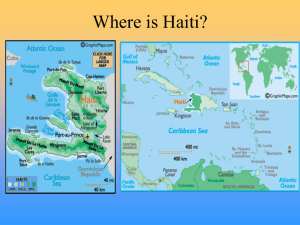
Heart regeneration
... which is intrinsically difficult to prove, or whether it occurs but at very low rates, which is not easy to detect but possible using highly sensitive approaches. This is more than an academic argument. Heart failure is a burgeoning public health problem, and some predict that it will reach epidemic ...
... which is intrinsically difficult to prove, or whether it occurs but at very low rates, which is not easy to detect but possible using highly sensitive approaches. This is more than an academic argument. Heart failure is a burgeoning public health problem, and some predict that it will reach epidemic ...
Solutions for all Natural Sciences Grade 9 Learner`s Book
... Hundreds of years ago scientists used glass lenses to magnify objects. The lenses did not magnify well and very small objects could not be seen. By the 16th century, scientists used microscopes, but they also did not magnify objects very well. It was only during the 17th century that microscopes wit ...
... Hundreds of years ago scientists used glass lenses to magnify objects. The lenses did not magnify well and very small objects could not be seen. By the 16th century, scientists used microscopes, but they also did not magnify objects very well. It was only during the 17th century that microscopes wit ...
Melanization and Hemocyte Homeostasis in the Freshwater
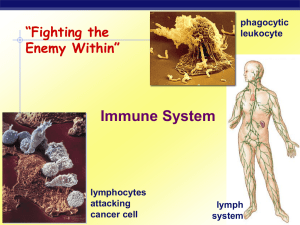
... that is present in all multicellular organisms, whereas adaptive immunity is found only in vertebrates. The major difference between these two systems is that the innate immune system lacks memory, which is produced in the form of antibodies, which are proteins that are produced by cells of lymphoid ...
... that is present in all multicellular organisms, whereas adaptive immunity is found only in vertebrates. The major difference between these two systems is that the innate immune system lacks memory, which is produced in the form of antibodies, which are proteins that are produced by cells of lymphoid ...
Organ
... Organ Systems where BLOOD Tissue is found: The Circulatory System is responsible for delivering oxygen and food to all the cells in the body. Circulatory System ...
... Organ Systems where BLOOD Tissue is found: The Circulatory System is responsible for delivering oxygen and food to all the cells in the body. Circulatory System ...
Respiratory
... The respiratory system structurally consists of paired lungs and the air conduction ways that connect to them. The latter includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea and extra-pulmonary bronchi. As in all large organ systems, the respiratory system performs a number of functions: 1. Respirat ...
... The respiratory system structurally consists of paired lungs and the air conduction ways that connect to them. The latter includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea and extra-pulmonary bronchi. As in all large organ systems, the respiratory system performs a number of functions: 1. Respirat ...
structural organisation in animals
... provide strength, elasticity and flexibility to the tissue. These cells also secrete modified polysaccharides, which accumulate between cells and fibres and act as matrix (ground substance). Connective tissues are classified into three types: (i) Loose connective tissue, (ii) Dense connective tissue ...
... provide strength, elasticity and flexibility to the tissue. These cells also secrete modified polysaccharides, which accumulate between cells and fibres and act as matrix (ground substance). Connective tissues are classified into three types: (i) Loose connective tissue, (ii) Dense connective tissue ...
Lymph nodes
... • Empties into venous circulation • Junction of left internal jugular and left subclavian veins • Drains three quarters of the body Right lymphatic duct - empties into right internal jugular and subclavian veins ...
... • Empties into venous circulation • Junction of left internal jugular and left subclavian veins • Drains three quarters of the body Right lymphatic duct - empties into right internal jugular and subclavian veins ...
Document
... • Living tissue. Contains nerves, blood vessels, cells • Formed by cells called ___________, which secrete collagen matrix in which Ca and P salts later deposited. These cells then called osteocytes. • Usually forms by replacing cartilage in embryo and at ends of major bones as they grow (endochondr ...
... • Living tissue. Contains nerves, blood vessels, cells • Formed by cells called ___________, which secrete collagen matrix in which Ca and P salts later deposited. These cells then called osteocytes. • Usually forms by replacing cartilage in embryo and at ends of major bones as they grow (endochondr ...
