a plant to make. Why bother? (Oddly enough, people used to think plants make flowers for the enjoyment of humans!) • Why do plants get pollinated? (Pollination is plant s ...
Section Review 22-1 1. Plants are multicellular eukaryotes whose
... multicellular embryos and carry out photosynthesis using the green pigments chlorophyll a and b. 2. The four basic needs of a plant are sunlight, water and minerals, gas exchange, and the transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant body. 3. The ancestors of the first land plants were simil ...
... multicellular embryos and carry out photosynthesis using the green pigments chlorophyll a and b. 2. The four basic needs of a plant are sunlight, water and minerals, gas exchange, and the transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant body. 3. The ancestors of the first land plants were simil ...
Native Plant Facts: Showy tick trefoil
... and nonnative plants are striped. The black line on the top graph shows the number of natural enemies in grass with no flowering plants (grass control). Plants are listed in order of peak bloom. ...
... and nonnative plants are striped. The black line on the top graph shows the number of natural enemies in grass with no flowering plants (grass control). Plants are listed in order of peak bloom. ...
Kingdom – Plantae Phylum - Anthophyta
... Phylum Anthophyta Also known as Angiosperms, or to most people flowering plants ...
... Phylum Anthophyta Also known as Angiosperms, or to most people flowering plants ...
Carissa macrocarpa > Universiteit van Pretoria
... Distribution: It occurs in coastal bush, on sand dunes and at the margins of coastal forest, from the vicinity of Humansdorp northwards through KwaZulu-Natal and just into Mozambique. Name derivation: Carissa is probably derived from “Corissa”, a local name for one of the Indian species. Macrocarpa ...
... Distribution: It occurs in coastal bush, on sand dunes and at the margins of coastal forest, from the vicinity of Humansdorp northwards through KwaZulu-Natal and just into Mozambique. Name derivation: Carissa is probably derived from “Corissa”, a local name for one of the Indian species. Macrocarpa ...
18.1 & 18.2
... D. In Lesson 9, you counted the number of Fast Plants that displayed a purple pigment in their stem and leaves. You recorded this number in your science notebook. You pollinated these plants and harvested their seeds. You chose 36 of these seeds and set them up for germination in your group’s petri ...
... D. In Lesson 9, you counted the number of Fast Plants that displayed a purple pigment in their stem and leaves. You recorded this number in your science notebook. You pollinated these plants and harvested their seeds. You chose 36 of these seeds and set them up for germination in your group’s petri ...
Effects of pollinators and seed predators on female and hermaphrodite... Polemonium foliosissimum
... Gretel L. Clarke, Department of Biology, University of Vermont, Burlington VT ...
... Gretel L. Clarke, Department of Biology, University of Vermont, Burlington VT ...
Dante Matero
... 2. apomixes: asexual production of seeds B. Advantages and Disadvantages of Asexual Versus Sexual Reproduction 1. Vegetative Reproduction: asexual reproduction in plants 2. Can happen very often in vegetables 3. Sexual can increase genetic diversity ...
... 2. apomixes: asexual production of seeds B. Advantages and Disadvantages of Asexual Versus Sexual Reproduction 1. Vegetative Reproduction: asexual reproduction in plants 2. Can happen very often in vegetables 3. Sexual can increase genetic diversity ...
Ecology of Banksia

The ecology of Banksia refers to all the relationships and interactions among the plant genus Banksia and its environment. Banksia has a number of adaptations that have so far enabled the genus to survive despite dry, nutrient-poor soil, low rates of seed set, high rates of seed predation and low rates of seedling survival. These adaptations include proteoid roots and lignotubers; specialised floral structures that attract nectariferous animals and ensure effective pollen transfer; and the release of seed in response to bushfire.The arrival of Europeans in Australia has brought new ecological challenges. European colonisation of Australia has directly affected Banksia through deforestation, exploitation of flowers and changes to the fire regime. In addition, the accidental introduction and spread of plant pathogens such as Phytophthora cinnamomi (dieback) pose a serious threat to the genus's habitat and biodiversity. Various conservation measures have been put in place to mitigate these threats, but a number of taxa remain endangered.