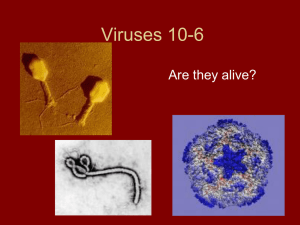
High titre BacMAM viruses improve transduction efficiency of mammalian cells
... an essential gene that results in consistent, very high titre budded virus so that transduction efficiencies using 200+ particles per cell can be achieved without recourse to concentration of virus or addition of chemicals to enhance virus uptake. ...
... an essential gene that results in consistent, very high titre budded virus so that transduction efficiencies using 200+ particles per cell can be achieved without recourse to concentration of virus or addition of chemicals to enhance virus uptake. ...
Viruses - Killeen ISD
... – Virus DNA gets copied everytime host cells copy – At some point, virus goes into lytic cycle and kills host cells – Has long incubation time (months-years) – Ex: HIV, warts, shingles, herpes ...
... – Virus DNA gets copied everytime host cells copy – At some point, virus goes into lytic cycle and kills host cells – Has long incubation time (months-years) – Ex: HIV, warts, shingles, herpes ...
Demodex CIS - the Bilton Veterinary Centre
... A dog is not considered cured of demodicosis until a year has passed since any mites were documented on skin scrapings. Some dogs may continue to have mites seen on skin scrapings despite appropriate therapy or they will repetitively relapse whenever medications are discontinued. In such cases li ...
... A dog is not considered cured of demodicosis until a year has passed since any mites were documented on skin scrapings. Some dogs may continue to have mites seen on skin scrapings despite appropriate therapy or they will repetitively relapse whenever medications are discontinued. In such cases li ...
xap_mayer0125_supp
... million people ages12 and older, or 1 out of 5 of the total adolescent and adult population, are infected with the herpes virus. The onset of the disease caused by the Ebola virus is rapid: symptoms can occur within 2 to 21 days after infection. Once symptoms begin to show, death can occur within da ...
... million people ages12 and older, or 1 out of 5 of the total adolescent and adult population, are infected with the herpes virus. The onset of the disease caused by the Ebola virus is rapid: symptoms can occur within 2 to 21 days after infection. Once symptoms begin to show, death can occur within da ...
sars
... peptide and a cleavage site (probability 0.540). Both TMpred (27) and TMHMM predict the existence of three transmembrane regions spanning approximately residues 34 to 56, 77 to 99, and 103 to 125. The most likely model from these analyses is that the C terminus and a large 149–amino acid N-terminal ...
... peptide and a cleavage site (probability 0.540). Both TMpred (27) and TMHMM predict the existence of three transmembrane regions spanning approximately residues 34 to 56, 77 to 99, and 103 to 125. The most likely model from these analyses is that the C terminus and a large 149–amino acid N-terminal ...
rotaviruses
... unique among icosahedral viruses in that they have a structure called a “fiber” projecting ...
... unique among icosahedral viruses in that they have a structure called a “fiber” projecting ...
canine hip dysplasia
... Canine hip dysplasia results from abnormal development of the coxofemoral joint and is most commonly seen in the large/heavy breeds of dog. It occurs equally in both sexes. The age at which the disease first appears clinically varies from a few months to old age. In, this thesis the various aetiolog ...
... Canine hip dysplasia results from abnormal development of the coxofemoral joint and is most commonly seen in the large/heavy breeds of dog. It occurs equally in both sexes. The age at which the disease first appears clinically varies from a few months to old age. In, this thesis the various aetiolog ...
CHILDHOOD ILLNESSES
... HEPATITIS B Hepatitis B is an infection of the liver caused by a virus called HBV (Hepatitis B Virus). This viral infection may occur in two phases. The first phase is the acute phase. The acute phase may cause mild flu-like symptoms, diminished appetite, fatigue, abdominal pain, an enlarged liver, ...