What is Blood?
... How does this help the release of oxygen? The size of a red blood cell forces it to slow down as it passes through a capillary. The surface of the red blood cell is exposed to the surface of the capillary and so gas exchange will definitely happen. 19 of 40 ...
... How does this help the release of oxygen? The size of a red blood cell forces it to slow down as it passes through a capillary. The surface of the red blood cell is exposed to the surface of the capillary and so gas exchange will definitely happen. 19 of 40 ...
Primary endothelial cells isolated from the yolk sac
... The primary sites of hematopoiesis change during murine ontogeny. The murine yolk sac is well known as the first site of blood cell production.1 Primitive erythroid colony-forming cells (EryP) emerge at embryonic 7.0 days after coitus (dpc) along with minimal numbers of macrophage and megakaryocyte ...
... The primary sites of hematopoiesis change during murine ontogeny. The murine yolk sac is well known as the first site of blood cell production.1 Primitive erythroid colony-forming cells (EryP) emerge at embryonic 7.0 days after coitus (dpc) along with minimal numbers of macrophage and megakaryocyte ...
Cells, diffusion and osmosis - Pearson-Global
... each began as just a single cell. How do all these different cells arise? In a tiny embryo, each cell has the ability to divide and form new cells, and these new cells are able to turn into any of the different kinds of cells that make up your body (Figure 2.1). Cells that can do this are called ste ...
... each began as just a single cell. How do all these different cells arise? In a tiny embryo, each cell has the ability to divide and form new cells, and these new cells are able to turn into any of the different kinds of cells that make up your body (Figure 2.1). Cells that can do this are called ste ...
BIOL_105_PRACTICE__FINAL_Exam_Q
... A) mitosis with no increase in cell size. B) mitosis with increase in cell size. C) migration of cells after division. D) formation of the extra-embryonic membranes. 11. The _____ is where fetal blood exchanges molecules with maternal blood. A) uterus B) vagina C) placenta D) umbilical cord 12. The ...
... A) mitosis with no increase in cell size. B) mitosis with increase in cell size. C) migration of cells after division. D) formation of the extra-embryonic membranes. 11. The _____ is where fetal blood exchanges molecules with maternal blood. A) uterus B) vagina C) placenta D) umbilical cord 12. The ...
Researcher Faked Evidence of Human Cloning, Koreans Report
... extraordinary number, given the pain and difficulty of extracting eggs from their donors. The cell colony he presented in his 2004 report as being derived from a person was in fact a human egg, induced to develop by parthenogenesis, also known informally as virgin birth because no sperm is used. Wit ...
... extraordinary number, given the pain and difficulty of extracting eggs from their donors. The cell colony he presented in his 2004 report as being derived from a person was in fact a human egg, induced to develop by parthenogenesis, also known informally as virgin birth because no sperm is used. Wit ...
Extracellular matrix stiffness in regulation of intestinal stem cell
... The balance between self-renewal and differentiation of the stem cells is crucial for accurate tissue renewal. What are the characteristics determining which progeny goes through transit amplification followed by terminal differentiation and which retains its stemness and exists as a stem cell? The ...
... The balance between self-renewal and differentiation of the stem cells is crucial for accurate tissue renewal. What are the characteristics determining which progeny goes through transit amplification followed by terminal differentiation and which retains its stemness and exists as a stem cell? The ...
Tissues
... by these two major groups of organisms, particularly in their different feeding methods. Also, they are differently adapted for a sedentary existence on one hand (plants) and active locomotion on the other (animals), contributing to this difference in organ system design. It is with reference to the ...
... by these two major groups of organisms, particularly in their different feeding methods. Also, they are differently adapted for a sedentary existence on one hand (plants) and active locomotion on the other (animals), contributing to this difference in organ system design. It is with reference to the ...
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
... amplification of the loxP-KAN-loxP construct in plasmid pUG6 and pFA6a and primers specific for the gene of interest (Longtine et al, 1998). Strains were then selected on the appropriate selective media and specific disruption was confirmed by PCR analysis of genomic DNA. For the LMB treatment, cell ...
