Essential Standard Marine Biology
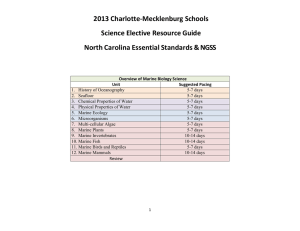
... 11. Marine Birds and Reptiles 5-7 days 12. Marine Mammals 10-14 days Review ...
... 11. Marine Birds and Reptiles 5-7 days 12. Marine Mammals 10-14 days Review ...
Ocean`s Role in Climate Change
... are a major factor. Precautions where appropriate. Assess adaptation strategies. ...
... are a major factor. Precautions where appropriate. Assess adaptation strategies. ...
Temperate East Commonwealth marine reserves
... key ecological features, they have also been largely left out of the proposed Commonwealth marine reserve network in the draft marine reserve proposal for the Temperate East. The absence of the continental shelf from the list of key ecological features ignores the critical importance it has to ocean ...
... key ecological features, they have also been largely left out of the proposed Commonwealth marine reserve network in the draft marine reserve proposal for the Temperate East. The absence of the continental shelf from the list of key ecological features ignores the critical importance it has to ocean ...
Aquatic viruses: the emerging story
... The probable ubiquity of viral infection has implications for biodiversity. While viruses fall outside the usual de¢nitions of ‘living’, they clearly can evolve and they deserve, and have, their own taxonomy and, of course, molecular phylogeny. While viruses are unlikely to attract much interest fro ...
... The probable ubiquity of viral infection has implications for biodiversity. While viruses fall outside the usual de¢nitions of ‘living’, they clearly can evolve and they deserve, and have, their own taxonomy and, of course, molecular phylogeny. While viruses are unlikely to attract much interest fro ...
Chemical and Physical Properties of Seawater
... In some locations, large volumes of water may sink or rise. Water sinks due to changes in temperature and salinity – this is known as an area of down-welling. Down-welling brings gases from the surface to deeper layers. Areas of upwelling come from currents that push deeper waters toward the surface ...
... In some locations, large volumes of water may sink or rise. Water sinks due to changes in temperature and salinity – this is known as an area of down-welling. Down-welling brings gases from the surface to deeper layers. Areas of upwelling come from currents that push deeper waters toward the surface ...
Guided Notes on Seafloor Spreading
... Echo-sounding technology, such as SONAR, uses sound waves to measure water depth. The sound waves bounce off the ocean floor and back to a receiver. ...
... Echo-sounding technology, such as SONAR, uses sound waves to measure water depth. The sound waves bounce off the ocean floor and back to a receiver. ...
Slide 1
... continental barriers affect surface currents Identify the major factor that determines the direction in which a surface current circulates Explain how differences in the density of ocean water affects the flow of deep currents ...
... continental barriers affect surface currents Identify the major factor that determines the direction in which a surface current circulates Explain how differences in the density of ocean water affects the flow of deep currents ...
Biomes
... • Continental shelf ecosystems provide abundant resources • Neritic waters: waters over the shelves – High concentrations of nitrates and other nutrient – Shallow, up welling occurs here • 99% of ocean food supply comes from neritic waters • Petroleum comes almost exclusively from shelves ...
... • Continental shelf ecosystems provide abundant resources • Neritic waters: waters over the shelves – High concentrations of nitrates and other nutrient – Shallow, up welling occurs here • 99% of ocean food supply comes from neritic waters • Petroleum comes almost exclusively from shelves ...
Ch 58 Notes
... • Continental shelf ecosystems provide abundant resources • Neritic waters: waters over the shelves – High concentrations of nitrates and other nutrient – Shallow, up welling occurs here • 99% of ocean food supply comes from neritic waters • Petroleum comes almost exclusively from shelves ...
... • Continental shelf ecosystems provide abundant resources • Neritic waters: waters over the shelves – High concentrations of nitrates and other nutrient – Shallow, up welling occurs here • 99% of ocean food supply comes from neritic waters • Petroleum comes almost exclusively from shelves ...
