AND8143/D A General Approach for Optimizing Dynamic Response for Buck
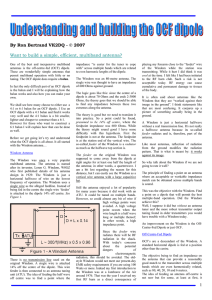
... These two blocks are commonly grouped as the modulator. Gc(s) is the compensation network transfer function. It will be discussed in the next section. The modeling of the low−frequency behavior of power switches in square−wave power converters is explained in [1]. The circuit of a buck ...
... These two blocks are commonly grouped as the modulator. Gc(s) is the compensation network transfer function. It will be discussed in the next section. The modeling of the low−frequency behavior of power switches in square−wave power converters is explained in [1]. The circuit of a buck ...
UNIT 2: POWER AND ROOTS
... as ordinary numbers. Scientific notation is commonly used in calculators and by scientists, mathematicians and engineers. In scientific notation all numbers are written in the form of (a times ten raised to the power of b), where the exponent b is an integer, and the coefficient a is a decimal numbe ...
... as ordinary numbers. Scientific notation is commonly used in calculators and by scientists, mathematicians and engineers. In scientific notation all numbers are written in the form of (a times ten raised to the power of b), where the exponent b is an integer, and the coefficient a is a decimal numbe ...
MAX7057EVKIT.pdf
... Connects PAVDD to TP40. Must apply an external voltage between TP40 and TP41 (GND) to power PAVDD. ...
... Connects PAVDD to TP40. Must apply an external voltage between TP40 and TP41 (GND) to power PAVDD. ...
1. Revision Description Reflect and Review Teasers
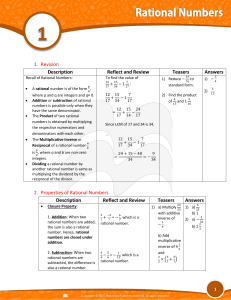
... rational numbers a, b and c, (a – b) – c a – (b – c). Hence, subtraction is not associative for rational numbers. 3. Multiplication: For any three rational numbers a, b and c, (a × b) × c = a × (b × c). Hence, multiplication is associative for rational numbers. 4. Division: For any three rational ...
... rational numbers a, b and c, (a – b) – c a – (b – c). Hence, subtraction is not associative for rational numbers. 3. Multiplication: For any three rational numbers a, b and c, (a × b) × c = a × (b × c). Hence, multiplication is associative for rational numbers. 4. Division: For any three rational ...
Frequency of Primes Instructions (Word Format)
... 3. In #2 you found consecutive primes whose difference is 2. There are also consecutive primes whose difference is 4, such as 7 and 3, 17 and 13, 23 and 19. Check intervals of 100 to see if such primes exist in each interval. Do the number of such primes appear to be increasing or decreasing from in ...
... 3. In #2 you found consecutive primes whose difference is 2. There are also consecutive primes whose difference is 4, such as 7 and 3, 17 and 13, 23 and 19. Check intervals of 100 to see if such primes exist in each interval. Do the number of such primes appear to be increasing or decreasing from in ...
Theorems here
... stratified random sampling- It is used to assure that the sample has the same characteristics as the population. ...
... stratified random sampling- It is used to assure that the sample has the same characteristics as the population. ...
Low Power CMOS Rectifier Design for RFID Applications
... these components together are presented. Our measured RF ...
... these components together are presented. Our measured RF ...
22(2)
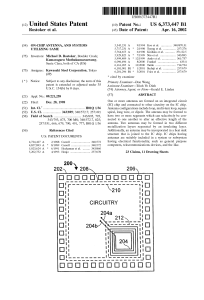
... However, the representation can be made unique as follows. To represent a positive number n9 find the largest bi that is less than or equal to n. The representation of n will have a one in the i th digit. Now find the largest bj less than or equal to n - b^ . The representation will also have a one ...
... However, the representation can be made unique as follows. To represent a positive number n9 find the largest bi that is less than or equal to n. The representation of n will have a one in the i th digit. Now find the largest bj less than or equal to n - b^ . The representation will also have a one ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.