... HEPATITIS B Hepatitis B is an infection of the liver caused by a virus called HBV (Hepatitis B Virus). This viral infection may occur in two phases. The first phase is the acute phase. The acute phase may cause mild flu-like symptoms, diminished appetite, fatigue, abdominal pain, an enlarged liver, ...
CHILDHOOD ILLNESSES
... HEPATITIS B Hepatitis B is an infection of the liver caused by a virus called HBV (Hepatitis B Virus). This viral infection may occur in two phases. The first phase is the acute phase. The acute phase may cause mild flu-like symptoms, diminished appetite, fatigue, abdominal pain, an enlarged liver, ...
... HEPATITIS B Hepatitis B is an infection of the liver caused by a virus called HBV (Hepatitis B Virus). This viral infection may occur in two phases. The first phase is the acute phase. The acute phase may cause mild flu-like symptoms, diminished appetite, fatigue, abdominal pain, an enlarged liver, ...
CHILDHOOD ILLNESSES
... HEPATITIS B Hepatitis B is an infection of the liver caused by a virus called HBV (Hepatitis B Virus). This viral infection may occur in two phases. The first phase is the acute phase. The acute phase may cause mild flu-like symptoms, diminished appetite, fatigue, abdominal pain, an enlarged liver, ...
... HEPATITIS B Hepatitis B is an infection of the liver caused by a virus called HBV (Hepatitis B Virus). This viral infection may occur in two phases. The first phase is the acute phase. The acute phase may cause mild flu-like symptoms, diminished appetite, fatigue, abdominal pain, an enlarged liver, ...
INFLUENZA
... Very rarely (7 in 1,000,000 cases) 1-10 years after initial infection. progressive, fatal disease. defective forms of the virus in the brain ...
... Very rarely (7 in 1,000,000 cases) 1-10 years after initial infection. progressive, fatal disease. defective forms of the virus in the brain ...
viruses - Images
... What is a Virus? A virus infects a host. A host is a living thing that provides a home and food for a parasite. A parasite is an organism that survives by living on or in a host organism, thus harming it. ...
... What is a Virus? A virus infects a host. A host is a living thing that provides a home and food for a parasite. A parasite is an organism that survives by living on or in a host organism, thus harming it. ...
Rodent Zoonoses
... can be infected by inhalation and by contact with tissues or fluids from infected animals. Symptoms include fever, myalgia, headache and malaise. More severe symptoms can occur such as lymphadeopathy, meningoencephalitis and neurologic signs. Prevention: Serologic surveillance of animal colonies at ...
... can be infected by inhalation and by contact with tissues or fluids from infected animals. Symptoms include fever, myalgia, headache and malaise. More severe symptoms can occur such as lymphadeopathy, meningoencephalitis and neurologic signs. Prevention: Serologic surveillance of animal colonies at ...
Hookwrms - Alpine Animal Hospital
... Fortunately, treatment is safe, simple, and relatively inexpensive. After administration of the deworming medication (called an anthelmintic), the adult worms are killed. Two treatments are needed; they are typically performed at a 23 week interval. Ideally, kittens are dewormed during their vaccina ...
... Fortunately, treatment is safe, simple, and relatively inexpensive. After administration of the deworming medication (called an anthelmintic), the adult worms are killed. Two treatments are needed; they are typically performed at a 23 week interval. Ideally, kittens are dewormed during their vaccina ...
Case Study - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... All have flexible nucleocapsids with helical symmetry. All have an envelope containing virally encoded glycoprotein spikes that are involved in attachment and penetration. All have genomes without a 5’ cap or a 3’ poly A tail Penetrates through cell-mediated endocytosis with pH-dependent fus ...
... All have flexible nucleocapsids with helical symmetry. All have an envelope containing virally encoded glycoprotein spikes that are involved in attachment and penetration. All have genomes without a 5’ cap or a 3’ poly A tail Penetrates through cell-mediated endocytosis with pH-dependent fus ...
Antibodies from Reconvalescent Donors for the Prevention and
... testing the donations will be an imperfect solution. Despite the implementation of even elaborate nucleic acid test (NAT) algorithms, non-virus inactivated transfusable blood components still occasionally transmit West Nile Virus in the U.S., and similar situations need to be expected in West Africa ...
