Biology - Arizona Educator Proficiency Assessments
... the processes of embryonic development. For example: structures and functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems; the transmission of nerve impulses within and between neurons; structures of the endocrine system and the functions of specific hormones; structures and functions of the male ...
... the processes of embryonic development. For example: structures and functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems; the transmission of nerve impulses within and between neurons; structures of the endocrine system and the functions of specific hormones; structures and functions of the male ...
Chapter 8- Carbon Chemistry
... Recall that the atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that the nucleus of a carbon atom contains 6 protons. Surrounding the nucleus are 6 electrons. Of these electrons, four are valence electrons-the electrons available for bonding. As you have learned, a chemical bond is the force that holds tw ...
... Recall that the atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that the nucleus of a carbon atom contains 6 protons. Surrounding the nucleus are 6 electrons. Of these electrons, four are valence electrons-the electrons available for bonding. As you have learned, a chemical bond is the force that holds tw ...
APG Phytochemical Database - American Pistachio Growers
... Amino Acid Building block for making proteins. (See Protein) Arginine maintains arteries flexible and enhances blood flow by boosting nitric oxide, a compound that relaxes blood vessels. ...
... Amino Acid Building block for making proteins. (See Protein) Arginine maintains arteries flexible and enhances blood flow by boosting nitric oxide, a compound that relaxes blood vessels. ...
Chemicals of life
... 1. Label two test tubes as A and B. 2. Pour 2 cm3 of glucose solution into tube A, and 2 cm3 of distilled water into tube B. 3. Add 2 cm3 of Benedict’s solution to each tube and shake gently. 4. Boil the test tubes in a water bath for 5 minutes. Shake the tubes at intervals. Note the colour changes ...
... 1. Label two test tubes as A and B. 2. Pour 2 cm3 of glucose solution into tube A, and 2 cm3 of distilled water into tube B. 3. Add 2 cm3 of Benedict’s solution to each tube and shake gently. 4. Boil the test tubes in a water bath for 5 minutes. Shake the tubes at intervals. Note the colour changes ...
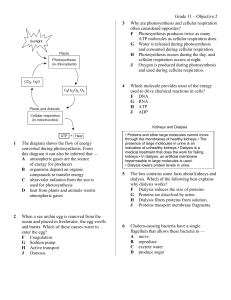
Grade 11 – Objective 2 1 The diagram shows the flow
... 21 In all plant and animal cells, the nucleus contains long molecules of DNA. Which of the following best describes the function of DNA? F DNA provides the shape and structure of the nucleus. G DNA packages materials for transport through the nucleus. H DNA carries materials into and out of the ...
... 21 In all plant and animal cells, the nucleus contains long molecules of DNA. Which of the following best describes the function of DNA? F DNA provides the shape and structure of the nucleus. G DNA packages materials for transport through the nucleus. H DNA carries materials into and out of the ...
Nutrition Essentials: Protein
... Protein is a nutrient that is comprised of amino acids. Sometimes these amino acids are referred to as building blocks for protein. Each amino acid has the same basic structure and includes carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and a unique side group. The side group is different on each amino acid an ...
... Protein is a nutrient that is comprised of amino acids. Sometimes these amino acids are referred to as building blocks for protein. Each amino acid has the same basic structure and includes carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and a unique side group. The side group is different on each amino acid an ...
MLHS-Biology Honors
... Define hydrogen bonding, and explain how this results from polarity, using water as an example. List and describe many important properties of water for living things, including high solvency, cohesion, adhesion, high heat capacity, high heat of fusion, high heat of vaporization, capillary actio ...
... Define hydrogen bonding, and explain how this results from polarity, using water as an example. List and describe many important properties of water for living things, including high solvency, cohesion, adhesion, high heat capacity, high heat of fusion, high heat of vaporization, capillary actio ...
Honors Chapter 1 and 2 learning objectives
... 18. Describe patterns observed in data, and whether any observed trends are positive or weak 19. Develop/discuss alternative explanations for patterns in data; decide which most likely fits the data/evidence. ...
... 18. Describe patterns observed in data, and whether any observed trends are positive or weak 19. Develop/discuss alternative explanations for patterns in data; decide which most likely fits the data/evidence. ...
1강 - KOCW
... • A system is a combination of components that function together • Systems biology constructs models for the dynamic behavior of whole biological systems • The systems approach poses questions such as – How does a drug for blood pressure affect other organs? – How does increasing CO2 alter the biosp ...
... • A system is a combination of components that function together • Systems biology constructs models for the dynamic behavior of whole biological systems • The systems approach poses questions such as – How does a drug for blood pressure affect other organs? – How does increasing CO2 alter the biosp ...
Bio Frames - Lee County School District
... Define a problem based on a specific body of knowledge for example: biology, chemistry, physics, and earth/space science and do the following: (DOK High) (1) pose quesons about the natural world, (2) conduct systemic observa ons, (3) examine books and other sources of informa on to see what is already ...
... Define a problem based on a specific body of knowledge for example: biology, chemistry, physics, and earth/space science and do the following: (DOK High) (1) pose quesons about the natural world, (2) conduct systemic observa ons, (3) examine books and other sources of informa on to see what is already ...
Reading for a Purpose: Molecules the Human Body Needs
... such as headings and visual representations, can help them find information quickly. ...
... such as headings and visual representations, can help them find information quickly. ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... protein crystallography, Linus Pauling in the United States, John Randall and Maurice Wilkins at the King's College, London, to name a few, working on similar problems. One of the central problems in biology was to explain how genetic information is replicated and transmitted from generation to gene ...
