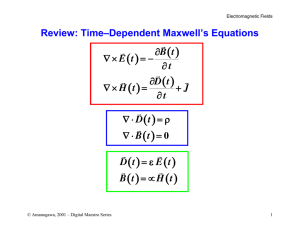
Relativistic Néel-Order Fields Induced by Electrical Current in
... Commercial spin-based memory and storage devices rely on one type of magnetic order, ferromagnetism, and one basic principle, that the opposite spin orientations in a ferromagnet (FM) represent the 0 s and 1 s [1]. Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) is a solid-state-memory variant of the hard disk ...
... Commercial spin-based memory and storage devices rely on one type of magnetic order, ferromagnetism, and one basic principle, that the opposite spin orientations in a ferromagnet (FM) represent the 0 s and 1 s [1]. Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) is a solid-state-memory variant of the hard disk ...
Primitive Virtual Negative Charge
... order of magnitude of its mass4, the effects from the vacuum particle’s charges are dominant in the process of the rearrangement. With this fact, it can be explained why gravitational interaction is attractive. In the gravitational interaction between two massive objects, vacuum particle’s charge d ...
... order of magnitude of its mass4, the effects from the vacuum particle’s charges are dominant in the process of the rearrangement. With this fact, it can be explained why gravitational interaction is attractive. In the gravitational interaction between two massive objects, vacuum particle’s charge d ...
Ion dynamics in electron beam–plasma interaction: particle-in
... plasma (e.g., solar wind), the Doppler shift may enlarge the frequency difference such that high-resolution detectors are able to identify the two peaks. It turned out that, in several cases, using estimated beam velocities, the predictions of the three-wave parametric decay via ion sound waves are ...
... plasma (e.g., solar wind), the Doppler shift may enlarge the frequency difference such that high-resolution detectors are able to identify the two peaks. It turned out that, in several cases, using estimated beam velocities, the predictions of the three-wave parametric decay via ion sound waves are ...
Chapter 23
... exerted by one sphere on the other. (b) What If? The spheres are connected by a conducting wire. Find the electric force each exerts on the other after they have come to equilibrium. 20. A small object of mass 3.80 g and charge –18.0 C is suspended motionless above the ground when immersed in a uni ...
... exerted by one sphere on the other. (b) What If? The spheres are connected by a conducting wire. Find the electric force each exerts on the other after they have come to equilibrium. 20. A small object of mass 3.80 g and charge –18.0 C is suspended motionless above the ground when immersed in a uni ...
Answers to Parent Pages L98-L103
... Lines, Rays, and Angles . . . . . . . Parallel Lines and Perpendicular Lines Classify Triangles . . . . . . . . . . . Classify Quadrilaterals . . . . . . . . ...
... Lines, Rays, and Angles . . . . . . . Parallel Lines and Perpendicular Lines Classify Triangles . . . . . . . . . . . Classify Quadrilaterals . . . . . . . . ...
Evanescent Wave Illumination Evanescent Wave Microscopy
... where λ0 is the illumination wavelength, n1 is the index of the immersion medium, M is the magnification and e is the smallest distance that can be resolved by the detector. The DOF can be quite large for low magnification or low numerical aperture (NA) objectives, and even for high magnification, l ...
... where λ0 is the illumination wavelength, n1 is the index of the immersion medium, M is the magnification and e is the smallest distance that can be resolved by the detector. The DOF can be quite large for low magnification or low numerical aperture (NA) objectives, and even for high magnification, l ...
Chapter 12
... field will experience an electrostatic force in the direction of the electric field. An external force F, equal in magnitude to the electrostatic force qE, will move the charge q a distance d in the uniform field. The external force does work on the charge and increases the potential energy of th ...
... field will experience an electrostatic force in the direction of the electric field. An external force F, equal in magnitude to the electrostatic force qE, will move the charge q a distance d in the uniform field. The external force does work on the charge and increases the potential energy of th ...
Chapter 12 Electrostatic Phenomena
... uniform electric field of 1000 N/C between them, as shown. A particle with a charge of +0.005 C is moved from the bottom (negative) plate to the top plate. What is the change in potential energy of the charge? a) ...
