Sculptures of the Sixth Century
... • The Cycladic figures originally looked quite different because they were painted • Most depict women, but male figures also exist • Their function remains unknown, but some scholars suggest they were used for home worship and then buried with their owner ...
... • The Cycladic figures originally looked quite different because they were painted • Most depict women, but male figures also exist • Their function remains unknown, but some scholars suggest they were used for home worship and then buried with their owner ...
Ancient Greece - WordPress.com
... Oracle of Delphi Dating back to 1400 BC, the Oracle of Delphi was the most important shrine in all Greece, and in theory all Greeks respected its independence. Built around a sacred spring, Delphi was considered to be the omphalos - the center (literal navel) of the world. People came from all over ...
... Oracle of Delphi Dating back to 1400 BC, the Oracle of Delphi was the most important shrine in all Greece, and in theory all Greeks respected its independence. Built around a sacred spring, Delphi was considered to be the omphalos - the center (literal navel) of the world. People came from all over ...
Greece, Anon. Kore, painted marble c.530 BC
... water appear. Athena took Poseidon water and caused an olive tree to grow. The olive tree was considered the greatest gift and so Athena was chosen to be the goddess of the city. The temple uses the ionic column order, known for the scroll like design on the capital. Ionic was a slender graceful col ...
... water appear. Athena took Poseidon water and caused an olive tree to grow. The olive tree was considered the greatest gift and so Athena was chosen to be the goddess of the city. The temple uses the ionic column order, known for the scroll like design on the capital. Ionic was a slender graceful col ...
Classical Greece: Politics, Geography, and Economy
... • Citizens loyal to city-state (“Polis”), not all Greece • Each polis had its own patron god/ess ...
... • Citizens loyal to city-state (“Polis”), not all Greece • Each polis had its own patron god/ess ...
Minoa and Mycenae - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... human traits. Men could go against the gods and win, but not often. ...
... human traits. Men could go against the gods and win, but not often. ...
Athenian Government What was an Independent Polis, in ancient
... motorcycle or delivery truck. Temple of Olympian Zeus- The graceful ruins originally had 104 Corinthian columns, each 17 meters high; 48 of these stood in triple rows under the pediments and 56 in double rows at the sides. Only 15 columns remain standing today, with lovely Corinthian capitals still ...
... motorcycle or delivery truck. Temple of Olympian Zeus- The graceful ruins originally had 104 Corinthian columns, each 17 meters high; 48 of these stood in triple rows under the pediments and 56 in double rows at the sides. Only 15 columns remain standing today, with lovely Corinthian capitals still ...
Honors 680
... What’s a playwright to do when his society seems bent on its own destruction? Is there anything he can do with his art to change reckless attitudes or to halt ruinous policies? Should he provide his fellow citizens with a critical perspective on their folly or offer them a temporary escape and relie ...
... What’s a playwright to do when his society seems bent on its own destruction? Is there anything he can do with his art to change reckless attitudes or to halt ruinous policies? Should he provide his fellow citizens with a critical perspective on their folly or offer them a temporary escape and relie ...
The City of Athens 21H.237
... Reading the Acropolis One of the main challenges in ‘reading’ the Athenian Acropolis is developing an interpretation that accounts both for the many and various details of the archaeological remains of the site (e.g. the Parthenon pediments, metopes, frieze, statue of Athena, the Nike temple decorat ...
... Reading the Acropolis One of the main challenges in ‘reading’ the Athenian Acropolis is developing an interpretation that accounts both for the many and various details of the archaeological remains of the site (e.g. the Parthenon pediments, metopes, frieze, statue of Athena, the Nike temple decorat ...
Ancient Greece: Day 2
... – Thermopylae; attack by Xerxes (son of Darius), Persia won (480 BCE) – Naval battle of Salamis, Athens won – Final battle of Platea, land battle won by Spartans, drove off Persians ...
... – Thermopylae; attack by Xerxes (son of Darius), Persia won (480 BCE) – Naval battle of Salamis, Athens won – Final battle of Platea, land battle won by Spartans, drove off Persians ...
here - CBE Project Server
... produced a huge stream of gushing seawater. He promised the civilians great success with trade over seas. The Greeks were tired of all the warfare at sea and Poseidon’s gift reminded them of war too much. They anxiously awaited to see Athena’s gift. Athena then struck her staff on the Acropolis rock ...