Strand: Interrelationships in Earth/Space Systems
... geological characteristics (continental shelf, slope, rise); physical characteristics (depth, salinity, major currents); biological characteristics (ecosystems); and public policy decisions related to the ocean environment (assessment of marine organism populations, pollution prevention). ...
... geological characteristics (continental shelf, slope, rise); physical characteristics (depth, salinity, major currents); biological characteristics (ecosystems); and public policy decisions related to the ocean environment (assessment of marine organism populations, pollution prevention). ...
C O H
... linked. The health of marine ecosystems is affected by human activities such as pollution, global warming, and fishing. But in addition, human health depends on thriving ocean ecosystems. A better understanding about the many ways marine organisms affect human health, both for good by providing drug ...
... linked. The health of marine ecosystems is affected by human activities such as pollution, global warming, and fishing. But in addition, human health depends on thriving ocean ecosystems. A better understanding about the many ways marine organisms affect human health, both for good by providing drug ...
UKSeaMap - Defra Science Search
... Frontal probability - this indicates the presence of fronts which provide some distinct horizontal boundary zones in the water column. Given the high degree of change in the water column over the course of a year, the data were processed according to four separate seasons (winter, spring, summer and ...
... Frontal probability - this indicates the presence of fronts which provide some distinct horizontal boundary zones in the water column. Given the high degree of change in the water column over the course of a year, the data were processed according to four separate seasons (winter, spring, summer and ...
Doing Hands-On Science with Students
... EP 5 Ocean supports great diversity of life FC d. Ocean biology provides unique examples of adaptations FC f. Ocean habitats defined by environmental factors…such as…light ...
... EP 5 Ocean supports great diversity of life FC d. Ocean biology provides unique examples of adaptations FC f. Ocean habitats defined by environmental factors…such as…light ...
Anders_Omstedt
... Use P and N observations from the Eastern Gotland Basin and plot the surface properties of PO4 and NO3 of the last 5 years. Discuss the dynamics. Problem 1.14.1 Use pH observations from the Eastern Gotland Basin and plot the surface values. Discuss what is controlling the seasonal and long-term vari ...
... Use P and N observations from the Eastern Gotland Basin and plot the surface properties of PO4 and NO3 of the last 5 years. Discuss the dynamics. Problem 1.14.1 Use pH observations from the Eastern Gotland Basin and plot the surface values. Discuss what is controlling the seasonal and long-term vari ...
Sea Floor Spreading Barrows
... Scientists studied the rock patterns in the ocean floor . They found that the rock on the ocean floor lies in a pattern of magnetized stripes Magnetic stripes in ocean floor rocks are formed by the reversal of the Earth’s magnetic poles. The last reversal happened 780,000 years ago. The pattern of s ...
... Scientists studied the rock patterns in the ocean floor . They found that the rock on the ocean floor lies in a pattern of magnetized stripes Magnetic stripes in ocean floor rocks are formed by the reversal of the Earth’s magnetic poles. The last reversal happened 780,000 years ago. The pattern of s ...
OCEAN-ATMOSPHERIC INTERACTION IN THE SUBTROPICAL
... surface temperature were the two key factors contributed to the development of the extra tropical cyclone and its accompanying heavy precipitation over Shandong Peninsula. ...
... surface temperature were the two key factors contributed to the development of the extra tropical cyclone and its accompanying heavy precipitation over Shandong Peninsula. ...
CH 2 Notes Floor Etc Student Notetaker
... zones where ______________, heated by the hot, newly-formed oceanic crust, escapes through _______ in the oceanic crust into surrounding water along ______ ...
... zones where ______________, heated by the hot, newly-formed oceanic crust, escapes through _______ in the oceanic crust into surrounding water along ______ ...
Dr. Joaquim Goes - (UConn) Marine Sciences
... warming trend have not been confined to the SWM alone. During the northeast monsoon (NEM) also, chlorophyll a concentrations have been on the rise due to unprecedented blooms of a mixotrophic dinoflagellate, Noctiluca scintillans (Noctiluca). First seen in smaller numbers off the coast of Oman, Noct ...
