chemical reaction - Willmar Public Schools
... Despite its dangers, radioactivity has several uses. For example, it can be used to determine the ages of ancient rocks and fossils. It can also be used as a source of power to generate electricity. Radioactivity can even be used to diagnose and treat diseases, including cancer. A radioisotope decay ...
... Despite its dangers, radioactivity has several uses. For example, it can be used to determine the ages of ancient rocks and fossils. It can also be used as a source of power to generate electricity. Radioactivity can even be used to diagnose and treat diseases, including cancer. A radioisotope decay ...
Absorption and Biological Effects of Ionising Radiation
... on Earth is dependant in the flow of energy from the Sun, which is utilised by plants to construct complex molecules from simpler ones. However, the increase in order that results on Earth is more than compensated by the decrease in order on the Sun through the thermonuclear process responsible for ...
... on Earth is dependant in the flow of energy from the Sun, which is utilised by plants to construct complex molecules from simpler ones. However, the increase in order that results on Earth is more than compensated by the decrease in order on the Sun through the thermonuclear process responsible for ...
Nuclear Force - International Journal of Science and Technology
... force is related to the mass of exchanged particle, It is assumed that the π0-meson is contained virtually in a proton. If this virtual particle travels with the velocity of light as might be expected for a field particle, then the greatest distance the meson could travel in this time is also known ...
... force is related to the mass of exchanged particle, It is assumed that the π0-meson is contained virtually in a proton. If this virtual particle travels with the velocity of light as might be expected for a field particle, then the greatest distance the meson could travel in this time is also known ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Somerset Academy
... • Gamma rays almost always accompany alpha and beta radiation, as they account for most of the energy loss that occurs as a nucleus decays. ...
... • Gamma rays almost always accompany alpha and beta radiation, as they account for most of the energy loss that occurs as a nucleus decays. ...
Nickel-Hydrogen Cold Fusion by Intermediate Rydberg State of
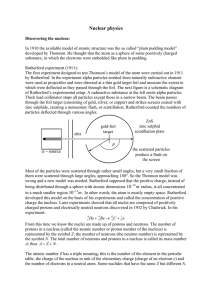
... mechanical (QM) models of atoms are based on the Rutherford-Bohr planetary model of hydrogen. The nuclear size is determined by scattering experiments, while the nuclear shape for all atoms is assumed spherical and solid (without geometrical shape and structure). Using this assumption Rutherford pro ...
... mechanical (QM) models of atoms are based on the Rutherford-Bohr planetary model of hydrogen. The nuclear size is determined by scattering experiments, while the nuclear shape for all atoms is assumed spherical and solid (without geometrical shape and structure). Using this assumption Rutherford pro ...
25.1 Nuclear Radiation
... Nuclear reactions, which account for radioactivity, differ from chemical reactions in a number of important ways. In chemical reactions, atoms tend to attain stable electron configurations by losing electrons or sharing electrons. In nuclear reactions, the nuclei of unstable isotopes, called radiois ...
... Nuclear reactions, which account for radioactivity, differ from chemical reactions in a number of important ways. In chemical reactions, atoms tend to attain stable electron configurations by losing electrons or sharing electrons. In nuclear reactions, the nuclei of unstable isotopes, called radiois ...
Radioactive decay of nucleus
... The half-lives of isotopes vary from element to element. It is unique to the isotope. Radium-226 has a half-life 1600 years. It means, it takes 1600 years of a given half quantity of Ra-226 to decay. The level of radioactivity shown by a radioactive substance is proportional to the mass of the s ...
... The half-lives of isotopes vary from element to element. It is unique to the isotope. Radium-226 has a half-life 1600 years. It means, it takes 1600 years of a given half quantity of Ra-226 to decay. The level of radioactivity shown by a radioactive substance is proportional to the mass of the s ...
Physics 228 Today: April 22, 2012 Ch. 43 Nuclear
... nucleus is less than the sum of the masses of the constituent nucleons. The mass of a nucleus is roughly proportional to the number of nucleons times 931.5 MeV = 1.66x10-27 kg = 1 u, an atomic mass unit. You can see from this that nucleons are bound into a nucleus by ≈ 939 - 931 = 8 MeV, about 1% of ...
