UbD (Understanding by Design) Lesson Plan
... a. Build new mathematical knowledge through problem solving. b. Solve problems that arise in mathematics and in other contexts. c. Apply and adapt a variety of appropriate strategies to solve problems. d. Monitor and reflect on the process of mathematical problem solving. M7P2. Students will reason ...
... a. Build new mathematical knowledge through problem solving. b. Solve problems that arise in mathematics and in other contexts. c. Apply and adapt a variety of appropriate strategies to solve problems. d. Monitor and reflect on the process of mathematical problem solving. M7P2. Students will reason ...
B - math.fme.vutbr.cz
... Properties of real numbers R is ordered by the relation Every equation a + x = b where a,b are real has a real solution Every equation a . x = b where a,b are real and a 0, has a real solution Every equation x2 = b where b > 0 is real has a real solution In every -neighbourhood of a real numbe ...
... Properties of real numbers R is ordered by the relation Every equation a + x = b where a,b are real has a real solution Every equation a . x = b where a,b are real and a 0, has a real solution Every equation x2 = b where b > 0 is real has a real solution In every -neighbourhood of a real numbe ...
Palette of Problems 2 - Narragansett Schools
... we know that Ben is not the tallest. By (c), Ben is the second shortest and Ashley is not the tallest. By (b), Ashley is taller than Duane, so Ashley is neither the shortest nor the tallest. Ben is the second shortest, so Ashley must be the third shortest person (taller than Ben, but not the tallest ...
... we know that Ben is not the tallest. By (c), Ben is the second shortest and Ashley is not the tallest. By (b), Ashley is taller than Duane, so Ashley is neither the shortest nor the tallest. Ben is the second shortest, so Ashley must be the third shortest person (taller than Ben, but not the tallest ...
Mathematical Diversions
... One thing one can observe is that the card that was in position k, after the shuffle ends in position 2k mod 9. This suggests or shows that the number of shuffles that take the deck back to its original position is the first n such that 2n = 1 mod 9. That number turns out to be 6. One might remember ...
... One thing one can observe is that the card that was in position k, after the shuffle ends in position 2k mod 9. This suggests or shows that the number of shuffles that take the deck back to its original position is the first n such that 2n = 1 mod 9. That number turns out to be 6. One might remember ...
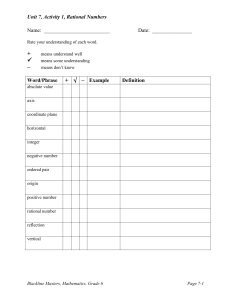
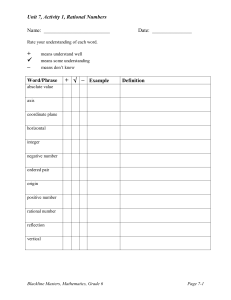
MAT_GR6_U7_BLM_Final
... Using the above coordinate grid, answer the following questions: 1. What are the coordinates of point D? (1, 5) 2. Do the coordinates (2, 5) and (5, 2) describe the location of the same point? No, the first number describes how far to move on the x-axis and the second number describes how far to mov ...
... Using the above coordinate grid, answer the following questions: 1. What are the coordinates of point D? (1, 5) 2. Do the coordinates (2, 5) and (5, 2) describe the location of the same point? No, the first number describes how far to move on the x-axis and the second number describes how far to mov ...