Example 1
... A measure of central tendency is a single value that attempts to describe a set of data by identifying the central position within that set of data. As such, measures of central tendency are sometimes called measures of central location. They are also classed as summary statistics. The mean (often c ...
... A measure of central tendency is a single value that attempts to describe a set of data by identifying the central position within that set of data. As such, measures of central tendency are sometimes called measures of central location. They are also classed as summary statistics. The mean (often c ...
Document
... The above diagram shows the sort of thing that can make an inverse function impossible. If two (or more) inputs produce that same output, then there can be no inverse, since in this case we would have x1 = f −1(y) and x2 = f −1(y). Then x1 and x2 would be equal, contrary to assumption. ...
... The above diagram shows the sort of thing that can make an inverse function impossible. If two (or more) inputs produce that same output, then there can be no inverse, since in this case we would have x1 = f −1(y) and x2 = f −1(y). Then x1 and x2 would be equal, contrary to assumption. ...
Propositional Logic - faculty.cs.tamu.edu
... denote deg p, as the number of occurrences of logical connectives in p. In other words, the degree function satisfies the following properties: D1. An element in S has degree 0. D2. If a in Prop has degree n, then ¬a has degree n + 1. D3. If a and b in Prop are respectively of degree na and nb , the ...
... denote deg p, as the number of occurrences of logical connectives in p. In other words, the degree function satisfies the following properties: D1. An element in S has degree 0. D2. If a in Prop has degree n, then ¬a has degree n + 1. D3. If a and b in Prop are respectively of degree na and nb , the ...
Sequences and Series I. What do you do when you see sigma
... c. Arithmetic Series An arithmetic series is the sum of all indicated terms in a given sequence, defined as Sn (the partial sum). The formula for the partial sum of an arithmetic sequence is given on the formula sheet. Sn = (n/2)(A1 + An) ...
... c. Arithmetic Series An arithmetic series is the sum of all indicated terms in a given sequence, defined as Sn (the partial sum). The formula for the partial sum of an arithmetic sequence is given on the formula sheet. Sn = (n/2)(A1 + An) ...
ANSWERS STATISTICS SPRING 2015
... Statistics – Spring 2015 Dr. Sybil M. DeVeaux Your Name____________________________________________________________ 1. Indicate whether each of the following statements typifies descriptive or inferential statistics: a) On the average, students in my statistics class are 20 years old. DESCRIPTIVE b) ...
... Statistics – Spring 2015 Dr. Sybil M. DeVeaux Your Name____________________________________________________________ 1. Indicate whether each of the following statements typifies descriptive or inferential statistics: a) On the average, students in my statistics class are 20 years old. DESCRIPTIVE b) ...
Chapter 2: Introduction to Propositional Logic
... Recursive step: if we already have two formulas A, B, then we adopt the expression: (A ∩ B), (A ∪ B), (A ⇒ B), (A ⇔ B) and also ¬A as formulas. ...
... Recursive step: if we already have two formulas A, B, then we adopt the expression: (A ∩ B), (A ∪ B), (A ⇒ B), (A ⇔ B) and also ¬A as formulas. ...
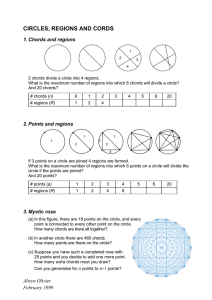
Circles, regions and chords
... It is clear that at the first point there are 6 chords. At the second point there are 5 new chords, because the chord to the first point has already been counted at the first point. Similarly, at the third point there are 4 new chords, etc. So we have C(7) = 6 + 5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 Again we emphasise ...
... It is clear that at the first point there are 6 chords. At the second point there are 5 new chords, because the chord to the first point has already been counted at the first point. Similarly, at the third point there are 4 new chords, etc. So we have C(7) = 6 + 5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 Again we emphasise ...
Functional programming and NLP
... Of course there are other examples of NLP where functional programming is a good tool, and here is a short list. • Functional morphology. Higher-order functions, statis typing and laziness can be a good basic framework for writing morphological specifications for different languages. One simply trie ...
... Of course there are other examples of NLP where functional programming is a good tool, and here is a short list. • Functional morphology. Higher-order functions, statis typing and laziness can be a good basic framework for writing morphological specifications for different languages. One simply trie ...
Ambiguity

Ambiguity is a type of uncertainty of meaning in which several interpretations are plausible. It is thus an attribute of any idea or statement whose intended meaning cannot be definitively resolved according to a rule or process with a finite number of steps. (The ambi- part of the name reflects an idea of ""two"" as in two meanings.)The concept of ambiguity is generally contrasted with vagueness. In ambiguity, specific and distinct interpretations are permitted (although some may not be immediately apparent), whereas with information that is vague, it is difficult to form any interpretation at the desired level of specificity.Context may play a role in resolving ambiguity. For example, the same piece of information may be ambiguous in one context and unambiguous in another.