... nucleus is less than the sum of the masses of the constituent nucleons. The mass of a nucleus is roughly proportional to the number of nucleons times 931.5 MeV = 1.66x10-27 kg = 1 u, an atomic mass unit. You can see from this that nucleons are bound into a nucleus by ≈ 939 - 931 = 8 MeV, about 1% of ...
nuclear physics - Sakshi Education
... Assertion(A): Nuclear forces arise from strong Coulombic interactions between protons and neutrons. Reason (R): Nuclear forces are independent of the charge of the nucleons. 1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A ...
... Assertion(A): Nuclear forces arise from strong Coulombic interactions between protons and neutrons. Reason (R): Nuclear forces are independent of the charge of the nucleons. 1) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A ...
Complexation Reactions In Nuclear Separations
... nuclear incident sites such as the Mayak site in Russia, where there was a catastrophic nuclear waste explosion that spread radioactivity over a large area. The colloid may also be used beneficially in the preparation of nuclear fuels by sol-gel processes as note above for uranium. ...
... nuclear incident sites such as the Mayak site in Russia, where there was a catastrophic nuclear waste explosion that spread radioactivity over a large area. The colloid may also be used beneficially in the preparation of nuclear fuels by sol-gel processes as note above for uranium. ...
Nuclear medicine physics - The Canadian Organization of Medical
... (b) Should the patient's urine be collected? If so, for how long should it be kept and how should it be disposed of? What are the arguments against such collection? 28. The chairman of the local university physics department is referred to the nuclear medicine department for a bone scan. During the ...
... (b) Should the patient's urine be collected? If so, for how long should it be kept and how should it be disposed of? What are the arguments against such collection? 28. The chairman of the local university physics department is referred to the nuclear medicine department for a bone scan. During the ...
ch10_sec1_rc
... 〉How do scientists predict when an atom will undergo radioactive decay? 〉It is impossible to predict the moment when any particular nucleus will decay, but it is possible to predict the time required for half of the nuclei in a given radioactive sample to decay. • half-life: the time required for ha ...
... 〉How do scientists predict when an atom will undergo radioactive decay? 〉It is impossible to predict the moment when any particular nucleus will decay, but it is possible to predict the time required for half of the nuclei in a given radioactive sample to decay. • half-life: the time required for ha ...
Chapter 16 Atomic Energy
... What is the source of nuclear power? • An uncontrolled chain reaction gives off huge amounts of energy very quickly. ...
... What is the source of nuclear power? • An uncontrolled chain reaction gives off huge amounts of energy very quickly. ...
7.2 Powerpoint
... energy per nucleon against nucleon number Rather than looking at the total binding energy of nuclei, we often look at the binding energy per nucleon. This number tells us about how difficult it is to remove each nucleon from the nucleus. The bigger the binding energy per nucleon, the more stable ...
... energy per nucleon against nucleon number Rather than looking at the total binding energy of nuclei, we often look at the binding energy per nucleon. This number tells us about how difficult it is to remove each nucleon from the nucleus. The bigger the binding energy per nucleon, the more stable ...
nuclear radiation, continued
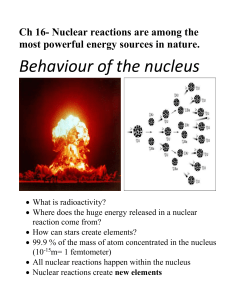
... Before studying about nuclear chemistry, answer the following items to refresh your memory about the structure of the nucleus. 1. Label the diagram below. ...
... Before studying about nuclear chemistry, answer the following items to refresh your memory about the structure of the nucleus. 1. Label the diagram below. ...
Chapter 32 Applied Nucleonics
... The discovery of nuclear fission in 1938 by Hahn and Strassman suggested the possibility of tapping the energy of the nucleus. Recall that it is a conversion of some of the nuclear binding energy into kinetic energy that characterizes both fission and fusion. The basis of this conversion can be seen ...
... The discovery of nuclear fission in 1938 by Hahn and Strassman suggested the possibility of tapping the energy of the nucleus. Recall that it is a conversion of some of the nuclear binding energy into kinetic energy that characterizes both fission and fusion. The basis of this conversion can be seen ...
