Sample Exam Key
... . Give your answer using interval notation and graph 2x 6 your answer on the number line. Find the domain of h( x) ...
... . Give your answer using interval notation and graph 2x 6 your answer on the number line. Find the domain of h( x) ...
Chapter 2
... • Hence, the system function becomes H ( jw) H ( s) |s jw H ( jw) M ( w)e j ( w) ...
... • Hence, the system function becomes H ( jw) H ( s) |s jw H ( jw) M ( w)e j ( w) ...
Slide 1
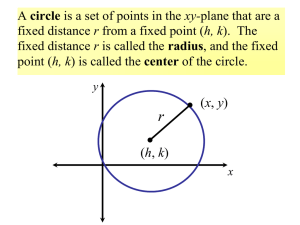
... A circle is a set of points in the xy-plane that are a fixed distance r from a fixed point (h, k). The fixed distance r is called the radius, and the fixed point (h, k) is called the center of the circle. y ...
... A circle is a set of points in the xy-plane that are a fixed distance r from a fixed point (h, k). The fixed distance r is called the radius, and the fixed point (h, k) is called the center of the circle. y ...
Document
... Clearly, in order to control a system as complex as this requires significant coordination between the phases and frequencies of the different oscillators. Both CPGs and reflexes seem to be involved. ...
... Clearly, in order to control a system as complex as this requires significant coordination between the phases and frequencies of the different oscillators. Both CPGs and reflexes seem to be involved. ...
The Mole - TeacherWeb
... characteristics of both waves and particulate matter. A quanta of EM is called a photon. So, here is where it gets a little deep… We know that when white light is diffracted, it separates into a continuous spectrum of colors (ROYGBIV). However, then the light emitted from an excited element is diffr ...
... characteristics of both waves and particulate matter. A quanta of EM is called a photon. So, here is where it gets a little deep… We know that when white light is diffracted, it separates into a continuous spectrum of colors (ROYGBIV). However, then the light emitted from an excited element is diffr ...
Original
... is reflected about the vertical axis, the result is the graph of f ( x ) = "x as is shown in the following figure. It is important to recognize that the point (0, 0) is on ...
... is reflected about the vertical axis, the result is the graph of f ( x ) = "x as is shown in the following figure. It is important to recognize that the point (0, 0) is on ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.