Physiography of the Seafloor
... • 20% of ocean area – Continental shelf, 1/1000 slope, up to 400 km wide, extends to shelf break at ~130 m depth – Continental shelf formed 20Ky bp during the last ...
... • 20% of ocean area – Continental shelf, 1/1000 slope, up to 400 km wide, extends to shelf break at ~130 m depth – Continental shelf formed 20Ky bp during the last ...
File
... Surface zone-shallow area of seawater that gets the most sunlight. Middle zone-Receives only faint blue-green light. Deep zone-No light. Plants do not grow. Some animals make their own light. ...
... Surface zone-shallow area of seawater that gets the most sunlight. Middle zone-Receives only faint blue-green light. Deep zone-No light. Plants do not grow. Some animals make their own light. ...
Dr Thomas M. Cronin - QMplus - Queen Mary University of London
... understanding of Arctic Ocean sea ice, temperature, and climatic history, and discuss how it can be used as a framework for understanding future manmade changes to the climate in the Arctic. Sea-ice history reconstructed from fossils preserved in Arctic Ocean sediments is revealing its significant s ...
... understanding of Arctic Ocean sea ice, temperature, and climatic history, and discuss how it can be used as a framework for understanding future manmade changes to the climate in the Arctic. Sea-ice history reconstructed from fossils preserved in Arctic Ocean sediments is revealing its significant s ...
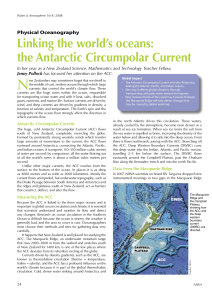
Linking the world`s oceans: the Antarctic Circumpolar Current
... flows through the ridge. The instruments collected data continuously for a year before the moorings were retrieved in April 2008. The data showed that the speed of the current passing through the Macquarie Ridge is about 4 km per hour – the speed an adult would walk quickly, and very fast for an oce ...
... flows through the ridge. The instruments collected data continuously for a year before the moorings were retrieved in April 2008. The data showed that the speed of the current passing through the Macquarie Ridge is about 4 km per hour – the speed an adult would walk quickly, and very fast for an oce ...
Limestone Rocky Shores - Perth Beachcombers Education Kit
... If you look along our rocky shores, from the highest to lowest tide levels, it is easy to see that a wide variety of marine animals live there. The high tide level is usually occupied by large numbers of small snails, normally found in groups around the edges of small pools, or near cracks and crevi ...
... If you look along our rocky shores, from the highest to lowest tide levels, it is easy to see that a wide variety of marine animals live there. The high tide level is usually occupied by large numbers of small snails, normally found in groups around the edges of small pools, or near cracks and crevi ...
Slides - IW:LEARN
... current. The Agulhas current flows south along the continental shelf of Mozambique and South Africa, and includes Comoros, Seychelles, La Réunion, Mauritius, and Madagascar. It pushes against the near-freezing waters of Antarctica before meeting the cold Benguela current off the Cape of Good Hope. ...
... current. The Agulhas current flows south along the continental shelf of Mozambique and South Africa, and includes Comoros, Seychelles, La Réunion, Mauritius, and Madagascar. It pushes against the near-freezing waters of Antarctica before meeting the cold Benguela current off the Cape of Good Hope. ...
NANOOS
... international network of observations and data transmission, data management and communications, and data analyses and modeling that systematically and efficiently acquires and disseminates data and information on past, present and future states of the oceans and U.S. coastal1 waters to the head of ...
... international network of observations and data transmission, data management and communications, and data analyses and modeling that systematically and efficiently acquires and disseminates data and information on past, present and future states of the oceans and U.S. coastal1 waters to the head of ...
Key concepts
... -be able to identify the features of a continental margin (continental shelf, shelf break, continental slope, continental rise) -know what factors affect continental shelf width -know what oceanic ridges are and the process occurring at them -be able to describe the formation of hydrothermal vents & ...
... -be able to identify the features of a continental margin (continental shelf, shelf break, continental slope, continental rise) -know what factors affect continental shelf width -know what oceanic ridges are and the process occurring at them -be able to describe the formation of hydrothermal vents & ...
Exam 3 PRACTICE – Winter 2016 KEY
... a. A rapid change in water temperature with depth b. A rapid change in water salinity with depth c. A barrier to vertical water movement d. Not a barrier to vertical water movement e. All of the above f. None of the above g. (a) and (c) h. (b) and (d) 8. Tropical oceans have a thermocline… a. …all y ...
