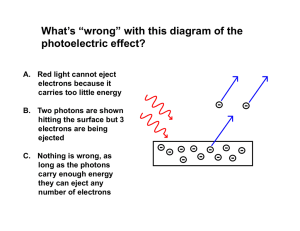
n - Egloos
... are mutually attracted is negative. For the system to be bound, the total energy, the sum of the positive kinetic energy and the total negative potential energy, must be negative. For a classical particle subject to an inverse-square attractive force (such as two oppositely charged particles or two ...
... are mutually attracted is negative. For the system to be bound, the total energy, the sum of the positive kinetic energy and the total negative potential energy, must be negative. For a classical particle subject to an inverse-square attractive force (such as two oppositely charged particles or two ...
Today: Bohr Model - University of Colorado Boulder
... separate positive and negative charges, and there is an increase in the electrostatic potential energy of the electron. c. energy of electron increases because it takes energy input to separate positive and negative charges, and there is a decrease in the electrostatic potential energy of the electr ...
... separate positive and negative charges, and there is an increase in the electrostatic potential energy of the electron. c. energy of electron increases because it takes energy input to separate positive and negative charges, and there is a decrease in the electrostatic potential energy of the electr ...
Document
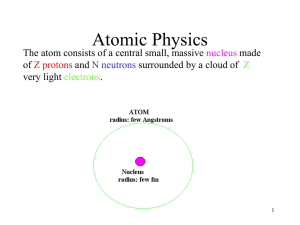
... Atomic Physics Early models of the atom Atomic spectra Bohr’s theory of hydrogen De Broglie wavelength in the atom Quantum mechanics and Spin Chapter 28 ...
... Atomic Physics Early models of the atom Atomic spectra Bohr’s theory of hydrogen De Broglie wavelength in the atom Quantum mechanics and Spin Chapter 28 ...
Lectures - University of Toronto Physics
... -international researchers give talks about their work -cookies & coffee available beforehand (3:45-4) in MP110 -first colloquium this year: Prof. Wolfgang Ketterle MIT (22 Sept) -many other talks/seminars offered every week. See posters near elevators or Physics Dept. website “EVENTS” page. ...
... -international researchers give talks about their work -cookies & coffee available beforehand (3:45-4) in MP110 -first colloquium this year: Prof. Wolfgang Ketterle MIT (22 Sept) -many other talks/seminars offered every week. See posters near elevators or Physics Dept. website “EVENTS” page. ...
Atoms: Some Basics
... good science) to study it in the simplest situation where it is manifest. With atoms it is evident that hydrogen is of paramount simplicity and, much of the “fundamental” physics which has been discovered in atoms has been discovered in hydrogen (but Na and other alkalis have taken over since tunabl ...
... good science) to study it in the simplest situation where it is manifest. With atoms it is evident that hydrogen is of paramount simplicity and, much of the “fundamental” physics which has been discovered in atoms has been discovered in hydrogen (but Na and other alkalis have taken over since tunabl ...
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics
... The Bohr model served well as a first approximation for a single electron atom. Bohr himself supported his model as only the first step toward a comprehensive quantum theory. In spite of refinements (such as elliptical orbits), the Bohr model could not account for some of the fine structure, and lin ...
... The Bohr model served well as a first approximation for a single electron atom. Bohr himself supported his model as only the first step toward a comprehensive quantum theory. In spite of refinements (such as elliptical orbits), the Bohr model could not account for some of the fine structure, and lin ...
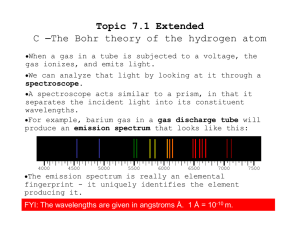
Topic 7_1_Ext C__The Bohr theory of the hydrogen atom
... in one of its bound states (allowed by n). It only does so when "dropping" from a higher state to a lower state." ...
... in one of its bound states (allowed by n). It only does so when "dropping" from a higher state to a lower state." ...
Electrons in Atoms
... Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 15. The electrons in an atom’s outermost orbitals are called ...
... Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 15. The electrons in an atom’s outermost orbitals are called ...
uncertainty: einstein, heisenberg, bohr, and the struggle for the soul
... atoms, influences their absorption and emission of light, and also transports energy between them. In addition, electrons were now to be seen not as orbiting nuclei in the atom, but as "virtual oscillators," each one corresponding to a particular spectroscopic line. However, contrary to classical ph ...
