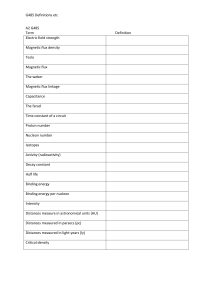
G485 Definitions etc A2 G485 Term Definition
... including stars, galaxies and radiation Describe the solar system in terms of the Sun, planets, planetary satellites and comets Describe the formation of a star, such as our Sun, from interstellar dust and gas Describe the Sun’s probable evolution into a red giant and white dwarf Describe how a star ...
... including stars, galaxies and radiation Describe the solar system in terms of the Sun, planets, planetary satellites and comets Describe the formation of a star, such as our Sun, from interstellar dust and gas Describe the Sun’s probable evolution into a red giant and white dwarf Describe how a star ...
Welcome to A-level Physics - Reigate Grammar School
... between divisions (this is clearly not possible with digital instrument anyway). Hence, the uncertainty cannot be less than ½ the smallest division of the instrument being used, and is recommended it be taken to be ± the smallest division. In some cases, however, it will be larger than this due to o ...
... between divisions (this is clearly not possible with digital instrument anyway). Hence, the uncertainty cannot be less than ½ the smallest division of the instrument being used, and is recommended it be taken to be ± the smallest division. In some cases, however, it will be larger than this due to o ...
8th Grade Math Unit 6: Kaleidoscopes, Hubcaps, and Mirrors
... listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. ...
... listed in alphabetical /numerical order not suggested teaching order. PLC’s must order the standards to form a reasonable unit for instructional purposes. ...
21.1 Electric Fields
... If it's being attracted south, negative charge must be somewhere south of it, so field must be in a southward direction. ...
... If it's being attracted south, negative charge must be somewhere south of it, so field must be in a southward direction. ...
Naturalness via scale invariance and non-trivial UV fixed points in a 4d O(N) scalar field model in the large-N limit
... the symmetry group of the standard model is O(4). Our approach is inspired by work on Yang-Mills theory, where we have learned that the theory has two different “classical” limits in which quantum fluctuations of some observables are small. Both the h̄ → 0 and N → ∞ limits (holding the other paramet ...
... the symmetry group of the standard model is O(4). Our approach is inspired by work on Yang-Mills theory, where we have learned that the theory has two different “classical” limits in which quantum fluctuations of some observables are small. Both the h̄ → 0 and N → ∞ limits (holding the other paramet ...
Why bouncing droplets are a pretty good model
... to adjust the forcing amplitude and frequency (correcting for the perturbation to the wave speed and height). Alternatively a droplet of ferrofluid might be de-weighted magnetically so it lands later in the cycle and travels faster. The forcing frequency might be adjusted to avoid the additional fac ...
... to adjust the forcing amplitude and frequency (correcting for the perturbation to the wave speed and height). Alternatively a droplet of ferrofluid might be de-weighted magnetically so it lands later in the cycle and travels faster. The forcing frequency might be adjusted to avoid the additional fac ...
Algebraic Quantum Field Theory on Curved Spacetimes
... t : M → R, i.e. t is a smooth function with a timelike and future directed gradient field ∇t; t is, hence, strictly increasing along any future directed timelike curve. In the following, we shall always consider smooth Cauchy surfaces, even in the cases where we do not mention it explicitly. In the ...
... t : M → R, i.e. t is a smooth function with a timelike and future directed gradient field ∇t; t is, hence, strictly increasing along any future directed timelike curve. In the following, we shall always consider smooth Cauchy surfaces, even in the cases where we do not mention it explicitly. In the ...
electric-force-and-field
... Chapter 18 ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS PREVIEW Electric charge is the fundamental quantity that underlies all electrical phenomena. There are two types of charges, positive and negative, and like charges repel each other, and unlike charges attract each other. A conductor is a material throu ...
... Chapter 18 ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS PREVIEW Electric charge is the fundamental quantity that underlies all electrical phenomena. There are two types of charges, positive and negative, and like charges repel each other, and unlike charges attract each other. A conductor is a material throu ...
Differential Forms and Electromagnetic Field Theory
... This matches the graphical representation in Figure 2(a), since the path shown in the figure crosses four surfaces. If the path were not of integer length, we would have to imagine fractional surfaces in between the unit spaced surfaces. A path from (0, 0, 0) to (0.25, 0, 0), for example, crosses 0. ...
... This matches the graphical representation in Figure 2(a), since the path shown in the figure crosses four surfaces. If the path were not of integer length, we would have to imagine fractional surfaces in between the unit spaced surfaces. A path from (0, 0, 0) to (0.25, 0, 0), for example, crosses 0. ...
Fields - Univerzita Karlova v Praze
... 10.2 Fields at work Gravitational fields Recall the definition of work: work W = Fd cos where is the angle between the force F and the displacement d. Consider the movement of a ball from the ground to the table via displacements d1 and d2: Along the displacement d1, gravity does work ...
... 10.2 Fields at work Gravitational fields Recall the definition of work: work W = Fd cos where is the angle between the force F and the displacement d. Consider the movement of a ball from the ground to the table via displacements d1 and d2: Along the displacement d1, gravity does work ...
A CP - Indico
... Time reversal symmetry (invariance under change of time direction) does certainly not correspond to our daily experience. The macroscopic violation of T symmetry follows from maximising thermodynamic entropy (leaving a parking spot has a larger solution space than entering it). In the microscopic wo ...
... Time reversal symmetry (invariance under change of time direction) does certainly not correspond to our daily experience. The macroscopic violation of T symmetry follows from maximising thermodynamic entropy (leaving a parking spot has a larger solution space than entering it). In the microscopic wo ...
Chapter 23: Electric Potential The voltage between the cathode and
... A. The gradient of the potential must have a larger magnitude at a place where the electric field is stronger. B. The gradient of the potential must have a smaller magnitude at a place where the electric field is stronger. C. The potential must be larger at a place where the electric field is strong ...
... A. The gradient of the potential must have a larger magnitude at a place where the electric field is stronger. B. The gradient of the potential must have a smaller magnitude at a place where the electric field is stronger. C. The potential must be larger at a place where the electric field is strong ...