Infinitive Петухова
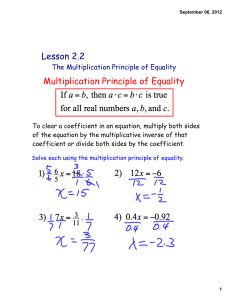
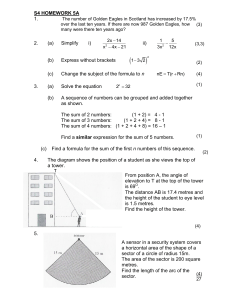
... The scientific theory is said to be definite according to Husserl. This case is likely to be called consistent. “Lines of forces” are known to be introduced by Faraday. These people were certain to live in a spherical universe. The surface of a globe was found to have only two dimensions. ...
... The scientific theory is said to be definite according to Husserl. This case is likely to be called consistent. “Lines of forces” are known to be introduced by Faraday. These people were certain to live in a spherical universe. The surface of a globe was found to have only two dimensions. ...
Plane Waves and Polarization The simplest EM waves are uniform
... The simplest EM waves are uniform plane waves propagating in some fixed direction, say the z-direction, in a lossless medium {ε,μ}. The assumption means that the field has no dependence on the transverse coordinates x,y and are function only of z, t. Thus we look for solution of Maxwell Equations fo ...
... The simplest EM waves are uniform plane waves propagating in some fixed direction, say the z-direction, in a lossless medium {ε,μ}. The assumption means that the field has no dependence on the transverse coordinates x,y and are function only of z, t. Thus we look for solution of Maxwell Equations fo ...
Class06
... – Since the transmitted signal is not a simple sine wave, it has a bandwidth of Fourier components – FM is easier to amplify, since only the frequency determines the signal. ...
... – Since the transmitted signal is not a simple sine wave, it has a bandwidth of Fourier components – FM is easier to amplify, since only the frequency determines the signal. ...
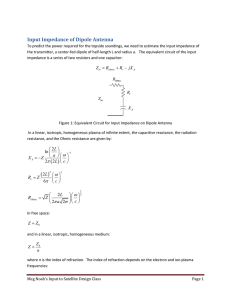
An antenna is a transducer designed to transmit or receive radio
... An antenna is a transducer designed to transmit or receive radio waves which are a class of electromagnetic waves. In other words, antennas convert radio frequency electrical currents into electromagnetic waves and vice versa. Physically, an antenna is an arrangement of conductors that generate a ra ...
... An antenna is a transducer designed to transmit or receive radio waves which are a class of electromagnetic waves. In other words, antennas convert radio frequency electrical currents into electromagnetic waves and vice versa. Physically, an antenna is an arrangement of conductors that generate a ra ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.





![m1-] 63 NOTE ON THE NUMBER OF LINEARLY INDEPEND](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/012997862_1-d2f38d28dd32ef9691afaab3955d0a2a-300x300.png)