Nuclear physics α −
... shell and a potential difference is applied between them, creating a strong radial electric field. The counter contains a low-pressure inert gas. A particle of radiation entering the device through the window ionizes a few of the gas atoms. The resulting free electrons are drawn to the positive wire ...
... shell and a potential difference is applied between them, creating a strong radial electric field. The counter contains a low-pressure inert gas. A particle of radiation entering the device through the window ionizes a few of the gas atoms. The resulting free electrons are drawn to the positive wire ...
Radioactive Decay
... Nuclides can be written with the name or symbol, followed by a dash with the mass number: Chlorine-35 or Cl-35, or as follows: Atomic mass = ...
... Nuclides can be written with the name or symbol, followed by a dash with the mass number: Chlorine-35 or Cl-35, or as follows: Atomic mass = ...
radioactivity - the Scientia Review
... accident occurred in Pennsylvania in 1979 at the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant. ...
... accident occurred in Pennsylvania in 1979 at the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant. ...
Radiation Tutorial Questions
... 1. The activity of a source starts at 80 MBq. After 10 days it has fallen to 2.5 MBq. Calculate the half-life. 2. What is the half-life of a radioactive substance if its activity falls from 400 kBq to 100 kBq in 12 days? 3. What is the half-life of a radioactive isotope if the activity falls from 3 ...
... 1. The activity of a source starts at 80 MBq. After 10 days it has fallen to 2.5 MBq. Calculate the half-life. 2. What is the half-life of a radioactive substance if its activity falls from 400 kBq to 100 kBq in 12 days? 3. What is the half-life of a radioactive isotope if the activity falls from 3 ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction. • The minimum amount of nuclide that provides the number of neutrons needed to sustain a chain reaction is called the critical mass. • Nuclear reactors use controlled-fission chain reactions to produce ener ...
... material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction. • The minimum amount of nuclide that provides the number of neutrons needed to sustain a chain reaction is called the critical mass. • Nuclear reactors use controlled-fission chain reactions to produce ener ...
Photo chapter opener 21 Subatomic particle tracks in a bubble
... (a)The net effect of b-particle production is to change a neutron to a proton. (b)The nuclides lie above the zone of stability. (c)The ratios of neutron/proton are too high. ...
... (a)The net effect of b-particle production is to change a neutron to a proton. (b)The nuclides lie above the zone of stability. (c)The ratios of neutron/proton are too high. ...
Nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents

A nuclear and radiation accident is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as ""an event that has led to significant consequences to people, the environment or the facility."" Examples include lethal effects to individuals, large radioactivity release to the environment, or reactor core melt."" The prime example of a ""major nuclear accident"" is one in which a reactor core is damaged and significant amounts of radioactivity are released, such as in the Chernobyl disaster in 1986.The impact of nuclear accidents has been a topic of debate practically since the first nuclear reactors were constructed in 1954. It has also been a key factor in public concern about nuclear facilities. Some technical measures to reduce the risk of accidents or to minimize the amount of radioactivity released to the environment have been adopted. Despite the use of such measures, human error remains, and ""there have been many accidents with varying impacts as well near misses and incidents"".Worldwide there have been 99 accidents at nuclear power plants. Fifty-seven accidents have occurred since the Chernobyl disaster, and 57% (56 out of 99) of all nuclear-related accidents have occurred in the USA. Serious nuclear power plant accidents include the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster (2011), Chernobyl disaster (1986), Three Mile Island accident (1979), and the SL-1 accident (1961).Nuclear-powered submarine core meltdown and other mishaps include the K-19 (1961), K-11 (1965), K-27 (1968), K-140 (1968), K-429 (1970), K-222 (1980), K-314 (1985), and K-431 (1985). Serious radiation accidents include the Kyshtym disaster, Windscale fire, radiotherapy accident in Costa Rica, radiotherapy accident in Zaragoza, radiation accident in Morocco, Goiania accident, radiation accident in Mexico City, radiotherapy unit accident in Thailand, and the Mayapuri radiological accident in India.The IAEA maintains a website reporting recent accidents.