Cytokines and Chemokines
... Integrin 3)Integrin family β1: VLA(very late appearing antigen) β2: LFA-1(lymphocyte function associated antigen-1) ligand:ICAM-1,2,3 β3: gpⅡbⅢa 4)Distribution:Expressed extensively ...
... Integrin 3)Integrin family β1: VLA(very late appearing antigen) β2: LFA-1(lymphocyte function associated antigen-1) ligand:ICAM-1,2,3 β3: gpⅡbⅢa 4)Distribution:Expressed extensively ...
Lecture 4 Antigen Recognition
... Pre-existence of of many different potential antibody producing cells Each cell displays surface receptors for specific antigens Antigen encounter selects cells ...
... Pre-existence of of many different potential antibody producing cells Each cell displays surface receptors for specific antigens Antigen encounter selects cells ...
bacterial agents and in vitro susceptibility patterns
... * T cells which recognize self peptide:self MHC continue maturation * T cells which do not recognize self peptide:self MHC commit apoptosis ...
... * T cells which recognize self peptide:self MHC continue maturation * T cells which do not recognize self peptide:self MHC commit apoptosis ...
PowerPoint Presentation to accompany Life: The Science of
... A T cell receptor recognizes processed antigen bound to a class I MHC protein on an infected cell. ...
... A T cell receptor recognizes processed antigen bound to a class I MHC protein on an infected cell. ...
HIV and immunity
... it stimulates proliferation of the specific B Cells that recognize its Antigens ...
... it stimulates proliferation of the specific B Cells that recognize its Antigens ...
Laboratory Applications of Poultry Lecture and Lab Overview
... Macrophages, Natural killer (NK) cells, lymphokine activated (LAK) cells, neutrophils(mammals), heterophils(avian), eosinophils, polymorphonuclear cells, dendritic cells, etc Can argue some specificity due to opsonization and other cellular protein cues given to the cells. ...
... Macrophages, Natural killer (NK) cells, lymphokine activated (LAK) cells, neutrophils(mammals), heterophils(avian), eosinophils, polymorphonuclear cells, dendritic cells, etc Can argue some specificity due to opsonization and other cellular protein cues given to the cells. ...
Immune System
... • Plasma cells: antibody-producing effector B-cells • Secondary immune response: immune response if the individual is exposed to the same antigen at some later time~ Immunological memory ...
... • Plasma cells: antibody-producing effector B-cells • Secondary immune response: immune response if the individual is exposed to the same antigen at some later time~ Immunological memory ...
Document
... molecules (protein, glycoprotein, or polysaccharide) on the surface of cells and viruses C. Pathogen: any antigen that causes a disruption in homeostasis a.k.a. normal, disease free, functions D. Antibody: a protein produced specifically in response to the presence of an antigen - neutralizes antige ...
... molecules (protein, glycoprotein, or polysaccharide) on the surface of cells and viruses C. Pathogen: any antigen that causes a disruption in homeostasis a.k.a. normal, disease free, functions D. Antibody: a protein produced specifically in response to the presence of an antigen - neutralizes antige ...
+ the statement is correct - the statement isn´t correct 1. Out of the
... 3) - Cytoplasmic membrane of human cells is composed of strongly amphipathic components, which cause a stronger interaction between membrane molecules, thus preventing the insertion of complement component C3b 4) + C3-convertase of alternative pathway is formed from C3b and factor Bb ...
... 3) - Cytoplasmic membrane of human cells is composed of strongly amphipathic components, which cause a stronger interaction between membrane molecules, thus preventing the insertion of complement component C3b 4) + C3-convertase of alternative pathway is formed from C3b and factor Bb ...
MHC and a Gal Expression in Porcine Fetal Neural Tissue
... murine model of the autoimmune liver disease primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), in which S J U J mice demonstrate histological’ and immunological’ features typical of human disease. EAC can be induced by sensitisation with non-self (bovine) pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (bPDC), the autoantigen in PBC ...
... murine model of the autoimmune liver disease primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), in which S J U J mice demonstrate histological’ and immunological’ features typical of human disease. EAC can be induced by sensitisation with non-self (bovine) pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (bPDC), the autoantigen in PBC ...
