18(3)
... (in the ring I[x9 y] of polynomials in x and y with integer coefficients) whenever m\n. Unlike the Fibonacci numbers, however, the polynomial is irreducible (in I[xs y]) whenever the index m is irreducible in I. Thus9 the divisibility properties of the more general sequence differ from those of the ...
... (in the ring I[x9 y] of polynomials in x and y with integer coefficients) whenever m\n. Unlike the Fibonacci numbers, however, the polynomial is irreducible (in I[xs y]) whenever the index m is irreducible in I. Thus9 the divisibility properties of the more general sequence differ from those of the ...
Slide 1
... In the last lecture, we saw the use of (shared) private key cryptography Example: E-banking (you may need to physically get password) Shared key cryptography does not solve all communication problems: Examples: Secure E-commerce (how did you exchange password with Amazon? with Yahoo shopping ?) We a ...
... In the last lecture, we saw the use of (shared) private key cryptography Example: E-banking (you may need to physically get password) Shared key cryptography does not solve all communication problems: Examples: Secure E-commerce (how did you exchange password with Amazon? with Yahoo shopping ?) We a ...
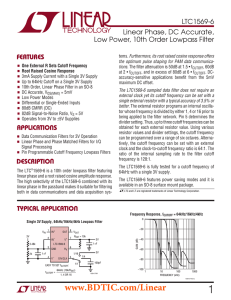
LTC1569-6 - Linear Phase, DC Accurate, Low Power, 10th Order Lowpass Filter
... The input signal range includes the full power supply range. The output range is typically (V – + 50mV) to (V + – 0.8V) when using a single 3V supply with the GND (Pin 3) voltage set to 1.11V. In other words, the output range is typically 2.1VP-P for a 3V supply. Similarly, the output range is typic ...
... The input signal range includes the full power supply range. The output range is typically (V – + 50mV) to (V + – 0.8V) when using a single 3V supply with the GND (Pin 3) voltage set to 1.11V. In other words, the output range is typically 2.1VP-P for a 3V supply. Similarly, the output range is typic ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.