Intensity interferometry experiments in a scanning
... angströms) or confined structures of a few nanometers. A way to reach this scale is by using cathodoluminescence (CL) performed in a scanning transmission electron microscope (CL-STEM), which has only recently been done [1]. However, when aiming at studying the statistical properties of the light c ...
... angströms) or confined structures of a few nanometers. A way to reach this scale is by using cathodoluminescence (CL) performed in a scanning transmission electron microscope (CL-STEM), which has only recently been done [1]. However, when aiming at studying the statistical properties of the light c ...
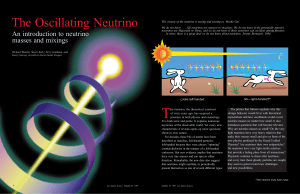
The Oscillating Neutrino
... the weak force and the neutrino has sometimes made their separate properties difficult to sort out. In fact, the theory that the neutrino is massless and left-handed (and the antineutrino righthanded) was invented to explain why the weak force violates the symmetry known as parity, also called right ...
... the weak force and the neutrino has sometimes made their separate properties difficult to sort out. In fact, the theory that the neutrino is massless and left-handed (and the antineutrino righthanded) was invented to explain why the weak force violates the symmetry known as parity, also called right ...
$doc.title
... • Calculation and visualization of all sorts of boundary conditions for oblique, horizontal, and vertical boundary planes between arbitrary media, without and with surface charges/currents on the plane • Graphical representation of complex numbers and movies of voltage and current phasor rotation in ...
... • Calculation and visualization of all sorts of boundary conditions for oblique, horizontal, and vertical boundary planes between arbitrary media, without and with surface charges/currents on the plane • Graphical representation of complex numbers and movies of voltage and current phasor rotation in ...
About Vortex Physics and Vortex Losses
... quantum physics. Which in turn often times has a lot to do with politics and not always with science. It could in fact be the case that vortex physics has been suppressed by its own “sister,” ever since it also has produced distinguished representatives. A mathematical derivation shows that the curr ...
... quantum physics. Which in turn often times has a lot to do with politics and not always with science. It could in fact be the case that vortex physics has been suppressed by its own “sister,” ever since it also has produced distinguished representatives. A mathematical derivation shows that the curr ...
HS-SCI-CP -- Chapter 16- Electric Forces and
... Electrostatic spray painting utilizes the principle of attraction between unlike charges. Paint droplets are given a negative charge, and the object to be painted is given a positive charge. In ordinary spray painting, many paint droplets drift past the object being painted. But in electrostatic spr ...
... Electrostatic spray painting utilizes the principle of attraction between unlike charges. Paint droplets are given a negative charge, and the object to be painted is given a positive charge. In ordinary spray painting, many paint droplets drift past the object being painted. But in electrostatic spr ...
Clifford M. Will Theory and Experiment in Gravitational Physics 1993
... Theory and Experiment in Gravitational Physics plate of the star field around the location of the radio source 3C48. Although they expected to find a cluster of galaxies, what they saw at the precise location of the radio source was an object that had a decidedly stellar appearance, an unusual spec ...
... Theory and Experiment in Gravitational Physics plate of the star field around the location of the radio source 3C48. Although they expected to find a cluster of galaxies, what they saw at the precise location of the radio source was an object that had a decidedly stellar appearance, an unusual spec ...
- Free Documents
... picture of radiation. The value of the electric field along the z axis at a given time and at a given point on the z axis as a function of time can be expressed by the formula E E cos wv t J This formula. In spectroscopy almost all attention is centered on the electric but. of the radiation. and als ...
... picture of radiation. The value of the electric field along the z axis at a given time and at a given point on the z axis as a function of time can be expressed by the formula E E cos wv t J This formula. In spectroscopy almost all attention is centered on the electric but. of the radiation. and als ...
Dynamics and Transport of Laser
... ated electron beams. Most commonly used tracking codes applied here and in the field of conventional particle acceleration are found to exhibit substantial deficits in the applied models for treating space charge in the regime of laser acceleration. The ensuing artifacts stem from common approximati ...
... ated electron beams. Most commonly used tracking codes applied here and in the field of conventional particle acceleration are found to exhibit substantial deficits in the applied models for treating space charge in the regime of laser acceleration. The ensuing artifacts stem from common approximati ...
Molecules in intense laser fields: Studies of ionization, high
... Charged particles in laser fields The first thing we must do is to set up the theoretical framework that describes the interaction between particles and electromagnetic fields. Although we often imagine that the particle under consideration is the electron, this chapter treats an arbitrary particle ...
... Charged particles in laser fields The first thing we must do is to set up the theoretical framework that describes the interaction between particles and electromagnetic fields. Although we often imagine that the particle under consideration is the electron, this chapter treats an arbitrary particle ...
Lecture 3b - web page for staff
... We cannot exactly and simultaneously know both the position and momentum of a particle along a given coordinate. There will be an uncertainty ∆x in the position and an uncertainty ∆px in the momentum of the particle and these uncertainties will be related by Heisenberg’s uncertainty relationship. He ...
... We cannot exactly and simultaneously know both the position and momentum of a particle along a given coordinate. There will be an uncertainty ∆x in the position and an uncertainty ∆px in the momentum of the particle and these uncertainties will be related by Heisenberg’s uncertainty relationship. He ...
Simon Candelaresi Magnetic helicity in astrophysical dynamos
... and the viscous forces. Charge separation makes the media highly conducting, which brings the Maxwell equations into play which couple the charges and currents with the electromagnetic field. Combining the Navier-Stokes and Maxwell equations gives the equations of magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) for cond ...
... and the viscous forces. Charge separation makes the media highly conducting, which brings the Maxwell equations into play which couple the charges and currents with the electromagnetic field. Combining the Navier-Stokes and Maxwell equations gives the equations of magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) for cond ...
Boundless Study Slides
... • scalar A quantity that has magnitude but not direction; compare vector. • static equilibrium the physical state in which all components of a system are at rest and the net force is equal to zero throughout the system • superposition The summing of two or more field contributions occupying the same ...
... • scalar A quantity that has magnitude but not direction; compare vector. • static equilibrium the physical state in which all components of a system are at rest and the net force is equal to zero throughout the system • superposition The summing of two or more field contributions occupying the same ...