Chapter 31 FUNGI
... 27. Angiosperm (tip of growing pollen tube headed towards egg). Stigma – style – ovary – micropyle ...
... 27. Angiosperm (tip of growing pollen tube headed towards egg). Stigma – style – ovary – micropyle ...
Plants
... • In seed plants, the haploid gametophytes are male and female; the males occur as pollen and the females occur as seeds • The seed growing on the diploid sporophyte ‘parent’ contains a haploid female gametophyte bearing an egg cell, and is fertilized by a pollen grain which contains a miniature mal ...
... • In seed plants, the haploid gametophytes are male and female; the males occur as pollen and the females occur as seeds • The seed growing on the diploid sporophyte ‘parent’ contains a haploid female gametophyte bearing an egg cell, and is fertilized by a pollen grain which contains a miniature mal ...
File
... o PR is more stable than PFR, so in darkness PFR very gradually changes into PR o PFR is the active form of phytochrome and that the receptor proteins are present in the cytoplasm to which PFR binds, but not PR o Long day plants o ...
... o PR is more stable than PFR, so in darkness PFR very gradually changes into PR o PFR is the active form of phytochrome and that the receptor proteins are present in the cytoplasm to which PFR binds, but not PR o Long day plants o ...
Seed plants notes
... 8 are enclosed within membrane called embryo sac 3 nuclei clump to form polar nuclei one of 3 will become egg other 2 lie on either side of egg nucleus remaining 3 die 2. Inside Anther diploid microspore mother cell produces 4 haploid microspores (meiosis) each becomes immature pollen ...
... 8 are enclosed within membrane called embryo sac 3 nuclei clump to form polar nuclei one of 3 will become egg other 2 lie on either side of egg nucleus remaining 3 die 2. Inside Anther diploid microspore mother cell produces 4 haploid microspores (meiosis) each becomes immature pollen ...
Seed Reproduction
... • Some seeds store food in cotyledons. • Other seeds store food in endosperm tissue ...
... • Some seeds store food in cotyledons. • Other seeds store food in endosperm tissue ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Eunmi LEE
... A flower is a bisexual “cone” (although unisexual flowers have evolved in many groups) ...
... A flower is a bisexual “cone” (although unisexual flowers have evolved in many groups) ...
TIC TAC Plant Parts
... from another flower to this one. • The pollen grains land on the stigma and a pollen tube grows down through the style to the ovary. • The nucleus of the pollen grain passes down the tube. It fertilizes the egg cell inside the ovule. • The fertilized egg cell develops into an embryo. The ovary becom ...
... from another flower to this one. • The pollen grains land on the stigma and a pollen tube grows down through the style to the ovary. • The nucleus of the pollen grain passes down the tube. It fertilizes the egg cell inside the ovule. • The fertilized egg cell develops into an embryo. The ovary becom ...
Lab 4: Seed Plant Diversity
... nucleus. Transfer of the pollen grains to the ovule is termed pollination and union of a sperm nucleus and an egg nucleus is termed fertilization, with a resulting diploid zygote. The zygote will ultimately develop into the new sporophyte generation. The zygote initially develops into an embryo with ...
... nucleus. Transfer of the pollen grains to the ovule is termed pollination and union of a sperm nucleus and an egg nucleus is termed fertilization, with a resulting diploid zygote. The zygote will ultimately develop into the new sporophyte generation. The zygote initially develops into an embryo with ...
topic7 BIOL1030NR
... Phylum Anthophyta – flowering plants (antho – flower) A. also known as angiosperms (angeion – vessel or enclosure; sperma – seed) B. ovules enclosed within carpel (parent diploid sporophytic tissue) at pollination ...
... Phylum Anthophyta – flowering plants (antho – flower) A. also known as angiosperms (angeion – vessel or enclosure; sperma – seed) B. ovules enclosed within carpel (parent diploid sporophytic tissue) at pollination ...
Pollination There are two main groups of plants on planet Earth
... female part of the flower and it has two main parts; a sticky end called the stigma and a hollow structure called an ovary that holds eggs or ovules. ...
