Seed Plants
... Sporophytes of seed plants do not release their spores. Therefore, the small gametophytes are protected and develop within the sporophyte. Both female spores and developing embryos were protected from drying and ...
... Sporophytes of seed plants do not release their spores. Therefore, the small gametophytes are protected and develop within the sporophyte. Both female spores and developing embryos were protected from drying and ...
Reproduction in Flowering Plants
... more carpels. Although the sepals and petals can play an indirect role in reproduction (for example, attracting pollinators), here we'll concentrate on the stamens and carpel—the parts directly involved in reproduction. The stamen, the pollen-containing structure, is composed of two parts: a stalk-l ...
... more carpels. Although the sepals and petals can play an indirect role in reproduction (for example, attracting pollinators), here we'll concentrate on the stamens and carpel—the parts directly involved in reproduction. The stamen, the pollen-containing structure, is composed of two parts: a stalk-l ...
No Slide Title
... • Just remember this: • Male forms haploid tube cell nucleus and generative cell (will form two sperm cells) within pollen grain • Female forms haploid egg and two polar nuclei within embryo sac • (three haploid cells each, to simplify) ...
... • Just remember this: • Male forms haploid tube cell nucleus and generative cell (will form two sperm cells) within pollen grain • Female forms haploid egg and two polar nuclei within embryo sac • (three haploid cells each, to simplify) ...
Sexual Reproduction of the Flowering Plant
... Spore - a reproductive cell capable of developing into a new individual without fusion with another reproductive cell Spores are different than seeds, they do not contain plant embryos or food stores A structure called sporangia produce the very tiny spores ...
... Spore - a reproductive cell capable of developing into a new individual without fusion with another reproductive cell Spores are different than seeds, they do not contain plant embryos or food stores A structure called sporangia produce the very tiny spores ...
Wonder of Flowering Plants
... Self-pollination is when pollen is transferred within the same plant and crosspollination is when pollen is transferred from one plant to another ...
... Self-pollination is when pollen is transferred within the same plant and crosspollination is when pollen is transferred from one plant to another ...
Dante Matero
... b. entire process happens within carpel’s ovary i. produces four haploid megaspores; only one survives ii. undergoes a complicated process which results in the ovule consisting of embryo sac and two surrounding integuments 12. Pollination a. defined as being the transfer of pollen from a single angi ...
... b. entire process happens within carpel’s ovary i. produces four haploid megaspores; only one survives ii. undergoes a complicated process which results in the ovule consisting of embryo sac and two surrounding integuments 12. Pollination a. defined as being the transfer of pollen from a single angi ...
Section 3
... Egg is produced in ovule in spring, male cones release clouds of pollen to fertilize female cones ...
... Egg is produced in ovule in spring, male cones release clouds of pollen to fertilize female cones ...
Worksheet-1 - Al Noor International School
... Self-pollination – pollination within the plant Cross-pollination – pollination with another plant Fertilisation – Fertilisation occurs after pollination. It is the process when a male pollen grain enzymatically ‘drills’ a pollen tube from the stigma down the style to the , and then fuses with ...
... Self-pollination – pollination within the plant Cross-pollination – pollination with another plant Fertilisation – Fertilisation occurs after pollination. It is the process when a male pollen grain enzymatically ‘drills’ a pollen tube from the stigma down the style to the , and then fuses with ...
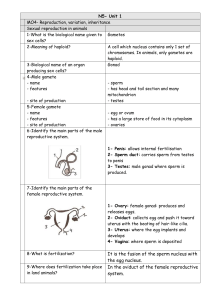
N5- Unit 1 MO4- Reproduction, variation, inheritance Sexual
... 7-Identify the main parts of the female reproductive system. 1- Ovary: female gonad: produces and releases eggs. 2- Oviduct: collects egg and push it toward uterus with the beating of hair-like cilia. 3- Uterus: where the egg implants and ...
... 7-Identify the main parts of the female reproductive system. 1- Ovary: female gonad: produces and releases eggs. 2- Oviduct: collects egg and push it toward uterus with the beating of hair-like cilia. 3- Uterus: where the egg implants and ...
Chapter 38
... •incomplete: lacking 1 or more floral organs •perfect: both stamens and carpels on 1 flower •imperfect: lacking either a stamen or carpel •monoecious: staminate and carpellate flowers on 1 plant) •dioecious: staminate and carpellate flowers on separate plants ...
... •incomplete: lacking 1 or more floral organs •perfect: both stamens and carpels on 1 flower •imperfect: lacking either a stamen or carpel •monoecious: staminate and carpellate flowers on 1 plant) •dioecious: staminate and carpellate flowers on separate plants ...
Reproduction in Angiospermophytes
... • Stamen (entire male part) • Complete – contain sepals, petals, stamen, and carpal • Incomplete – lack at least one part • Staminate – have only stamens • Carpellate – have only carpels ...
... • Stamen (entire male part) • Complete – contain sepals, petals, stamen, and carpal • Incomplete – lack at least one part • Staminate – have only stamens • Carpellate – have only carpels ...
