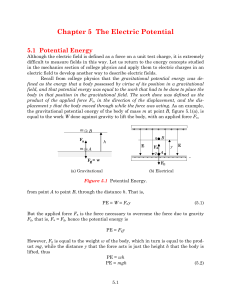
From Physics 212, one might get the impression that going... vacuum to electrostatics in a material is equivalent to replacing...
... an E-field. This impression is reinforced since both E and D are often calculated using Gauss’s Law. But there are important differences between E and D. One difference is that the curl of D is not zero in some non-Class A dielectrics. This means that the line integral of a D-field can depend on the ...
... an E-field. This impression is reinforced since both E and D are often calculated using Gauss’s Law. But there are important differences between E and D. One difference is that the curl of D is not zero in some non-Class A dielectrics. This means that the line integral of a D-field can depend on the ...
4 Impedance and collective effects
... where is the relativistic mass factor. Assuming a circular beam pipe with radius b (which is important only for the computation of the longitudinal force) and applying Gauss’s law, the electromagnetic fields can be computed for a bunch with Gaussian radial density (with rms x y ) u ...
... where is the relativistic mass factor. Assuming a circular beam pipe with radius b (which is important only for the computation of the longitudinal force) and applying Gauss’s law, the electromagnetic fields can be computed for a bunch with Gaussian radial density (with rms x y ) u ...
Symmetry and symmetry breaking, algebraic approach to - IME-USP
... The discovery of the molecular structure of DNA by Watson and Crick in 19531,2 is one of the landmarks in the history of science. The substance itself had been known since 1869 and had been recognized as the carrier of genetic information in 1944, but the basis of its biological function, of its sta ...
... The discovery of the molecular structure of DNA by Watson and Crick in 19531,2 is one of the landmarks in the history of science. The substance itself had been known since 1869 and had been recognized as the carrier of genetic information in 1944, but the basis of its biological function, of its sta ...
Many-Minds Relativity and Quantum Mechanics
... where F is the gravitational force between two bodies of mass m1 and m2 at distance r and G is the gravitational constant (≈ 9.81 meter per second2 ), you can e.g. predict by mathematical computation the coming position of the planets in our Solar system from their current positions and velocities. ...
... where F is the gravitational force between two bodies of mass m1 and m2 at distance r and G is the gravitational constant (≈ 9.81 meter per second2 ), you can e.g. predict by mathematical computation the coming position of the planets in our Solar system from their current positions and velocities. ...
instability of excitation waves induced by electrical fields
... typical examples of spontaneous pattern formation in macroscopic systems driven far from thermodynamic equilibrium [Bab86, Cro93]. They may show complex dynamics in time or both in time and in space, and they are sustained by the interplay of non-linear, selfaccelerating reaction kinetics (autocatal ...
... typical examples of spontaneous pattern formation in macroscopic systems driven far from thermodynamic equilibrium [Bab86, Cro93]. They may show complex dynamics in time or both in time and in space, and they are sustained by the interplay of non-linear, selfaccelerating reaction kinetics (autocatal ...
The Minimal CFL-Nuclear Interface
... pairs, is maximized when all three flavors have equal number density. This equality is enforced and the electrical neutrality of the CFL phase is undisturbed even in the presence of a nonzero strange quark mass ms (up to some critical value). Although the CFL ground state breaks the color and electr ...
... pairs, is maximized when all three flavors have equal number density. This equality is enforced and the electrical neutrality of the CFL phase is undisturbed even in the presence of a nonzero strange quark mass ms (up to some critical value). Although the CFL ground state breaks the color and electr ...
the electric field
... COULOMB ELECTRIC FORCE As discussed in Unit 411, every particle can be characterized by a quantity called its charge q, measured in terms of the SI unit “coulomb” (abbreviated “C”). If two particles are at rest relative to some inertial frame, the electric force on one particle due to the other is c ...
... COULOMB ELECTRIC FORCE As discussed in Unit 411, every particle can be characterized by a quantity called its charge q, measured in terms of the SI unit “coulomb” (abbreviated “C”). If two particles are at rest relative to some inertial frame, the electric force on one particle due to the other is c ...
Geometry and Material Effects in Casimir Physics
... Neutral objects exert a force on one another through electromagnetic fields even if they do not possess permanent multipole moments. Materials that couple to the electromagnetic field alter the spectrum of the field’s quantum and thermal fluctuations. The resulting change in energy depends on the re ...
... Neutral objects exert a force on one another through electromagnetic fields even if they do not possess permanent multipole moments. Materials that couple to the electromagnetic field alter the spectrum of the field’s quantum and thermal fluctuations. The resulting change in energy depends on the re ...
µ = / F c
... both media are isotropic (i.e. not birefringent). In the following discussion, we’ll suppose that light is travelling from a medium of permittivity ε1 to a medium of greater permittivity ε2. Both permeabilities are equal, and close to µ0. The electric and magnetic fields of the incident wave will be ...
... both media are isotropic (i.e. not birefringent). In the following discussion, we’ll suppose that light is travelling from a medium of permittivity ε1 to a medium of greater permittivity ε2. Both permeabilities are equal, and close to µ0. The electric and magnetic fields of the incident wave will be ...
Signatures of Majorana zero-modes in nanowires, quantum spin
... Majorana zero-modes, also referred to as Majorana bound states or Majorinos, are states in the middle of the excitation gap of a superconductor (so at zero excitation energy), bound to a magnetic vortex or other defect. The name goes back to a concept introduced by the Italian physicist Ettore Major ...
... Majorana zero-modes, also referred to as Majorana bound states or Majorinos, are states in the middle of the excitation gap of a superconductor (so at zero excitation energy), bound to a magnetic vortex or other defect. The name goes back to a concept introduced by the Italian physicist Ettore Major ...
From Principles to Diagrams
... The generalization of twistor diagrams to TGD framework has been very inspiring (and also frightening) mission impossible and allowed to gain deep insights about what TGD diagrams could be mathematically. I of course cannot provide explicit formulas but the general structure for the construction of ...
... The generalization of twistor diagrams to TGD framework has been very inspiring (and also frightening) mission impossible and allowed to gain deep insights about what TGD diagrams could be mathematically. I of course cannot provide explicit formulas but the general structure for the construction of ...
Reference - Wayne State Chemistry Department
... Time-dependent Hartree-Fock 共TD-HF兲 and time-dependent configuration interaction 共TD-CI兲 methods with Gaussian basis sets have been compared in modeling the response of hydrogen molecule, butadiene, and hexatriene exposed to very short, intense laser pulses 共760 nm, 3 cycles兲. After the electric fie ...
... Time-dependent Hartree-Fock 共TD-HF兲 and time-dependent configuration interaction 共TD-CI兲 methods with Gaussian basis sets have been compared in modeling the response of hydrogen molecule, butadiene, and hexatriene exposed to very short, intense laser pulses 共760 nm, 3 cycles兲. After the electric fie ...
Quantum Transport through Single and Double Quantum Dots
... low temperature the electronic levels in the source (drain) contact are filled from the bottom of the conduction band up to the electrochemical potential µS (µD ). In the quantum dot we can also define an electrochemical potential. It describes the energy necessary to add an electron to the dot, giv ...
... low temperature the electronic levels in the source (drain) contact are filled from the bottom of the conduction band up to the electrochemical potential µS (µD ). In the quantum dot we can also define an electrochemical potential. It describes the energy necessary to add an electron to the dot, giv ...