... a. A rapid change in water temperature with depth b. A rapid change in water salinity with depth c. A barrier to vertical water movement d. Not a barrier to vertical water movement e. All of the above f. None of the above g. (a) and (c) h. (b) and (d) 8. Tropical oceans have a thermocline… a. …all y ...
English
... most of catadromous species. Thus, it is necessary to manage and protect this sensitive ecosystem in a sustainable manner. Gulf of Mannar is a repository of over 3,600 species of plants and animals and the first biosphere reserve in the South-East Asian region. It is one of the most biologically div ...
... most of catadromous species. Thus, it is necessary to manage and protect this sensitive ecosystem in a sustainable manner. Gulf of Mannar is a repository of over 3,600 species of plants and animals and the first biosphere reserve in the South-East Asian region. It is one of the most biologically div ...
Chapter 3: Communities and Biomes
... • gravitational pull of sun and moon causes a rise and fall of the ocean • Intertidal Zone – portion of the shoreline that lies between the high and low tides – Size depends on slope of land and difference between high and low tide – high levels of sunlight, nutrients, and ...
... • gravitational pull of sun and moon causes a rise and fall of the ocean • Intertidal Zone – portion of the shoreline that lies between the high and low tides – Size depends on slope of land and difference between high and low tide – high levels of sunlight, nutrients, and ...
information booklet - The Australian Institute of Marine Science
... northern waters between the Great Barrier Reef and Ningaloo Reef, the Institute’s expertise is enlisted throughout the world. The Institute has working relationships with more than 90 organisations across all Australian states and territories, and in 20 countries around the globe. A joint venture wi ...
... northern waters between the Great Barrier Reef and Ningaloo Reef, the Institute’s expertise is enlisted throughout the world. The Institute has working relationships with more than 90 organisations across all Australian states and territories, and in 20 countries around the globe. A joint venture wi ...
Activities • Walter Geibert (Alfred-Wegener Institute, Bremerhaven
... 1) Bring together specialists working from widely different perspectives on geochemical studies in the Siberian Shelves Seas. 2) Exploring possibilities of cooperation in future studies by exchange of data, samples, cruise participants. 35 attendants, including 10 early career scientists, from 10 co ...
... 1) Bring together specialists working from widely different perspectives on geochemical studies in the Siberian Shelves Seas. 2) Exploring possibilities of cooperation in future studies by exchange of data, samples, cruise participants. 35 attendants, including 10 early career scientists, from 10 co ...
Increasing knowledge: the grand challenge in marine biotechnology
... While contemplating the main challenges in the field of marine biotechnology, I found myself transported back to when I was a six years old boy, strolling along the beach with my grandfather and marveling at the diverse world of marine creatures which were washed up by the tide. My grandfather would ...
... While contemplating the main challenges in the field of marine biotechnology, I found myself transported back to when I was a six years old boy, strolling along the beach with my grandfather and marveling at the diverse world of marine creatures which were washed up by the tide. My grandfather would ...
Chapter 19
... study the ocean. • Explain how sonar works The Water Planet global ocean the body of salt water that covers nearly three-fourths of Earth’s surface • The global ocean contains more than 97% of all of the water on Earth. • The global ocean is divided into five major oceans. These major oceans are the ...
... study the ocean. • Explain how sonar works The Water Planet global ocean the body of salt water that covers nearly three-fourths of Earth’s surface • The global ocean contains more than 97% of all of the water on Earth. • The global ocean is divided into five major oceans. These major oceans are the ...
Strand: Interrelationships in Earth/Space Systems
... 12. The ocean’s salinity (saltiness) varies, depending on: (choose all correct items) a. runoff from nearby land b. the amount of evaporation c. the amount of salt used on food by local people. 13. True of False: Marine organisms are dependent on the dissolved gases in the ocean for survival. ...
... 12. The ocean’s salinity (saltiness) varies, depending on: (choose all correct items) a. runoff from nearby land b. the amount of evaporation c. the amount of salt used on food by local people. 13. True of False: Marine organisms are dependent on the dissolved gases in the ocean for survival. ...
6th Grade Science Sample Assessment Items S6E3c.
... Describe how the flow of weathered and dissolved rock material towards the ocean affect the chemical composition (makeup) of the ocean? ...
... Describe how the flow of weathered and dissolved rock material towards the ocean affect the chemical composition (makeup) of the ocean? ...