... warming trend have not been confined to the SWM alone. During the northeast monsoon (NEM) also, chlorophyll a concentrations have been on the rise due to unprecedented blooms of a mixotrophic dinoflagellate, Noctiluca scintillans (Noctiluca). First seen in smaller numbers off the coast of Oman, Noct ...
A New Carbon-Based Algal Biomass Proxy for Photoacclimation
... Photoacclimation changes the intracellular chlorophyll-a concentration (Chl), and is not currently taken into account by standard ocean color algorithms. Chl production is a process enhanced under high nutrient and low light conditions (e.g. winter and spring in the Mediterranean Sea). Historically, ...
... Photoacclimation changes the intracellular chlorophyll-a concentration (Chl), and is not currently taken into account by standard ocean color algorithms. Chl production is a process enhanced under high nutrient and low light conditions (e.g. winter and spring in the Mediterranean Sea). Historically, ...
Surface Currents
... Upwelling is the vertical movement of water toward the ocean’s surface. occurs when wind blows across the ocean’s surface and pushes water away from an area. Deeper colder water then rises to ...
... Upwelling is the vertical movement of water toward the ocean’s surface. occurs when wind blows across the ocean’s surface and pushes water away from an area. Deeper colder water then rises to ...
Impacts - 3 - Green Resistance
... the world's seas, said increasing levels of carbon dioxide being released into the atmosphere by industrialised countries was gradually changing the acid level of waters across the world. If the trend continued, the shells of thousands of species would be eroded and the creatures eventually wiped ou ...
... the world's seas, said increasing levels of carbon dioxide being released into the atmosphere by industrialised countries was gradually changing the acid level of waters across the world. If the trend continued, the shells of thousands of species would be eroded and the creatures eventually wiped ou ...
Oceanographic Autonomous Observations
... Originally initialized by SEREAD (Scientific Educational Resources and Experience Associated with the Deployment of Argo profiling floats in the South Pacific Ocean), now enlarged to biogeochemistry: • School classes may follow a profiling float during its scientific journey • Possibility to analyze ...
... Originally initialized by SEREAD (Scientific Educational Resources and Experience Associated with the Deployment of Argo profiling floats in the South Pacific Ocean), now enlarged to biogeochemistry: • School classes may follow a profiling float during its scientific journey • Possibility to analyze ...
Marine biology

Marine biology is the scientific study of organisms in the ocean or other marine or brackish bodies of water. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. Marine biology differs from marine ecology as marine ecology is focused on how organisms interact with each other and the environment, while biology is the study of the organisms themselves.A large proportion of all life on Earth lives in the ocean. Exactly how large the proportion is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world covering about 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habitats include coral reefs, kelp forests, seagrass meadows, the surrounds of seamounts and thermal vents, tidepools, muddy, sandy and rocky bottoms, and the open ocean (pelagic) zone, where solid objects are rare and the surface of the water is the only visible boundary. The organisms studied range from microscopic phytoplankton and zooplankton to huge cetaceans (whales) 30 meters (98 feet) in length.Marine life is a vast resource, providing food, medicine, and raw materials, in addition to helping to support recreation and tourism all over the world. At a fundamental level, marine life helps determine the very nature of our planet. Marine organisms contribute significantly to the oxygen cycle, and are involved in the regulation of the Earth's climate. Shorelines are in part shaped and protected by marine life, and some marine organisms even help create new land.Many species are economically important to humans, including food fish (both finfish and shellfish). It is also becoming understood that the well-being of marine organisms and other organisms are linked in very fundamental ways. The human body of knowledge regarding the relationship between life in the sea and important cycles is rapidly growing, with new discoveries being made nearly every day. These cycles include those of matter (such as the carbon cycle) and of air (such as Earth's respiration, and movement of energy through ecosystems including the ocean). Large areas beneath the ocean surface still remain effectively unexplored.