... atoms, influences their absorption and emission of light, and also transports energy between them. In addition, electrons were now to be seen not as orbiting nuclei in the atom, but as "virtual oscillators," each one corresponding to a particular spectroscopic line. However, contrary to classical ph ...
Section 1 - Tutor
... Section 30.5 The Quantum Mechanical Picture of the Hydrogen Atom 26. According to the quantum mechanical picture of the atom, which one of the following is a true statement concerning the ground state electron in a hydrogen atom? (a) The ground state electron has zero kinetic energy. (b) The groun ...
... Section 30.5 The Quantum Mechanical Picture of the Hydrogen Atom 26. According to the quantum mechanical picture of the atom, which one of the following is a true statement concerning the ground state electron in a hydrogen atom? (a) The ground state electron has zero kinetic energy. (b) The groun ...
Limits of classical physics II.
... But: electrons in the ground state do not radiate!!! Electrons do not fell into the core. ...
... But: electrons in the ground state do not radiate!!! Electrons do not fell into the core. ...
PHYS 1001 Physics for Future Presidents
... This course covers topics in physics with an emphasis on conceptual understanding, technology applications related to current events, and the ethical dimensions of technological choices. It will give students the solid foundation in physics they need to be critically thinking, scientifically literat ...
... This course covers topics in physics with an emphasis on conceptual understanding, technology applications related to current events, and the ethical dimensions of technological choices. It will give students the solid foundation in physics they need to be critically thinking, scientifically literat ...
Chapter 30: Quantum Physics
... Chapter 30: Quantum Physics 8. Predict/Calculate A Famous Double Star Albireo in the constellation Cygnus, which appears as a single star to the naked eye, is actually a beautiful double-star system, as shown in FIGURE 30-24. The brighter of the two stars is referred to as A (or Beta-01 Cygni), with ...
... Chapter 30: Quantum Physics 8. Predict/Calculate A Famous Double Star Albireo in the constellation Cygnus, which appears as a single star to the naked eye, is actually a beautiful double-star system, as shown in FIGURE 30-24. The brighter of the two stars is referred to as A (or Beta-01 Cygni), with ...
5.1 Student - Van Buren Public Schools
... energy levels in an atom are not equally spaced. The higher the energy level occupied by an electron, the less energy it takes to move from that energy level to the next higher energy level. Slide 7 of 26 © Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... energy levels in an atom are not equally spaced. The higher the energy level occupied by an electron, the less energy it takes to move from that energy level to the next higher energy level. Slide 7 of 26 © Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
Compton Effect and Spectral Lines
... 1) A photon of initial energy 5.8 103 eV is deflected by 130 in a collision with a free electron, which is initially at rest. What is the wavelength of the scattered photon? What energy (in eV) does the electron acquire in the collision? What is the velocity of the recoil electron? 2) An electron ...
... 1) A photon of initial energy 5.8 103 eV is deflected by 130 in a collision with a free electron, which is initially at rest. What is the wavelength of the scattered photon? What energy (in eV) does the electron acquire in the collision? What is the velocity of the recoil electron? 2) An electron ...
- Vijay Education Academy
... The electron in hydrogen atom is initially in the third excited state. What is the maximum number of spectral lines which can be emitted when it finally moves to the ground state? Page 2 ...
... The electron in hydrogen atom is initially in the third excited state. What is the maximum number of spectral lines which can be emitted when it finally moves to the ground state? Page 2 ...
ZCT 104 Test II solution
... Balmer series corresponds to the spectral lines emitted when the electron in a hydrogen atom makes transitions from higher states to the n = 1 state II(F) Lyman series corresponds to the spectral lines emitted when the electron in a hydrogen atom makes transitions from higher states to the n = 2 sta ...
... Balmer series corresponds to the spectral lines emitted when the electron in a hydrogen atom makes transitions from higher states to the n = 1 state II(F) Lyman series corresponds to the spectral lines emitted when the electron in a hydrogen atom makes transitions from higher states to the n = 2 sta ...
Structure of Atom
... Consider the hydrogen atom to be a proton embedded in a cavity of radius a o (Bohr radius) whose charge in neutralized by the addition of an electron to the cavity in vacuum, infinitely slowly. Estimate the average total energy of an electron in its ground state in a hydr5ogen atom as the work done ...
