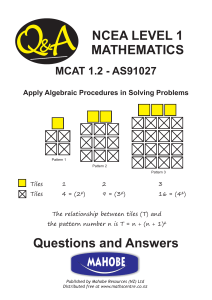
Target Sheet Ch. 2
... Division Rule: Never divide…change to a multiplication problem by taking the multiplicative inverse of the second term, then multiply and apply multiplication sign rule Sign Rules: Subtracting two real numbers…change to addition problem, then use addition sign rule Adding two real numbers… use the s ...
... Division Rule: Never divide…change to a multiplication problem by taking the multiplicative inverse of the second term, then multiply and apply multiplication sign rule Sign Rules: Subtracting two real numbers…change to addition problem, then use addition sign rule Adding two real numbers… use the s ...
Discussion
... using the both the commutative and associative laws of addition, could be to change the order and groupings of the numbers. In our example, the first grouping could be the largest number with the smallest number (i.e. 1 + 16), next grouping the second largest number with the second smallest number ( ...
... using the both the commutative and associative laws of addition, could be to change the order and groupings of the numbers. In our example, the first grouping could be the largest number with the smallest number (i.e. 1 + 16), next grouping the second largest number with the second smallest number ( ...
A Primer on Proving
... In a classroom setting, a problem that starts off with “prove this theorem” is an exercise in which students are assured that what they are working on can be proven by the word “theorem” in the problem statement. Neither teachers nor mathematicians call a statement “theorem” unless it’s been proved. ...
... In a classroom setting, a problem that starts off with “prove this theorem” is an exercise in which students are assured that what they are working on can be proven by the word “theorem” in the problem statement. Neither teachers nor mathematicians call a statement “theorem” unless it’s been proved. ...