... amplification of the loxP-KAN-loxP construct in plasmid pUG6 and pFA6a and primers specific for the gene of interest (Longtine et al, 1998). Strains were then selected on the appropriate selective media and specific disruption was confirmed by PCR analysis of genomic DNA. For the LMB treatment, cell ...
Multicellular Organisms National 5 Biology: Learning Outcomes
... 4. Explain how xylem vessels are specialised to their function. 5. Describe the movement of water through a plant from the root to the leaf. 6. Define transpiration. 7. Give examples of environmental factors that could increase transpiration ...
... 4. Explain how xylem vessels are specialised to their function. 5. Describe the movement of water through a plant from the root to the leaf. 6. Define transpiration. 7. Give examples of environmental factors that could increase transpiration ...
2010-2011 Human Body Systems iv
... For homework tonight… Complete a new unit title page on the left side of your notebook under today’s bell work. For your unit page for this unit, I want you to draw two body systems INSIDE the human body. The first is the system with which you are most familiar. The second system should be one that ...
... For homework tonight… Complete a new unit title page on the left side of your notebook under today’s bell work. For your unit page for this unit, I want you to draw two body systems INSIDE the human body. The first is the system with which you are most familiar. The second system should be one that ...
Red Blood Cells
... and acts as a solvent to dissolve materials such as waste products, salts, glucose, food molecules, vitamins, hormones and proteins that are carried by the blood to all parts of the body. What is Plasma Continue ...
... and acts as a solvent to dissolve materials such as waste products, salts, glucose, food molecules, vitamins, hormones and proteins that are carried by the blood to all parts of the body. What is Plasma Continue ...
K CHAPTER 2: BODY TISSUES AND MEMBRANES At the end of
... reach the epithelium; thus, all gases and nutrients carried in the blood must reach the epithelium by diffusing from blood vessels with many layers of cells, the most metabolically active cells are close to the basement membrane, 6. Epithelial cells retain the ability to undergo mitosis and therefor ...
... reach the epithelium; thus, all gases and nutrients carried in the blood must reach the epithelium by diffusing from blood vessels with many layers of cells, the most metabolically active cells are close to the basement membrane, 6. Epithelial cells retain the ability to undergo mitosis and therefor ...
Summary/Reflection of Dan Freedman`s article, Science Education
... Compare this with positive feedback, in which an action intensifies a condition so that it is driven further beyond normal limits. a. Such positive feedback is uncommon but does occur during childbirth (labor contractions), lactation (where milk production increases in response to an increase in nur ...
... Compare this with positive feedback, in which an action intensifies a condition so that it is driven further beyond normal limits. a. Such positive feedback is uncommon but does occur during childbirth (labor contractions), lactation (where milk production increases in response to an increase in nur ...
LEH Physiology.tst
... 66) Which of the following correctly lists the order of the parts of the human digestive system, from first to last contact with food matter? A) oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine B) pharynx, oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, large intestine C) esophagus, phar ...
... 66) Which of the following correctly lists the order of the parts of the human digestive system, from first to last contact with food matter? A) oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine B) pharynx, oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, large intestine C) esophagus, phar ...
Hematopoietic stem cell
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the blood cells that give rise to all the other blood cells and are derived from mesoderm. They are located in the red bone marrow, which is contained in the core of most bones.They give rise to both the myeloid and lymphoid lineages of blood cells. (Myeloid cells include monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, erythrocytes, dendritic cells, and megakaryocytes or platelets. Lymphoid cells include T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.) The definition of hematopoietic stem cells has changed in the last two decades. The hematopoietic tissue contains cells with long-term and short-term regeneration capacities and committed multipotent, oligopotent, and unipotent progenitors. HSCs constitute 1:10.000 of cells in myeloid tissue.HSCs are a heterogeneous population. The third category consists of the balanced (Bala) HSC, whose L/M ratio is between 3 and 10. Only the myeloid-biased and -balanced HSCs have durable self-renewal properties. In addition, serial transplantation experiments have shown that each subtype preferentially re-creates its blood cell type distribution, suggesting an inherited epigenetic program for each subtype.HSC studies through much of the past half century have led to a much deeper understanding. More recent advances have resulted in the use of HSC transplants in the treatment of cancers and other immune system disorders.