... Consider the hydrogen atom to be a proton embedded in a cavity of radius a o (Bohr radius) whose charge in neutralized by the addition of an electron to the cavity in vacuum, infinitely slowly. Estimate the average total energy of an electron in its ground state in a hydr5ogen atom as the work done ...
Chapter 5 : Electrons in Atoms
... Heisenberg showed it is impossible to take any measurement of an object without disturbing it. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the velocity and position of a particle at the same time. The only quantity that can be known is the p ...
... Heisenberg showed it is impossible to take any measurement of an object without disturbing it. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the velocity and position of a particle at the same time. The only quantity that can be known is the p ...
Interaction of Photons with Matter
... The usual unit of Energy is the Joule = 1 kg m2sec-2. = 1 ampere Volt Second. This again is a very large unit. There is another set of units that is also used to describe Energy. As some particles are charged ( the proton, electron) they can be accelerated through a potential difference giving them ...
... The usual unit of Energy is the Joule = 1 kg m2sec-2. = 1 ampere Volt Second. This again is a very large unit. There is another set of units that is also used to describe Energy. As some particles are charged ( the proton, electron) they can be accelerated through a potential difference giving them ...
Physics Week 15(Sem. 2)
... quantum numbers, n, l ,ml , ms.” They can have any combination of numbers such that they aren’t identical, so the last number can be the only difference. ...
... quantum numbers, n, l ,ml , ms.” They can have any combination of numbers such that they aren’t identical, so the last number can be the only difference. ...
Physics UVM P
... you cool atoms to very low temperatures, they tend not to stick to other surfaces,” Clougherty continues. “This is classically counterintuitive. You’d suspect cold atoms are moving very slowly, so it would be very easy to get them to stick to surfaces. And yet, these cold atoms tend to be reflected ...
... you cool atoms to very low temperatures, they tend not to stick to other surfaces,” Clougherty continues. “This is classically counterintuitive. You’d suspect cold atoms are moving very slowly, so it would be very easy to get them to stick to surfaces. And yet, these cold atoms tend to be reflected ...
Chapter 3 Atomic Structure
... The Quantum Model Principle energy levels (shells): Roughly correlate to the distance that an electron is from an atom’s nucleus. Sublevels (subshells): Each principle energy level (n) is divided into n sublevels. Orbitals: Orbitals are a region in space representing a high probability of locating a ...
... The Quantum Model Principle energy levels (shells): Roughly correlate to the distance that an electron is from an atom’s nucleus. Sublevels (subshells): Each principle energy level (n) is divided into n sublevels. Orbitals: Orbitals are a region in space representing a high probability of locating a ...
James Franck

James Franck (26 August 1882 – 21 May 1964) was a German physicist who won the 1925 Nobel Prize for Physics with Gustav Hertz ""for their discovery of the laws governing the impact of an electron upon an atom"". He completed his doctorate in 1906 and his habilitation in 1911 at the Frederick William University in Berlin, where he lectured and taught until 1918, having reached the position of professor extraordinarius. He served as a volunteer in the German Army during World War I. He was seriously injured in 1917 in a gas attack and was awarded the Iron Cross 1st Class.Franck became the Head of the Physics Division of the Kaiser Wilhelm Gesellschaft for Physical Chemistry. In 1920, Franck became professor ordinarius of experimental physics and Director of the Second Institute for Experimental Physics at the University of Göttingen. While there he worked on quantum physics with Max Born, who was Director of the Institute of Theoretical Physics. His work included the Franck–Hertz experiment, an important confirmation of the Bohr model of the atom. He promoted the careers of women in physics, notably Lise Meitner, Hertha Sponer and Hilde Levi.After the NSDAP came to power in Germany in 1933, Franck resigned his post in protest against the dismissal of fellow academics. He assisted Frederick Lindemann in helping dismissed Jewish scientists find work overseas, before he left Germany in November 1933. After a year at the Niels Bohr Institute in Denmark, he moved to the United States, where he worked at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore and then the University of Chicago. During this period he became interested in photosynthesis.Franck participated in the Manhattan Project during World War II as Director of the Chemistry Division of the Metallurgical Laboratory. He was also the chairman of the Committee on Political and Social Problems regarding the atomic bomb, which is best known for the compilation of the Franck Report, which recommended that the atomic bombs not be used on the Japanese cities without warning.