Click here to - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.3 AFS Chakeri
... KVS has been preparing and distributing Study/Support Material in different subjects for the students of Classes X and XII with the aim of helping them to do well in Board Examinations. KVS Chennai Region was privileged to be assigned the task of preparing this Study/Support Material in Physics for ...
... KVS has been preparing and distributing Study/Support Material in different subjects for the students of Classes X and XII with the aim of helping them to do well in Board Examinations. KVS Chennai Region was privileged to be assigned the task of preparing this Study/Support Material in Physics for ...
Chapter 11 File
... developed the concept of fields to describe these forces. field: a region of influence A field is defined as a region of influence surrounding an object. surrounding an object The concept of fields helps explain the laws of universal gravitation, which you studied in Chapter 4. Consider a space modu ...
... developed the concept of fields to describe these forces. field: a region of influence A field is defined as a region of influence surrounding an object. surrounding an object The concept of fields helps explain the laws of universal gravitation, which you studied in Chapter 4. Consider a space modu ...
ABSTRACT Title of Document:
... The unevenness of charge distribution generates an electric field which pulls together electrons and ions, but since electrons are much lighter than ions they are the ones which move towards the positive region. As they move they gain momentum and when they reach the positive region they overshoot a ...
... The unevenness of charge distribution generates an electric field which pulls together electrons and ions, but since electrons are much lighter than ions they are the ones which move towards the positive region. As they move they gain momentum and when they reach the positive region they overshoot a ...
canonical theories of lagrangian dynamical systems in physics
... fronts are concerned (see above), a disease which does not exist in the algebraically more complicated theory of Carathéodory. As Lepage’s very rich and interesting canonical framework including HJ theories for fields is not generally known, it is the main purpose of this article to draw attention t ...
... fronts are concerned (see above), a disease which does not exist in the algebraically more complicated theory of Carathéodory. As Lepage’s very rich and interesting canonical framework including HJ theories for fields is not generally known, it is the main purpose of this article to draw attention t ...
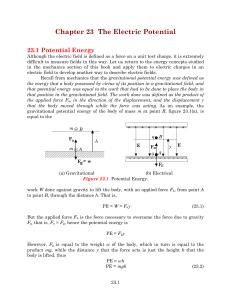
Chapter 23 The Electric Potential
... acting on the charge is not a constant then a new formulation for the work done and hence the electric potential is required. As an example suppose we have two point charges and we wish to move the second charge toward the first charge. How much work will be done? The force acting on the second char ...
... acting on the charge is not a constant then a new formulation for the work done and hence the electric potential is required. As an example suppose we have two point charges and we wish to move the second charge toward the first charge. How much work will be done? The force acting on the second char ...
DISCRETE 2016: Fifth Symposium on Prospects in the Physics of
... the standard seesaw model what is the minimum value the mass of a right-handed (RH) neutrino must have for allowing successful leptogenesis via CP-violating decays? I show that, for low RH neutrino masses and thanks to thermal effects, leptogenesis turns out to proceed efficiently from the decay of ...
... the standard seesaw model what is the minimum value the mass of a right-handed (RH) neutrino must have for allowing successful leptogenesis via CP-violating decays? I show that, for low RH neutrino masses and thanks to thermal effects, leptogenesis turns out to proceed efficiently from the decay of ...
Magnetic Fields
... A Voltmeter is a device that measures the voltage across a circuit element. • It must be connected in parallel with the element. • An ideal voltmeter should measure the voltage without ...
... A Voltmeter is a device that measures the voltage across a circuit element. • It must be connected in parallel with the element. • An ideal voltmeter should measure the voltage without ...
Ans - WordPress.com
... Ans: Quarter wave plate- It is a uniaxial doubly refracting crystal plate, cut with its axis parallel to the refracting faces, and can produce a phase difference of π/2 or a path difference of λ/4 between the ordinary and extra-ordinary rays. Half wave plate - It is a uniaxial doubly refracting crys ...
... Ans: Quarter wave plate- It is a uniaxial doubly refracting crystal plate, cut with its axis parallel to the refracting faces, and can produce a phase difference of π/2 or a path difference of λ/4 between the ordinary and extra-ordinary rays. Half wave plate - It is a uniaxial doubly refracting crys ...
THEORETICAL AND COMPUTATIONAL METHODS
... Physical arrangement of particles mapped into configuration space by hyperspherical coordinates ρ, θ and ϕ; these coordinates define particle configuration size (ρ) and shape (θ, ϕ). Although it is difficult to tell from the figure, the two-dimensional space of hyperangles displays C3v symmetry (sec ...
... Physical arrangement of particles mapped into configuration space by hyperspherical coordinates ρ, θ and ϕ; these coordinates define particle configuration size (ρ) and shape (θ, ϕ). Although it is difficult to tell from the figure, the two-dimensional space of hyperangles displays C3v symmetry (sec ...
Microscopic and macroscopic polarization within a combined quantum
... also include the so-called local field factors, i.e., the difference between the macroscopic electric field and the actual electric field felt by the solute. This will enable the calculation of effective microscopic properties which can be related to the macroscopic susceptibilities. The macroscopic ...
... also include the so-called local field factors, i.e., the difference between the macroscopic electric field and the actual electric field felt by the solute. This will enable the calculation of effective microscopic properties which can be related to the macroscopic susceptibilities. The macroscopic ...
Electric Forces and Fields
... The fact that there are two types of electric charge allows the electric force to be either attractive or repulsive. In contrast, there is only one type of mass and all masses attract each other via gravitational interaction. Electrical forces between like charges (either both positive or both negat ...
... The fact that there are two types of electric charge allows the electric force to be either attractive or repulsive. In contrast, there is only one type of mass and all masses attract each other via gravitational interaction. Electrical forces between like charges (either both positive or both negat ...