... female part of the flower and it has two main parts; a sticky end called the stigma and a hollow structure called an ovary that holds eggs or ovules. ...
The First Flowers Spring - Bob Armstrong`s Nature Alaska
... flower to the female part, or from male to female flowers. Pollination is necessary to produce seeds, one of the ways in which plants reproduce. We can think of a number of ways that being first out of the starting gate would help plants with pollination. Perhaps competition for insects or birds to ...
... flower to the female part, or from male to female flowers. Pollination is necessary to produce seeds, one of the ways in which plants reproduce. We can think of a number of ways that being first out of the starting gate would help plants with pollination. Perhaps competition for insects or birds to ...
Male Parts Anther
... The structure of the flower that develops into a seed when fertilized. (eggs) ...
... The structure of the flower that develops into a seed when fertilized. (eggs) ...
KINGDOMS OF ORGANISMS
... Pollen lands on the stigma Pollen tube grows down through the style to the ovary Sperm nuclei are carried along the pollen tube Pollen tube enters the ovule Sperm nucleus fuses with the egg and forms a zygote ...
... Pollen lands on the stigma Pollen tube grows down through the style to the ovary Sperm nuclei are carried along the pollen tube Pollen tube enters the ovule Sperm nucleus fuses with the egg and forms a zygote ...
sexual-reproduction-in-plants-2
... in ovules in the plant. d) The male gamete present in the pollen grain fertilizes the female gamete present in the ovule to produce a zygote, which undergoes further divisions to form an embryo. e) The fertilized ovules grow and become seeds. f) The seeds give rise to new plants when they germinate. ...
... in ovules in the plant. d) The male gamete present in the pollen grain fertilizes the female gamete present in the ovule to produce a zygote, which undergoes further divisions to form an embryo. e) The fertilized ovules grow and become seeds. f) The seeds give rise to new plants when they germinate. ...
Plant Ecology - Chapter 7
... Wind-pollinated flowers are not showy Waste of energy to produce big, colorful petals, scents, nectar Grasses often lack petals, sepals (interfere with pollen transfer by wind) ...
... Wind-pollinated flowers are not showy Waste of energy to produce big, colorful petals, scents, nectar Grasses often lack petals, sepals (interfere with pollen transfer by wind) ...
The Temple of Flora
... flower of a male is sprinkled, it ripens the fruit and prevents its falling off. The males in all trees are more dense and branching, harder and less fat; their fruits are small and do not ripen; with the females, however, it is the other way round. Many times, when the wind is strong, it carries th ...
... flower of a male is sprinkled, it ripens the fruit and prevents its falling off. The males in all trees are more dense and branching, harder and less fat; their fruits are small and do not ripen; with the females, however, it is the other way round. Many times, when the wind is strong, it carries th ...
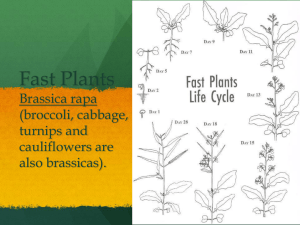
Fast Plants
... Seeds mature and ripen. Lower leaves yellow and dry. Twenty days after final pollination plants should be removed from water. Day 38 – 45: Plants dry down and pods turn yellow. Day 45: Pods can be removed from dried plants. Seeds can be harvested. The cycle is complete. ...
... Seeds mature and ripen. Lower leaves yellow and dry. Twenty days after final pollination plants should be removed from water. Day 38 – 45: Plants dry down and pods turn yellow. Day 45: Pods can be removed from dried plants. Seeds can be harvested. The cycle is complete. ...
American Basketflower Fact Sheet
... high in sugar and amino acids. Pollen is high in protein. The plant is visited by a wide variety of hummingbirds, songbirds, butterflies, moths, bees, beetles and a host of other insects. Stamens are reported to suddenly contract and push pollen onto pollinator when touched. Bumblebees are major vis ...
... high in sugar and amino acids. Pollen is high in protein. The plant is visited by a wide variety of hummingbirds, songbirds, butterflies, moths, bees, beetles and a host of other insects. Stamens are reported to suddenly contract and push pollen onto pollinator when touched. Bumblebees are major vis ...