... protein crystallography, Linus Pauling in the United States, John Randall and Maurice Wilkins at the King's College, London, to name a few, working on similar problems. One of the central problems in biology was to explain how genetic information is replicated and transmitted from generation to gene ...
Chapter 9
... Bases are purines (A and G) and pyrimidines (C and T) • Purines have a pair of fused rings; pyrimidines only have one • A and T are connected by two hydrogen bonds; G and C are connected by three hydrogen bonds • The number of bonds is the basis of specific pairing between the bases (cont.) Copyrigh ...
... Bases are purines (A and G) and pyrimidines (C and T) • Purines have a pair of fused rings; pyrimidines only have one • A and T are connected by two hydrogen bonds; G and C are connected by three hydrogen bonds • The number of bonds is the basis of specific pairing between the bases (cont.) Copyrigh ...
Identification and Quantification of Oxidized Proteins
... Advantages and disadvantages of using proteins as markers of oxidative stress ...
... Advantages and disadvantages of using proteins as markers of oxidative stress ...
1 The diagram shows part of a pre-mRNA molecule. 1 (a) (i) Name
... 1 (c) (ii) Explain why the percentages of bases from the middle part of the chromosome and the end part are different. ...
... 1 (c) (ii) Explain why the percentages of bases from the middle part of the chromosome and the end part are different. ...
Review Presentation on the Digestive System
... The liver has many functions, including (but not limited to): 1. to produce substances that break down fats 2. produce urea (the main substance of urine) 3. make certain amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) 4. filter harmful substances from the blood (such as alcohol) 5. The liver is also ...
... The liver has many functions, including (but not limited to): 1. to produce substances that break down fats 2. produce urea (the main substance of urine) 3. make certain amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) 4. filter harmful substances from the blood (such as alcohol) 5. The liver is also ...
Section 4 pp from textbook
... Values of n ranging from three to seven are called simple sugars, or monosaccharides. Two monosaccharides joined together form a disaccharide. ...
... Values of n ranging from three to seven are called simple sugars, or monosaccharides. Two monosaccharides joined together form a disaccharide. ...
Biology Study List - MCAT Prep Course
... ¾ Understand the basic functions and structures of the major chemical components of living cells and their surroundings: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleotides, water and minerals (in order of importance) Enzymes: ¾ Understand the function and mode of action of enzymes ¾ Know the concept and m ...
... ¾ Understand the basic functions and structures of the major chemical components of living cells and their surroundings: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleotides, water and minerals (in order of importance) Enzymes: ¾ Understand the function and mode of action of enzymes ¾ Know the concept and m ...
Preview Sample 1
... 28. (p. 24) Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins? A. They form enzymes to speed up reactions. B. They form the backbone of cell membranes. C. They form body parts such as muscle. D. They form antibodies to protect the body from disease. Phospholipids form the backbone of cell membran ...
... 28. (p. 24) Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins? A. They form enzymes to speed up reactions. B. They form the backbone of cell membranes. C. They form body parts such as muscle. D. They form antibodies to protect the body from disease. Phospholipids form the backbone of cell membran ...
File - Biology @ Aldenham School
... Chapter 2: The Variety of Living Organisms • Describe the levels of organisation within organisms: organelles, cells, tissues, organs and systems. • There is a wide variety of living organisms and biology classifies organisms on the basis of their structure and how they function • Describe the commo ...
... Chapter 2: The Variety of Living Organisms • Describe the levels of organisation within organisms: organelles, cells, tissues, organs and systems. • There is a wide variety of living organisms and biology classifies organisms on the basis of their structure and how they function • Describe the commo ...
FREE Sample Here
... 28. (p. 24) Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins? A. They form enzymes to speed up reactions. B. They form the backbone of cell membranes. C. They form body parts such as muscle. D. They form antibodies to protect the body from disease. Phospholipids form the backbone of cell membran ...
... 28. (p. 24) Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins? A. They form enzymes to speed up reactions. B. They form the backbone of cell membranes. C. They form body parts such as muscle. D. They form antibodies to protect the body from disease. Phospholipids form the backbone of cell membran ...
FREE Sample Here
... 28. (p. 24) Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins? A. They form enzymes to speed up reactions. B. They form the backbone of cell membranes. C. They form body parts such as muscle. D. They form antibodies to protect the body from disease. Phospholipids form the backbone of cell membran ...
... 28. (p. 24) Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins? A. They form enzymes to speed up reactions. B. They form the backbone of cell membranes. C. They form body parts such as muscle. D. They form antibodies to protect the body from disease. Phospholipids form the backbone of cell membran ...
AB Balance Lecture 1_2015
... important then the plasma proteins as it is present in about twice the concentration and contains about three times the number of histidine residues per molecule. For example if blood pH changed from 7.5 to 6.5, haemoglobin would buffer 27.5 mmol/l of H+ and total plasma protein buffering would acco ...
... important then the plasma proteins as it is present in about twice the concentration and contains about three times the number of histidine residues per molecule. For example if blood pH changed from 7.5 to 6.5, haemoglobin would buffer 27.5 mmol/l of H+ and total plasma protein buffering would acco ...
BIO315109 Part 1
... In February 2013 a group of Norwegian scientists published results of an investigation into the effects of the vitamin folic acid when taken in tablet form by women in the early stages of pregnancy. This research took place between 2002 and 2008. Information was collected using questionnaires given ...
... In February 2013 a group of Norwegian scientists published results of an investigation into the effects of the vitamin folic acid when taken in tablet form by women in the early stages of pregnancy. This research took place between 2002 and 2008. Information was collected using questionnaires given ...