... uniform electric field of 1000 N/C between them, as shown. A particle with a charge of +0.005 C is moved from the bottom (negative) plate to the top plate. What is the change in potential energy of the charge? a) ...
Electric Fields
... ring. It too contributes the field magnitude dE but the field vector leans at angle θ in the opposite direction from the vector from our first charge element, as indicated in the side view of Figure (bottom). Thus the two perpendicular components cancel. All around the ring, this cancelation occurs ...
... ring. It too contributes the field magnitude dE but the field vector leans at angle θ in the opposite direction from the vector from our first charge element, as indicated in the side view of Figure (bottom). Thus the two perpendicular components cancel. All around the ring, this cancelation occurs ...
Chapter 12
... field will experience an electrostatic force in the direction of the electric field. An external force F, equal in magnitude to the electrostatic force qE, will move the charge q a distance d in the uniform field. The external force does work on the charge and increases the potential energy of th ...
... field will experience an electrostatic force in the direction of the electric field. An external force F, equal in magnitude to the electrostatic force qE, will move the charge q a distance d in the uniform field. The external force does work on the charge and increases the potential energy of th ...
Fine Structure of the Hydrogen Atom. Part I
... experimental accuracy, a large number of small experimental and theoretical e8ects must be taken into account in the analysis of the data. It is felt that if all of these matters were also incorporated into one paper, the result would be unwieldy, and not do justice to the simple basic ideas involve ...
... experimental accuracy, a large number of small experimental and theoretical e8ects must be taken into account in the analysis of the data. It is felt that if all of these matters were also incorporated into one paper, the result would be unwieldy, and not do justice to the simple basic ideas involve ...
Untitled
... particle, this one of charge − 32.8 × 10 −9 C , is on the x axis at x = 14.0 cm. Find the point, or points, on the x axis, at which the electric field is zero. 4) A particle of charge 11.2 × 10 −8 C is at the origin of a Cartesian coordinate system. A second particle, this one also having a positive ...
... particle, this one of charge − 32.8 × 10 −9 C , is on the x axis at x = 14.0 cm. Find the point, or points, on the x axis, at which the electric field is zero. 4) A particle of charge 11.2 × 10 −8 C is at the origin of a Cartesian coordinate system. A second particle, this one also having a positive ...
Introduction toElementary Particle Phenomenology
... in the new accelerator experiments. The long lifetimes of these particles suggested that, although the final states often only contained strongly interacting particles, they did not decay via the strong interaction; they were thus deemed strange. The τ + and the θ+ are now known to be one and the sa ...
... in the new accelerator experiments. The long lifetimes of these particles suggested that, although the final states often only contained strongly interacting particles, they did not decay via the strong interaction; they were thus deemed strange. The τ + and the θ+ are now known to be one and the sa ...
Some Photographs of the Tracks of Penetrating Radiation Author(s
... For when this latter method is used it is only on a small fraction of the photographs that a track will be found. The average number of photographs required to obtain one track will depend on the size and orientation of the chamber and on the effective time of expansion. The latter is not likely to ...
... For when this latter method is used it is only on a small fraction of the photographs that a track will be found. The average number of photographs required to obtain one track will depend on the size and orientation of the chamber and on the effective time of expansion. The latter is not likely to ...
Bipolaron recombination in conjugated polymers Linköping University Post Print
... other when they first interact at about 500 fs. Under the influence of the external electric field, they move towards each other a second time and interact again at about 900 fs. This time they recombine in a way very similar to the process described above. If the on-site Coulomb interaction U0 incr ...
... other when they first interact at about 500 fs. Under the influence of the external electric field, they move towards each other a second time and interact again at about 900 fs. This time they recombine in a way very similar to the process described above. If the on-site Coulomb interaction U0 incr ...
Chapter 23 Objective Questions The magnitude of the electric force
... are fixed in space and separated by a distance d. A third particle with charge –Q is free to move and lies initially at rest on the perpendicular bisector of the two fixed charges a distance x from the midpoint between those charges (Fig. P23.14). (a) Show that if x is small compared with d, the mot ...
... are fixed in space and separated by a distance d. A third particle with charge –Q is free to move and lies initially at rest on the perpendicular bisector of the two fixed charges a distance x from the midpoint between those charges (Fig. P23.14). (a) Show that if x is small compared with d, the mot ...