Honors Physics – Midterm Review 2010
... 32. Safety engineers estimate that an elevator “car” can hold 20 persons of 75kg average mass. The car itself has a mass of 500kg. Tensile strength tests show that the cable supporting the car can tolerate a maximum force of 29.6kN. What is the greatest acceleration that the elevator’s motor can pr ...
... 32. Safety engineers estimate that an elevator “car” can hold 20 persons of 75kg average mass. The car itself has a mass of 500kg. Tensile strength tests show that the cable supporting the car can tolerate a maximum force of 29.6kN. What is the greatest acceleration that the elevator’s motor can pr ...
Midterm 1
... d) While in a car rounding a corner one feels a force pulling them outward. Similarly, when one speeds up or slows down they feel forces pulling them backward and forward. What is the cause of these forces? (5) The cause of these forces is one’s tendency to move in a straight line at constant speed ...
... d) While in a car rounding a corner one feels a force pulling them outward. Similarly, when one speeds up or slows down they feel forces pulling them backward and forward. What is the cause of these forces? (5) The cause of these forces is one’s tendency to move in a straight line at constant speed ...
Coefficient of Sliding Friction
... perpendicular (or normal) force FN exerted on the object by the surface. Dependence (1) is quantified by the coefficient of kinetic friction µ, which is defined by the equation µ = Ffric/ FN . Ideally, the ...
... perpendicular (or normal) force FN exerted on the object by the surface. Dependence (1) is quantified by the coefficient of kinetic friction µ, which is defined by the equation µ = Ffric/ FN . Ideally, the ...
Physics Review #1
... near Earth’s surface. As a mass is moved from A to B, 100 joules of work are done against gravity. What is the amount of work done against gravity as an identical mass is moved from A to C? (A) 100 J (B) 173 J (C) 200 J (D) 273 J ...
... near Earth’s surface. As a mass is moved from A to B, 100 joules of work are done against gravity. What is the amount of work done against gravity as an identical mass is moved from A to C? (A) 100 J (B) 173 J (C) 200 J (D) 273 J ...
Circular Motion
... can breaks, it if often wrongly stated that centrifugal force pulls the can from its circular path. But in fact, when the string breaks the can goes off in a tangential straight-line path because no force acts on it. Now suppose there is a ladybug inside the whirling can. The can provides the centri ...
... can breaks, it if often wrongly stated that centrifugal force pulls the can from its circular path. But in fact, when the string breaks the can goes off in a tangential straight-line path because no force acts on it. Now suppose there is a ladybug inside the whirling can. The can provides the centri ...
PID Control (1) | 制御系CAD
... In the situation of the speed control, we are assumed to measure the velocity, that is, we don’t have to differentiate the position. So we need to feed back the value proportional to the measured velocity. On the other hand, in the situation of the position control, we are assumed to measure the pos ...
... In the situation of the speed control, we are assumed to measure the velocity, that is, we don’t have to differentiate the position. So we need to feed back the value proportional to the measured velocity. On the other hand, in the situation of the position control, we are assumed to measure the pos ...
Chapter 2
... to the 50 m mark & turns around to run back to the 20 m mark. He has ran a total of 70 m. Displacemetn includes distance & direction from the starting point ...
... to the 50 m mark & turns around to run back to the 20 m mark. He has ran a total of 70 m. Displacemetn includes distance & direction from the starting point ...
Circular Motion Test Review Name
... maximum tension that the string can withstand is 250 N, then what maximum linear speed can the mass have if the string is not to break? A) 19.4 m/s B) 22.4 m/s C) 25.0 m/s D) 32.7 m/s ...
... maximum tension that the string can withstand is 250 N, then what maximum linear speed can the mass have if the string is not to break? A) 19.4 m/s B) 22.4 m/s C) 25.0 m/s D) 32.7 m/s ...
Linear Motion
... for inclines: the steeper the incline, the greater the acceleration. (It was too hard to measure time for free-falls.) He also found that the size of the objects didn't matter. ...
... for inclines: the steeper the incline, the greater the acceleration. (It was too hard to measure time for free-falls.) He also found that the size of the objects didn't matter. ...