... testing the donations will be an imperfect solution. Despite the implementation of even elaborate nucleic acid test (NAT) algorithms, non-virus inactivated transfusable blood components still occasionally transmit West Nile Virus in the U.S., and similar situations need to be expected in West Africa ...
Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1
... Usually occurs in early childhood Rare after the age 30 Transmitted through many types of contact A kiss n Sharing eating utensils n Linens and towels n ...
... Usually occurs in early childhood Rare after the age 30 Transmitted through many types of contact A kiss n Sharing eating utensils n Linens and towels n ...
Science Media Centre Fact Sheet Schmallenberg virus
... The Schmallenberg virus is of the family Bunyavirus, genus Orthobunyavirus. Several viruses in the genus cause diseases in cattle and are transmitted by insects. Schmallenberg virus is in the Simbu serogroup of the Orthobunyavirus genus, which includes many different viruses that occur in Asia, Afri ...
... The Schmallenberg virus is of the family Bunyavirus, genus Orthobunyavirus. Several viruses in the genus cause diseases in cattle and are transmitted by insects. Schmallenberg virus is in the Simbu serogroup of the Orthobunyavirus genus, which includes many different viruses that occur in Asia, Afri ...
HIV-Related Conditions and Opportunistic Infections
... for years, causing accumulation in bones, skin, nervous tissue, heart, and arteries; lesions called gummas develop and are very destructive; at this stage, the patient has developed neurosyphilis because the syphilis was untreated and the brain and spinal ...
... for years, causing accumulation in bones, skin, nervous tissue, heart, and arteries; lesions called gummas develop and are very destructive; at this stage, the patient has developed neurosyphilis because the syphilis was untreated and the brain and spinal ...
Bacteria and Viruses Powerpoint
... TRANSCRIPTASE____. Reverse transcriptase- enzyme that copies viral RNA into DNA. HIV is an infection of the _WHITE BLOOD CELLS_____. The infected person’s white blood cells are damaged and their immune system fails which lead to other diseases and that is when the disease can be called AIDS_. ...
... TRANSCRIPTASE____. Reverse transcriptase- enzyme that copies viral RNA into DNA. HIV is an infection of the _WHITE BLOOD CELLS_____. The infected person’s white blood cells are damaged and their immune system fails which lead to other diseases and that is when the disease can be called AIDS_. ...
An Overview of Feline Viral Disease
... Known by its more common name, FIP is a leading killer among young and old cats. According to some sources only Feline Leukemia virus kills more cats than FIP and some put the death toll at close to half a million cats each year! It is caused by a corona virus (today’s insignificant trivia is that t ...
... Known by its more common name, FIP is a leading killer among young and old cats. According to some sources only Feline Leukemia virus kills more cats than FIP and some put the death toll at close to half a million cats each year! It is caused by a corona virus (today’s insignificant trivia is that t ...
Tuberculosis (TB) - Royal Berkshire Hospital
... body’s immune system stops the bacteria from multiplying and they may not even realise they have been infected. However, not all the bacteria (germs) may be killed but can remain dormant (inactive) for many years. If the body’s immune system begins to fail later in life (or when a patient gets anoth ...
... body’s immune system stops the bacteria from multiplying and they may not even realise they have been infected. However, not all the bacteria (germs) may be killed but can remain dormant (inactive) for many years. If the body’s immune system begins to fail later in life (or when a patient gets anoth ...
Canine parvovirus

Canine parvovirus type 2 (CPV2, colloquially parvo) is a contagious virus mainly affecting dogs, and thought to originate in cats. The current belief is that the feline panleukopenia mutated into CPV2. Parvo is highly contagious and is spread from dog to dog by direct or indirect contact with their faeces. Vaccines can prevent this infection, but mortality can reach 91% in untreated cases. Treatment often involves veterinary hospitalization. Canine parvovirus may infect other mammals; however, it will not infect humans.