Gualtieri, L., Vartanyan, S., Anderson, P. and
... The present landscape is structurally controlled by bedrock that has been enhanced by nivation, masswasting and permafrost-related processes. Rounded hilltops consist of frost-shattered bedrock that displays various kinds of patterned ground including sorted circles, polygons and stripes. The lack o ...
... The present landscape is structurally controlled by bedrock that has been enhanced by nivation, masswasting and permafrost-related processes. Rounded hilltops consist of frost-shattered bedrock that displays various kinds of patterned ground including sorted circles, polygons and stripes. The lack o ...
Climate effects on North Sea zooplankton
... There is an accumulating body of evidence to suggest that many marine ecosystems in the North Atlantic, both physically and biologically are responding to changes in regional climate caused predominately by the warming of air and sea surface temperatures (SST) and to a varying degree by the modifica ...
... There is an accumulating body of evidence to suggest that many marine ecosystems in the North Atlantic, both physically and biologically are responding to changes in regional climate caused predominately by the warming of air and sea surface temperatures (SST) and to a varying degree by the modifica ...
Plate Tectonics - personal.kent.edu
... Plate tectonics is the major control of the sedimentary record •Relief of source area for clastic sediments •Composition of siliciclastic sediments •Position, size and shape of sedimentary basins •Rates of subsidence •Directly or indirectly influences the position of sea level •Control types of Sed ...
... Plate tectonics is the major control of the sedimentary record •Relief of source area for clastic sediments •Composition of siliciclastic sediments •Position, size and shape of sedimentary basins •Rates of subsidence •Directly or indirectly influences the position of sea level •Control types of Sed ...
Decades of data on world`s oceans reveal a troubling
... "The oxygen in oceans has dynamic properties, and its concentration can change with natural climate variability," said Taka Ito, an associate professor in Georgia Tech's School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences who led the research. "The important aspect of our result is that the rate of global oxyg ...
... "The oxygen in oceans has dynamic properties, and its concentration can change with natural climate variability," said Taka Ito, an associate professor in Georgia Tech's School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences who led the research. "The important aspect of our result is that the rate of global oxyg ...
Protecting Ocean Hotspots Lesson 3 Presentation Content
... One albatross tagged over Cordell Bank, off California (see close-up) • Black circles indicate where a bird was located at noon. Arrows show their path. • Look at the map legend to find out what ocean depths this albatross flew over. ...
... One albatross tagged over Cordell Bank, off California (see close-up) • Black circles indicate where a bird was located at noon. Arrows show their path. • Look at the map legend to find out what ocean depths this albatross flew over. ...
01 - 6th Grade Science with Mrs. Harlow
... The Gulf Stream carries warm water from the tropics to the North Atlantic Ocean and transports more water than all the rivers in the world. 13. In which direction do global winds blow ocean currents near the equator? They blow from east to west 14. How do surface currents and deep currents compare? ...
... The Gulf Stream carries warm water from the tropics to the North Atlantic Ocean and transports more water than all the rivers in the world. 13. In which direction do global winds blow ocean currents near the equator? They blow from east to west 14. How do surface currents and deep currents compare? ...
Marine biology

Marine biology is the scientific study of organisms in the ocean or other marine or brackish bodies of water. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. Marine biology differs from marine ecology as marine ecology is focused on how organisms interact with each other and the environment, while biology is the study of the organisms themselves.A large proportion of all life on Earth lives in the ocean. Exactly how large the proportion is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world covering about 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habitats include coral reefs, kelp forests, seagrass meadows, the surrounds of seamounts and thermal vents, tidepools, muddy, sandy and rocky bottoms, and the open ocean (pelagic) zone, where solid objects are rare and the surface of the water is the only visible boundary. The organisms studied range from microscopic phytoplankton and zooplankton to huge cetaceans (whales) 30 meters (98 feet) in length.Marine life is a vast resource, providing food, medicine, and raw materials, in addition to helping to support recreation and tourism all over the world. At a fundamental level, marine life helps determine the very nature of our planet. Marine organisms contribute significantly to the oxygen cycle, and are involved in the regulation of the Earth's climate. Shorelines are in part shaped and protected by marine life, and some marine organisms even help create new land.Many species are economically important to humans, including food fish (both finfish and shellfish). It is also becoming understood that the well-being of marine organisms and other organisms are linked in very fundamental ways. The human body of knowledge regarding the relationship between life in the sea and important cycles is rapidly growing, with new discoveries being made nearly every day. These cycles include those of matter (such as the carbon cycle) and of air (such as Earth's respiration, and movement of energy through ecosystems including the ocean). Large areas beneath the ocean surface still remain effectively unexplored.