Name: Period: Date: Lesson 1-6 Study Guide Lesson 1: What are
... 2. How are perfect and imperfect flowers different? - A perfect flower contain both male and female parts. - An imperfect flower contains only male or only female parts. 3. What is the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination? - Self-pollination is when pollen from the same plant ar ...
... 2. How are perfect and imperfect flowers different? - A perfect flower contain both male and female parts. - An imperfect flower contains only male or only female parts. 3. What is the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination? - Self-pollination is when pollen from the same plant ar ...
Incomplete - Watermelon.org
... a flower. Plants with incomplete flowers are divided into two groups, dioecious or monoecious. Dioecious plants have only male or only female flowers on a single plant. The watermelon is part of the botanical family called Cucurbitaceae. These plants are monoecious – producing both male (staminate) ...
... a flower. Plants with incomplete flowers are divided into two groups, dioecious or monoecious. Dioecious plants have only male or only female flowers on a single plant. The watermelon is part of the botanical family called Cucurbitaceae. These plants are monoecious – producing both male (staminate) ...
Reproduction in Flowering Plants
... grains grow in the anther. • Filament- long thread that holds the anther. • When the grains are fully grown, the anther splits open. ...
... grains grow in the anther. • Filament- long thread that holds the anther. • When the grains are fully grown, the anther splits open. ...
Chapter 31.1
... (filament) capped with an anther, inside which pollen sacs enclose pollen grains Carpels: female parts, vessel shaped structures with an expanded lower ovary (with ovules), slender column (style), and an upper surface (stigma) for pollen landing ...
... (filament) capped with an anther, inside which pollen sacs enclose pollen grains Carpels: female parts, vessel shaped structures with an expanded lower ovary (with ovules), slender column (style), and an upper surface (stigma) for pollen landing ...
Bee, Butterfly, and Hummingbird Gardens
... individual scattered plants. Where space allows, make the clumps four feet or more in diameter. Have a diversity of plants flowering all season. By having several plant species flowering at once, and a sequence of plants flowering through spring, summer and fall, you can support a range of species t ...
... individual scattered plants. Where space allows, make the clumps four feet or more in diameter. Have a diversity of plants flowering all season. By having several plant species flowering at once, and a sequence of plants flowering through spring, summer and fall, you can support a range of species t ...
plantae - Baldwin Schools Teachers
... male part of the flower that produces the __________________ Pollen grains--sperm ...
... male part of the flower that produces the __________________ Pollen grains--sperm ...
Pollination

Pollination is a process by which pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma of the plant, thereby enabling fertilization and reproduction. It is unique to the angiosperms, the flower-bearing plants.In spite of a common perception that pollen grains are gametes, like the sperm cells of animals, this is incorrect; pollination is an event in the alternation of generations. Each pollen grain is a male haploid gametophyte, adapted to being transported to the female gametophyte, where it can effect fertilization by producing the male gamete (or gametes), in the process of double fertilization). A successful angiosperm pollen grain (gametophyte) containing the male gametes is transported to the stigma, where it germinates and its pollen tube grows down the style to the ovary. Its two gametes travel down the tube to where the gametophyte(s) containing the female gametes are held within the carpel. One nucleus fuses with the polar bodies to produce the endosperm tissues, and the other with the ovule to produce the embryo Hence the term: ""double fertilization"".In gymnosperms, the ovule is not contained in a carpel, but exposed on the surface of a dedicated support organ, such as the scale of a cone, so that the penetration of carpel tissue is unnecessary. Details of the process vary according to the division of gymnosperms in question.The receptive part of the carpel is called a stigma in the flowers of angiosperms. The receptive part of the gymnosperm ovule is called the micropyle. Pollination is a necessary step in the reproduction of flowering plants, resulting in the production of offspring that are genetically diverse.The study of pollination brings together many disciplines, such as botany, horticulture, entomology, and ecology. The pollination process as an interaction between flower and pollen vector was first addressed in the 18th century by Christian Konrad Sprengel. It is important in horticulture and agriculture, because fruiting is dependent on fertilization: the result of pollination. The study of pollination by insects is known as anthecology.