... produced a huge stream of gushing seawater. He promised the civilians great success with trade over seas. The Greeks were tired of all the warfare at sea and Poseidon’s gift reminded them of war too much. They anxiously awaited to see Athena’s gift. Athena then struck her staff on the Acropolis rock ...
Although he is of age and Athens is at war Hippolytos chooses not to
... shedding my dress of saffron, I served as a Bear for Artemis in the Brauronia festival; finally, having grown into a tall and comely young girl, I served as kanephoros and wore a necklace of figs.” ...
... shedding my dress of saffron, I served as a Bear for Artemis in the Brauronia festival; finally, having grown into a tall and comely young girl, I served as kanephoros and wore a necklace of figs.” ...
Chapter 4 Greece and Iran
... Taught that the world as we see it is a reflection of a higher, ideal reality. ...
... Taught that the world as we see it is a reflection of a higher, ideal reality. ...
HUM 2210 Name: Instructor: Paloma Rodriguez Summer 2010 http
... 3. F (T) Sparta came out of the Persian Wars as a ruling power. (Athens did so too, so this can be true or false. Athens emerged more as an imperial power than Sparta) 4. F Athens flourished after the Peloponnesian war.(Athens was defeated by the Spartans in the Peloponnesian war and it never recov ...
... 3. F (T) Sparta came out of the Persian Wars as a ruling power. (Athens did so too, so this can be true or false. Athens emerged more as an imperial power than Sparta) 4. F Athens flourished after the Peloponnesian war.(Athens was defeated by the Spartans in the Peloponnesian war and it never recov ...
the erechtheum
... The North Porch also had six Ionic columns, four in front and one at each side. In this area were the signs of Poseidon’s contest with Athena, namely the marks of his trident and a salt water well. The marks of the trident were to be found in a corner of this porch, above which was an opening in the ...
... The North Porch also had six Ionic columns, four in front and one at each side. In this area were the signs of Poseidon’s contest with Athena, namely the marks of his trident and a salt water well. The marks of the trident were to be found in a corner of this porch, above which was an opening in the ...
Greek City-States INFO
... games were held every Olympiad (i.e. every four years), the Olympic Games dating back possibly further than 776 BC. Olympia is also known for the gigantic ivory and gold statue of Zeus that used to stand there, sculpted by Pheidias, which was named one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World by An ...
... games were held every Olympiad (i.e. every four years), the Olympic Games dating back possibly further than 776 BC. Olympia is also known for the gigantic ivory and gold statue of Zeus that used to stand there, sculpted by Pheidias, which was named one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World by An ...
The Acropolis and Parthenon
... deity (goddess) of Athens. Each would give the city one gift and the Athenians would choose which they preferred. Poseidon struck the ground and a spring sprung up; the water was salty and not very useful, whereas Athena offered them the olive tree. The Athenians accepted the olive tree and Athena a ...
... deity (goddess) of Athens. Each would give the city one gift and the Athenians would choose which they preferred. Poseidon struck the ground and a spring sprung up; the water was salty and not very useful, whereas Athena offered them the olive tree. The Athenians accepted the olive tree and Athena a ...
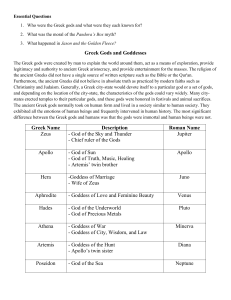
Greek Gods and Goddesses
... Furthermore, the ancient Greeks did not believe in absolute truth as practiced by modern faiths such as Christianity and Judaism. Generally, a Greek city-state would devote itself to a particular god or a set of gods, and depending on the location of the city-state, the characteristics of the gods c ...
... Furthermore, the ancient Greeks did not believe in absolute truth as practiced by modern faiths such as Christianity and Judaism. Generally, a Greek city-state would devote itself to a particular god or a set of gods, and depending on the location of the city-state, the characteristics of the gods c ...
The functions and rituals of these two temples are mostly different.
... Parthenon, the introduction would read as follows: On the left is the Temple of Amun-Ra, in Karnak, Egypt (c. 1280 BCE, New Kingdom Egypt) and on the right is the Parthenon, in Athens, Greece (c. 450 BCE, Classical Greece). They are similar in that they are monumental temples designed for limited ac ...