Angiosperms - El Camino College
... Pollination partly responsible for flower diversity Flowers have coevolved with specific animals attract them and assure pollination Bee pollinated flowers have nectar guides that reflect UV light Birds are attracted to bright red and orange but no particular scent Beetles are drawn to fruity odors ...
... Pollination partly responsible for flower diversity Flowers have coevolved with specific animals attract them and assure pollination Bee pollinated flowers have nectar guides that reflect UV light Birds are attracted to bright red and orange but no particular scent Beetles are drawn to fruity odors ...
PLANTS REPRODUCE FLOWERS
... Wind pollination: Other plants are not attractive to insects, but they have long stamens with a lot of pollen grains. The wind carries the pollen of these plants to the stigmas of other flowers. ►FERILIZATION ...
... Wind pollination: Other plants are not attractive to insects, but they have long stamens with a lot of pollen grains. The wind carries the pollen of these plants to the stigmas of other flowers. ►FERILIZATION ...
Plant Reproduction and Development
... adventitious roots and form a whole new plant. – A callus forms first and then the roots grow from that. • If a node is included in the fragment then the callus stage is skipped. ...
... adventitious roots and form a whole new plant. – A callus forms first and then the roots grow from that. • If a node is included in the fragment then the callus stage is skipped. ...
Control
... • Pollen grain- contains the sperm cell • Anthers- produces the pollen grains, located at the end of the stamen • Pollination- the process by which pollen gets from the male anther to the female pistil and down to the egg • Stigma- sticky tip of the pistil • Pollen tube- grows from pollen grain the ...
... • Pollen grain- contains the sperm cell • Anthers- produces the pollen grains, located at the end of the stamen • Pollination- the process by which pollen gets from the male anther to the female pistil and down to the egg • Stigma- sticky tip of the pistil • Pollen tube- grows from pollen grain the ...
CHAPTER 13 PLANT REPRODUCTIVE BIOLOGY REVIEW
... Autogamy–inbreeding that may occur within a single flower Geitonogamy–inbreeding that occurs between flowers derived from one individual. Allautogamy-plant species that have both crossing and selfing flowers. 15. Name some types of inbreeding mechanisms. Some plants are cleistogamous in which the pe ...
... Autogamy–inbreeding that may occur within a single flower Geitonogamy–inbreeding that occurs between flowers derived from one individual. Allautogamy-plant species that have both crossing and selfing flowers. 15. Name some types of inbreeding mechanisms. Some plants are cleistogamous in which the pe ...
Sample exam #2
... as the family and division to which the plant belongs, E) randomly assigned names in Latin without meaning 13. In which of the following taxonomic levels would you find plants that were most closely related? A) kingdom, B) genus, C) family, D) division 19. The pulp of fruit (e.g. the part of an appl ...
... as the family and division to which the plant belongs, E) randomly assigned names in Latin without meaning 13. In which of the following taxonomic levels would you find plants that were most closely related? A) kingdom, B) genus, C) family, D) division 19. The pulp of fruit (e.g. the part of an appl ...
ANGIOSPERMS “flowering plants”
... resemble female wasps. A visiting male wasp attempts to mate and becomes covered with pollen. • Wild orchid wasp mimic ...
... resemble female wasps. A visiting male wasp attempts to mate and becomes covered with pollen. • Wild orchid wasp mimic ...
Pollination

Pollination is a process by which pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma of the plant, thereby enabling fertilization and reproduction. It is unique to the angiosperms, the flower-bearing plants.In spite of a common perception that pollen grains are gametes, like the sperm cells of animals, this is incorrect; pollination is an event in the alternation of generations. Each pollen grain is a male haploid gametophyte, adapted to being transported to the female gametophyte, where it can effect fertilization by producing the male gamete (or gametes), in the process of double fertilization). A successful angiosperm pollen grain (gametophyte) containing the male gametes is transported to the stigma, where it germinates and its pollen tube grows down the style to the ovary. Its two gametes travel down the tube to where the gametophyte(s) containing the female gametes are held within the carpel. One nucleus fuses with the polar bodies to produce the endosperm tissues, and the other with the ovule to produce the embryo Hence the term: ""double fertilization"".In gymnosperms, the ovule is not contained in a carpel, but exposed on the surface of a dedicated support organ, such as the scale of a cone, so that the penetration of carpel tissue is unnecessary. Details of the process vary according to the division of gymnosperms in question.The receptive part of the carpel is called a stigma in the flowers of angiosperms. The receptive part of the gymnosperm ovule is called the micropyle. Pollination is a necessary step in the reproduction of flowering plants, resulting in the production of offspring that are genetically diverse.The study of pollination brings together many disciplines, such as botany, horticulture, entomology, and ecology. The pollination process as an interaction between flower and pollen vector was first addressed in the 18th century by Christian Konrad Sprengel. It is important in horticulture and agriculture, because fruiting is dependent on fertilization: the result of pollination. The study of pollination by insects is known as anthecology.