Unit 5 Notes - Killeen ISD
... 2. A Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma) – This is Newton’s 2nd Law 3. Balanced forces result in no change to an object’s motion. The two forces are both equal and opposite. 4. Unbalanced forces are when two forces are not equal; one force is greater than the other force and causes the obj ...
... 2. A Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma) – This is Newton’s 2nd Law 3. Balanced forces result in no change to an object’s motion. The two forces are both equal and opposite. 4. Unbalanced forces are when two forces are not equal; one force is greater than the other force and causes the obj ...
Interpreting the Graph
... In the third part, the object is again moving with constant speed while returning to its point of origin. It changed direction; therefore, it has velocity and it accelerated. ...
... In the third part, the object is again moving with constant speed while returning to its point of origin. It changed direction; therefore, it has velocity and it accelerated. ...
3.1 TQ Centrifugal Force Apparatus
... of motion, the centripetal force also produces an acceleration having the same direction it has. By definition, there exists a direct relationship between the centripetal force of a body and the square of its speed and an inverse relationship between the force and radial distance from the center of ...
... of motion, the centripetal force also produces an acceleration having the same direction it has. By definition, there exists a direct relationship between the centripetal force of a body and the square of its speed and an inverse relationship between the force and radial distance from the center of ...
Chapter 2: MOTION AND SPEED
... According to Newton’s first law of motion, an object moving at a constant velocity keeps moving at that velocity unless a net force acts on it (Part I—Car-CC). Also, if an object is at rest, it stays at rest, unless a net force acts on ...
... According to Newton’s first law of motion, an object moving at a constant velocity keeps moving at that velocity unless a net force acts on it (Part I—Car-CC). Also, if an object is at rest, it stays at rest, unless a net force acts on ...
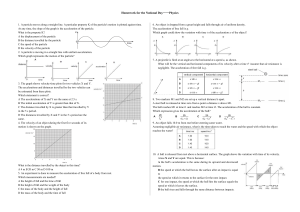
Homework for the National Day——Physics 1. A particle moves
... 18. A student investigates the speed of a trolley as it rolls down a slope, as illustrated in Fig. 2.1. The speed v of the trolley is measured using a speed sensor for different values of the time t that the trolley has moved from rest down the slope. Fig. 2.2 shows the variation with t of v. ...
... 18. A student investigates the speed of a trolley as it rolls down a slope, as illustrated in Fig. 2.1. The speed v of the trolley is measured using a speed sensor for different values of the time t that the trolley has moved from rest down the slope. Fig. 2.2 shows the variation with t of v. ...
2:00 pm
... A 1.00 kg block is at rest at the top of a smooth hemispherical surface of radius 2.00 m. It is attached to an unstretched elastic cord with spring stiffness of 5.00 N/m as shown on the left diagram below. The block is given a slight push to the right, causing it to slide down the surface. When the ...
... A 1.00 kg block is at rest at the top of a smooth hemispherical surface of radius 2.00 m. It is attached to an unstretched elastic cord with spring stiffness of 5.00 N/m as shown on the left diagram below. The block is given a slight push to the right, causing it to slide down the surface. When the ...
Speed - TGHSLevel1Science
... • At any moment in time, a moving object has instantaneous speed. Since this is difficult to calculate, we usually use average speed. ...
... • At any moment in time, a moving object has instantaneous speed. Since this is difficult to calculate, we usually use average speed. ...
Document
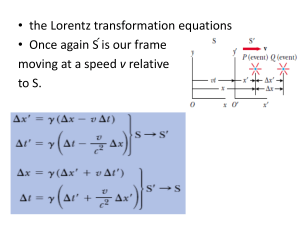
... say that the speed should be the sum of the two speeds, or 1.50c. This answer must be incorrect because it contradicts the assertion that no material object can travel faster than the speed of light. • Let two frames or reference be labelled b and d, and suppose that frame d is moving at velocity vd ...
... say that the speed should be the sum of the two speeds, or 1.50c. This answer must be incorrect because it contradicts the assertion that no material object can travel faster than the speed of light. • Let two frames or reference be labelled b and d, and suppose that frame d is moving at velocity vd ...
Investigation 1
... The following question looks again at linear motion with a constant acceleration but in the downward direction. (Refer to Questions 6 and 7.) The question in the last column is difficult only because the ball changes direction. In order to figure out the answers remember that the upward motion is s ...