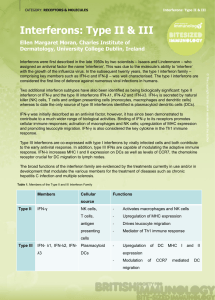
Interferon Type II & III - Bite
... interferon or IFN-γ and the type III interferons IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2 and IFN-λ3. IFN-γ is secreted by natural killer (NK) cells, T cells and antigen presenting cells (monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells) whereas to date the only source of type III interferons identified is plasmacytoid dendritic c ...
... interferon or IFN-γ and the type III interferons IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2 and IFN-λ3. IFN-γ is secreted by natural killer (NK) cells, T cells and antigen presenting cells (monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells) whereas to date the only source of type III interferons identified is plasmacytoid dendritic c ...
Foreign agenses, molecules, cells
... ethiology (synthetic epitopes) •are antigens able to bind on immunity receptors and not able to induce immunity reaction, not immunogenic •Hapten + immunogen (carrier) = immunity reaction against both. These substances not immunogenic by itself - If couple to a larger carrier molecule (albumin, glob ...
... ethiology (synthetic epitopes) •are antigens able to bind on immunity receptors and not able to induce immunity reaction, not immunogenic •Hapten + immunogen (carrier) = immunity reaction against both. These substances not immunogenic by itself - If couple to a larger carrier molecule (albumin, glob ...
Cell-mediated immunity
... is released by the pituitary and induces the release from the adrenal gland of corticosteroids which suppress the immune system. •Cytokines such as IL-1, IL-2, TGF-β and IFNs exert various affects on the central nervous system such as induce fever, stimulate proliferation of astrocytes, and foster n ...
... is released by the pituitary and induces the release from the adrenal gland of corticosteroids which suppress the immune system. •Cytokines such as IL-1, IL-2, TGF-β and IFNs exert various affects on the central nervous system such as induce fever, stimulate proliferation of astrocytes, and foster n ...
Prediction of binding free energies
... During a disease process, cells produce associated proteins (or antigens) which, after proteolysis, are transported to the cell surface as peptides. At the cell surface, the Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) I proteins display these peptides to immune cells known as Cytotoxic T cell lymphocytes ...
... During a disease process, cells produce associated proteins (or antigens) which, after proteolysis, are transported to the cell surface as peptides. At the cell surface, the Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) I proteins display these peptides to immune cells known as Cytotoxic T cell lymphocytes ...
The MHC complex
... • Exposure to select for expression of particular MHC alleles: strong association of HLA-B53 with recovery from malaria • Why not more MHC loci? For maintenance of self-tolerance ...
... • Exposure to select for expression of particular MHC alleles: strong association of HLA-B53 with recovery from malaria • Why not more MHC loci? For maintenance of self-tolerance ...
Theories of Autoimmunity
... • Response to tissue damage, necrosis or cell distress, e.g. infection or injury. • Inflammn. = response to danger signals mediated by effector mols. inc. cytokines. • BUT AIR can occur without tissue damage, e.g. immunisn. with self-ag; Tx; genetic defects. ...
... • Response to tissue damage, necrosis or cell distress, e.g. infection or injury. • Inflammn. = response to danger signals mediated by effector mols. inc. cytokines. • BUT AIR can occur without tissue damage, e.g. immunisn. with self-ag; Tx; genetic defects. ...
MICROBIO320 EXAM 1-Fall 2009 Name 1 True/False (1 point each
... MHC class II molecules are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum of many cell types. Genetically different individuals express different MHC class II alleles. MHC class II molecules are associated with b2-microglobulin on the cell surface. All are correct ...
... MHC class II molecules are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum of many cell types. Genetically different individuals express different MHC class II alleles. MHC class II molecules are associated with b2-microglobulin on the cell surface. All are correct ...
Ardolino, M. and D. H. Raulet. 2016. Cytokine therapy restores antitumor responses of NK cells rendered anergic in MHC I-deficient tumors. Oncoimmunology 5:e1002725.
... Natural Killer (NK) cells are key effectors in the response to tumor. They mediate tumor rejection via cytotoxicity and production of cytokines such as IFNg and TNF-a.1 NK cells are known to attack MHC-deficient tumor cells, due to the failure of such tumor cells to convey inhibitory signals mediate ...
... Natural Killer (NK) cells are key effectors in the response to tumor. They mediate tumor rejection via cytotoxicity and production of cytokines such as IFNg and TNF-a.1 NK cells are known to attack MHC-deficient tumor cells, due to the failure of such tumor cells to convey inhibitory signals mediate ...