... Parthenon, the introduction would read as follows: On the left is the Temple of Amun-Ra, in Karnak, Egypt (c. 1280 BCE, New Kingdom Egypt) and on the right is the Parthenon, in Athens, Greece (c. 450 BCE, Classical Greece). They are similar in that they are monumental temples designed for limited ac ...
greek art - TeacherWeb
... Nike, meaning "Victory", was a goddess who personified triumph and victory. She was capable of running and flying at great speeds. ...
... Nike, meaning "Victory", was a goddess who personified triumph and victory. She was capable of running and flying at great speeds. ...
Classical Antiquity review
... at the center of Greek culture. ► Proportion, balance and unity were key Greek ideals. ► The human body was considered beautiful and perfectly proportioned. ...
... at the center of Greek culture. ► Proportion, balance and unity were key Greek ideals. ► The human body was considered beautiful and perfectly proportioned. ...
Architecture in Ancient Greece
... You and your group members are Greek architects. You have been asked to design a new temple in Athens. The temple must reflect traditional Greek architecture. You must choose to build the temple in Doric, Ionic, or Corinthian style. Your model must be 3D and must be made entirely out of paper. You w ...
... You and your group members are Greek architects. You have been asked to design a new temple in Athens. The temple must reflect traditional Greek architecture. You must choose to build the temple in Doric, Ionic, or Corinthian style. Your model must be 3D and must be made entirely out of paper. You w ...
Ancient Greece - The Lesson Builder
... warriors – at the early age of 7 boys began learning fighting skills such as archery, javelin throwing, and sword-fighting Artemis and Ares-(god of war)were the patron gods – Artemis is the goddess of the hunt Spartans form of government was a monarchy and transitioned into a oligarchy - Spartan lea ...
... warriors – at the early age of 7 boys began learning fighting skills such as archery, javelin throwing, and sword-fighting Artemis and Ares-(god of war)were the patron gods – Artemis is the goddess of the hunt Spartans form of government was a monarchy and transitioned into a oligarchy - Spartan lea ...
Visual Locating Greece
... Communities dwelt on the green areas so they were isolated from one another. ...
... Communities dwelt on the green areas so they were isolated from one another. ...
Brauron

The sanctuary of Artemis at Brauron (Hellenic: Βραυρών; or Βραυρώνα Vravrona or Vravronas) is an early sacred site on the eastern coast of Attica near the Aegean Sea in a small inlet. The inlet has silted up since ancient times, pushing the current shoreline farther from the site. A nearby hill, c. 24 m high and 220 m to the southeast, was inhabited during the Neolithic era, c. 2000 BCE, and flourished particularly from Middle Helladic to early Mycenaean times (2000–1600 BC) as a fortified site (acropolis). Occupation ceased in the LHIIIb period, and the acropolis was never significantly resettled after this time. There is a gap in the occupation of the site from LHIIIb until the 8th century BCE. Brauron was one of the twelve ancient settlements of Attica prior to the synoikismos of Theseus, who unified them with Athens.The cult of Artemis Brauronia connected the coastal (rural) sanctuary at Brauron with another (urban) sanctuary on the acropolis in Athens, the Brauroneion, from which there was a procession every four years during the Arkteia festival. The tyrant Pisistratus was Brauronian by birth, and he is credited with transferring the cult to the Acropolis, thus establishing it on the statewide rather than local level. The sanctuary contained a small temple of Artemis, a unique stone bridge, cave shrines, a sacred spring, and a pi-shaped (Π) stoa that included dining rooms for ritual feasting. The unfortified site continued in use until tensions between the Athenians and the Macedonians the 3rd century BCE caused it to be abandoned. After that time, no archaeologically significant activity occurred at the site until the erection of a small church in the 6th century CE.Votive dedications at the sanctuary include a number of statues of young children of both sexes, as well as many items pertaining to feminine life, such as jewelry boxes and mirrors. Large numbers of miniature kraters (krateriskoi) have been recovered from the site, many depicting young girls — either nude or clothed — racing or dancing. The Archaeological Museum of Brauron — located around a small hill 330 m to the ESE — contains an extensive and important collection of finds from the site throughout its period of use.