... The following question looks again at linear motion with a constant acceleration but in the downward direction. (Refer to Questions 6 and 7.) The question in the last column is difficult only because the ball changes direction. In order to figure out the answers remember that the upward motion is s ...
What Is Motion?
... Motion and move begin the same way. Something in motion moves from one place or position to another. speed [SPEED] how the position of an object changes during a certain amount of time Speed and seconds begin with the same sound. Speed is how many seconds (minutes or hours) it takes to get from one ...
... Motion and move begin the same way. Something in motion moves from one place or position to another. speed [SPEED] how the position of an object changes during a certain amount of time Speed and seconds begin with the same sound. Speed is how many seconds (minutes or hours) it takes to get from one ...
Circular Motion
... Q5) A ball is whirled on the end of a string in a horizontal circle of radius R at constant speed v. The centripetal acceleration of the ball can be increased by a factor of 4 by 1) keeping the speed fixed and increasing the radius by a factor of 4. 2) keeping the radius fixed and increasing the spe ...
... Q5) A ball is whirled on the end of a string in a horizontal circle of radius R at constant speed v. The centripetal acceleration of the ball can be increased by a factor of 4 by 1) keeping the speed fixed and increasing the radius by a factor of 4. 2) keeping the radius fixed and increasing the spe ...
How? – Use a Note-taking System
... Forces can change an object’s shape, speed or direction of travel. A Newton balance (or spring balance) can be used to measure force. The balance contains a spring which becomes longer when a force is applied. The longer the spring, the bigger the force. The unit of force is the Newton (N). Weight i ...
... Forces can change an object’s shape, speed or direction of travel. A Newton balance (or spring balance) can be used to measure force. The balance contains a spring which becomes longer when a force is applied. The longer the spring, the bigger the force. The unit of force is the Newton (N). Weight i ...
Exam 1 F11
... 27) When a rock thrown straight upwards gets to the exact top of its path, its A) velocity is about 10 m/s and its acceleration is zero. B) velocity is about 10 m/s and its acceleration is about 10 meters per second per second. C) velocity is zero and its acceleration is about 10 meters per second ...
... 27) When a rock thrown straight upwards gets to the exact top of its path, its A) velocity is about 10 m/s and its acceleration is zero. B) velocity is about 10 m/s and its acceleration is about 10 meters per second per second. C) velocity is zero and its acceleration is about 10 meters per second ...
Speeds and feeds

The phrase speeds and feeds or feeds and speeds refers to two separate velocities in machine tool practice, cutting speed and feed rate. They are often considered as a pair because of their combined effect on the cutting process. Each, however, can also be considered and analyzed in its own right.Cutting speed (also called surface speed or simply speed) is the speed difference (relative velocity) between the cutting tool and the surface of the workpiece it is operating on. It is expressed in units of distance along the workpiece surface per unit of time, typically surface feet per minute (sfm) or meters per minute (m/min). Feed rate (also often styled as a solid compound, feedrate, or called simply feed) is the relative velocity at which the cutter is advanced along the workpiece; its vector is perpendicular to the vector of cutting speed. Feed rate units depend on the motion of the tool and workpiece; when the workpiece rotates (e.g., in turning and boring), the units are almost always distance per spindle revolution (inches per revolution [in/rev or ipr] or millimeters per revolution [mm/rev]). When the workpiece does not rotate (e.g., in milling), the units are typically distance per time (inches per minute [in/min or ipm] or millimeters per minute [mm/min]), although distance per revolution or per cutter tooth are also sometimes used.If variables such as cutter geometry and the rigidity of the machine tool and its tooling setup could be ideally maximized (and reduced to negligible constants), then only a lack of power (that is, kilowatts or horsepower) available to the spindle would prevent the use of the maximum possible speeds and feeds for any given workpiece material and cutter material. Of course, in reality those other variables are dynamic and not negligible; but there is still a correlation between power available and feeds and speeds employed. In practice, lack of rigidity is usually the limiting constraint.The phrases ""speeds and feeds"" or ""feeds and speeds"" have sometimes been used metaphorically to refer to the execution details of a plan, which only skilled technicians (as opposed to designers or managers) would know.