Geometry Module 2, Topic C, Lesson 12: Teacher
... curricula. In the past, congruence criteria have first been defined for triangles (e.g., SSS or ASA), and then, by extension, for polygonal figures, with similarity being treated in a like manner. However, the Common Core Standards approach these concepts via transformations, allowing one to accommo ...
... curricula. In the past, congruence criteria have first been defined for triangles (e.g., SSS or ASA), and then, by extension, for polygonal figures, with similarity being treated in a like manner. However, the Common Core Standards approach these concepts via transformations, allowing one to accommo ...
Parametric Decay and Anomalous Scattering from
... electromagnetic (pump) wave in the microwave/millimetre wave frequency range may be converted into two electrostatic daughter waves, one having a frequency comparable to that of the pump wave and one having a frequency much lower than that of the pump wave, with the sum/difference of the two daughte ...
... electromagnetic (pump) wave in the microwave/millimetre wave frequency range may be converted into two electrostatic daughter waves, one having a frequency comparable to that of the pump wave and one having a frequency much lower than that of the pump wave, with the sum/difference of the two daughte ...
Transverse Coherence of a VUV Free Electron Laser
... 1012 photons/(s mm2 mrad2 0.1% bandwidth), four orders of magnitude more than the brightest X-ray sources available previously. The synchrotron sources provide this high brilliance in a continuous spectrum over a very broad wavelength range, as compared to the characteristic lines of the X-ray tubes ...
... 1012 photons/(s mm2 mrad2 0.1% bandwidth), four orders of magnitude more than the brightest X-ray sources available previously. The synchrotron sources provide this high brilliance in a continuous spectrum over a very broad wavelength range, as compared to the characteristic lines of the X-ray tubes ...
Chapter 3: Electric Fields - Farmingdale State College
... Because Ex is negative, the angle φ lies in the second quadrant. The angle that the vector E makes with the positive x-axis is φ + 1800 = 98.80. ...
... Because Ex is negative, the angle φ lies in the second quadrant. The angle that the vector E makes with the positive x-axis is φ + 1800 = 98.80. ...
Matched Distributions in Cyclotrons with Higher Order Moments of
... where σk (t) are the k-th order moments of a distribution in the six-dimensional phase space and ◦, T represent operations on them. Equation (1.1) basically describes the general transport of moments from the initial state to any state in time t. If the condition (1.2) is fulfilled the system is sta ...
... where σk (t) are the k-th order moments of a distribution in the six-dimensional phase space and ◦, T represent operations on them. Equation (1.1) basically describes the general transport of moments from the initial state to any state in time t. If the condition (1.2) is fulfilled the system is sta ...
Spin in fractional quantum Hall systems
... quantum Hall systems: Since the Landau levels are highly (macroscopically) degenerate, so are the many–electron states in a non–interacting system; particularly for filling factors below one, where it is useful to be restricted to the lowest Landau level, all many–electron states have the same ener ...
... quantum Hall systems: Since the Landau levels are highly (macroscopically) degenerate, so are the many–electron states in a non–interacting system; particularly for filling factors below one, where it is useful to be restricted to the lowest Landau level, all many–electron states have the same ener ...
Bose-Einstein-Condensate Interferometer with
... We developed a weakly confining waveguide having ωx ≈ 3 Hz, ωz ≈ 3 Hz, ωy ≈ 1 Hz as characteristic oscillation frequencies. Weak confinement, specially along the “y” direction, means the condensate can displace along this axis and interaction energies of the atoms in the condensate are reduced [1]. ...
... We developed a weakly confining waveguide having ωx ≈ 3 Hz, ωz ≈ 3 Hz, ωy ≈ 1 Hz as characteristic oscillation frequencies. Weak confinement, specially along the “y” direction, means the condensate can displace along this axis and interaction energies of the atoms in the condensate are reduced [1]. ...
Statistical study of the location and size of the electron edge of the
... In this section we present an example of observation of a mid-altitude cusp crossing which exhibited an electron edge near the equatorward boundary of the LLBL/cusp. This crossing occurred on 10 September 2002, between 13:45– 14:10 UT. In order to provide the context for this event, solar wind param ...
... In this section we present an example of observation of a mid-altitude cusp crossing which exhibited an electron edge near the equatorward boundary of the LLBL/cusp. This crossing occurred on 10 September 2002, between 13:45– 14:10 UT. In order to provide the context for this event, solar wind param ...
Accelerator Physics and Technology
... The design of a circular accelerator is driven by the desire to achieve a high collision rate in the detector in order to investigate events with high statistics. The high revolution rate of circular accelerators makes this attractive. In a circular machine, however, a large number of magnets is nee ...
... The design of a circular accelerator is driven by the desire to achieve a high collision rate in the detector in order to investigate events with high statistics. The high revolution rate of circular accelerators makes this attractive. In a circular machine, however, a large number of magnets is nee ...
Investigation of the longitudinal charge distribution of electron
... regime. Since electron bunches with a high peakcurrent are required, investigation of the longitudinal bunch shape and bunch length is necessary. The transverse deflecting radio-frequency (RF) cavity LOLA streaks the electron beam and makes the longitudinal charge-distribution visible on a screen by ...
... regime. Since electron bunches with a high peakcurrent are required, investigation of the longitudinal bunch shape and bunch length is necessary. The transverse deflecting radio-frequency (RF) cavity LOLA streaks the electron beam and makes the longitudinal charge-distribution visible on a screen by ...
Effects of a tapered pitch helix on traveling wave
... portion of the outer sphere and the anode the inner sphere. The electrons leave the outer sphere and converge to form a high density electron stream near the inner sphere. The Pierce gun not only forms a laminar electron beam, but also accelerates the beam to a high velocity, typically on the order ...
... portion of the outer sphere and the anode the inner sphere. The electrons leave the outer sphere and converge to form a high density electron stream near the inner sphere. The Pierce gun not only forms a laminar electron beam, but also accelerates the beam to a high velocity, typically on the order ...
Ding_Muon_TeXtbook_v2.0
... being captured in the cloud chamber. Further experiments allowed physicists to increase their knowledge of these mysterious particles. When physicists applied a known magnetic field to these cloud chambers, several curved paths showed up. The moving charges felt a electromagnetic force from the exte ...
... being captured in the cloud chamber. Further experiments allowed physicists to increase their knowledge of these mysterious particles. When physicists applied a known magnetic field to these cloud chambers, several curved paths showed up. The moving charges felt a electromagnetic force from the exte ...
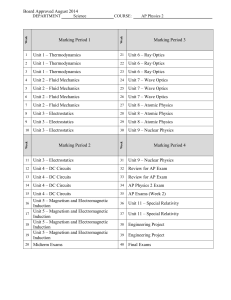
Marking Period 1 Marking Period 3 Unit 1 – Thermodynamics 21
... The AP Physics 1: Algebra-based and AP Physics 2: Algebra-based concepts are articulated together in one concept outline, providing the full scope of conceptual understandings a student should acquire by the end of an introductory sequence in college-level algebra-based physics. The key concepts and ...
... The AP Physics 1: Algebra-based and AP Physics 2: Algebra-based concepts are articulated together in one concept outline, providing the full scope of conceptual understandings a student should acquire by the end of an introductory sequence in college-level algebra-based physics. The key concepts and ...