1. Hypersensitivity What is Hypersensitivity? Chapter 18: Disorders of the Immune System
... • human MHC class I molecules are referred to as the HLA (human leukocyte antigen) complex • there are 3 HLA genes resulting in up to 6 different HLA proteins per individual • there are many different HLA alleles in the human population, so each person’s HLA make up is unique • close relatives are m ...
... • human MHC class I molecules are referred to as the HLA (human leukocyte antigen) complex • there are 3 HLA genes resulting in up to 6 different HLA proteins per individual • there are many different HLA alleles in the human population, so each person’s HLA make up is unique • close relatives are m ...
Document
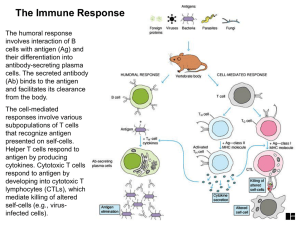
... their differentiation into antibody-secreting plasma cells. The secreted antibody (Ab) binds to the antigen and facilitates its clearance from the body. The cell-mediated responses involve various subpopulations of T cells that recognize antigen presented on self-cells. Helper T cells respond to ant ...
... their differentiation into antibody-secreting plasma cells. The secreted antibody (Ab) binds to the antigen and facilitates its clearance from the body. The cell-mediated responses involve various subpopulations of T cells that recognize antigen presented on self-cells. Helper T cells respond to ant ...
Introduction to immunology
... cells and on APC, B cells, monocytes/macrophages (class II) • They are targets for rejection • They are inherited from both parents as MHC haplotypes and are co-dominantly expressed ...
... cells and on APC, B cells, monocytes/macrophages (class II) • They are targets for rejection • They are inherited from both parents as MHC haplotypes and are co-dominantly expressed ...
IMMUNITY- humoral immunity, or antibody
... d. Antibodies- also known as "Ig"s (for immunoglobulins). Secreted by plasma cells or by activated B-cells i. Basic structure 1. "variable" region - antigen binding site 2. "constant" region - the stem) - determines the cells and chemicals an antibody can bind to, and how that class of antibody will ...
... d. Antibodies- also known as "Ig"s (for immunoglobulins). Secreted by plasma cells or by activated B-cells i. Basic structure 1. "variable" region - antigen binding site 2. "constant" region - the stem) - determines the cells and chemicals an antibody can bind to, and how that class of antibody will ...
Suggested Answers to Assignments
... Prior to beginning the educational session, the student must assess his level of education and his current knowledge about the treatment. The student’s answer will be based on the following information. The body must be able to differentiate between its own molecules and foreign antigens. MHC is r ...
... Prior to beginning the educational session, the student must assess his level of education and his current knowledge about the treatment. The student’s answer will be based on the following information. The body must be able to differentiate between its own molecules and foreign antigens. MHC is r ...
Major histocompatibility complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a set of cell surface molecules encoded by a large gene family which controls a major part of the immune system in all vertebrates. The major function of major histocompatibility complexes is to bind to peptide fragments derived from pathogens and display them on the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), which are immune cells, with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines compatibility of donors for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to an autoimmune disease via crossreacting immunization. In humans, the MHC is also called the human leukocyte antigen (HLA).In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own phenotype or of other biologic entities are continually synthesized and degraded. Each MHC molecule on the cell surface displays a molecular fraction of a protein, called epitope. The presented antigen can be either 'self' or 'nonself', thus preventing an organism`s immune system targeting its own cells. In its entirety, the MHC population is like a meter indicating the balance of proteins within the cell.The MHC gene family is divided into three subgroups: class I, class II, and class III. Class I MHC molecules have β2 subunits so can only be recognised by CD8 co-receptors. Class II MHC molecules have no β2 subunits so can be recognised by CD4 co-receptors. In this way MHC molecules chaperones which type of lymphocytes may bind to the given antigen with high affinity, since different lymphocytes express different TCR co-receptors. Diversity of antigen presentation, mediated by MHC classes I and II, is attained in at least three ways: (1) an organism's MHC repertoire is polygenic (via multiple, interacting genes); (2) MHC expression is codominant (from both sets of inherited alleles); (3) MHC gene variants are highly polymorphic (diversely varying from organism to organism within a species). Major histocompatibility complex and sexual selection has been observed in male mice making mate choices of females with different MHCs and thus demonstrating sexual selection.