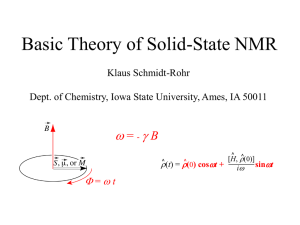
Axion Induced Oscillating Electric Dipole Moments
... The resulting EDM has been criticized for being proportional to and nonvanishing as ma -> 0. The same issue arises in the case of the anomaly. The result is intrinsically oscillatory (the nonlocal makes the source for the vector potential transverse, ie, not Coulombic) . The above Feynman amplitudes ...
... The resulting EDM has been criticized for being proportional to and nonvanishing as ma -> 0. The same issue arises in the case of the anomaly. The result is intrinsically oscillatory (the nonlocal makes the source for the vector potential transverse, ie, not Coulombic) . The above Feynman amplitudes ...
Investigating incompatibility: How to reconcile complementarity with EPR C
... Complementarity can be reconciled with EPR. It is Duality which is irreconcilable with EPR, but then again Duality, which has no use of the quantum, is now proved inconsistent with Complementarity, which demands the quantum. And if Duality, which does conflict with EPR, provides a mismatch with CTY, ...
... Complementarity can be reconciled with EPR. It is Duality which is irreconcilable with EPR, but then again Duality, which has no use of the quantum, is now proved inconsistent with Complementarity, which demands the quantum. And if Duality, which does conflict with EPR, provides a mismatch with CTY, ...
1 CHAPTER 7 ATOMIC SPECTRA 7.1 Introduction Atomic
... The model proposed in 1913 by the Danish physicist Niels Bohr (and later further developed by Arnold Sommerfeld) to describe the hydrogen spectrum was of great importance in the historical development of atomic theory. Even though it is very different from the modern description of an atom, it is di ...
... The model proposed in 1913 by the Danish physicist Niels Bohr (and later further developed by Arnold Sommerfeld) to describe the hydrogen spectrum was of great importance in the historical development of atomic theory. Even though it is very different from the modern description of an atom, it is di ...
History of Magnetism - School of Applied Non
... Atoms consist of Protons, Neutrons, and electrons. A stable or balanced atom will have the same number of (+) protons and (-) electrons. The neutrons are there to keep the positive charges from repelling each other, keeping the nucleus (centre) of the atom together and stable. To date we have no kno ...
... Atoms consist of Protons, Neutrons, and electrons. A stable or balanced atom will have the same number of (+) protons and (-) electrons. The neutrons are there to keep the positive charges from repelling each other, keeping the nucleus (centre) of the atom together and stable. To date we have no kno ...
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
... Lenz's Law An induced current flows in such a direction that the induced magnetic field it creates opposes the action of the inducing magnetic field. If you find this statement of Lenz’s law confusing, you are not alone. The problem stems from the number of events which are occurring simultaneously. ...
... Lenz's Law An induced current flows in such a direction that the induced magnetic field it creates opposes the action of the inducing magnetic field. If you find this statement of Lenz’s law confusing, you are not alone. The problem stems from the number of events which are occurring simultaneously. ...
Magnetic ordering of nuclear spins in an interacting two-dimensional electron... Pascal Simon, Bernd Braunecker, and Daniel Loss
... derived a rather general effective Hamiltonian for nuclear spins after integrating out electron degrees of freedom, and finally performed a spin wave analysis around a ferromagnetic ground state 共which we assumed to be the lowest energy state兲. We indeed showed that TC = 0 for noninteracting electro ...
... derived a rather general effective Hamiltonian for nuclear spins after integrating out electron degrees of freedom, and finally performed a spin wave analysis around a ferromagnetic ground state 共which we assumed to be the lowest energy state兲. We indeed showed that TC = 0 for noninteracting electro ...
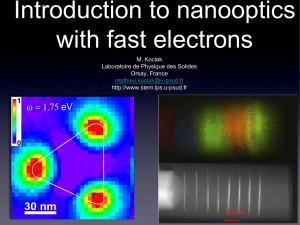
EELS
... • A fast electrons probe (less than a nm) can be formed and monitored in a Scanning (Transmission) Electron Microscope ...
... • A fast electrons probe (less than a nm) can be formed and monitored in a Scanning (Transmission) Electron Microscope ...
Lesson 2 Magnetism File
... • One end of the electromagnet is a north pole and the other end is a south pole. • If placed in a magnetic field, an electromagnet will align itself along the magnetic field lines, just as a compass needle will. • An electromagnet also will attract magnetic materials and be attracted or repelled by ...
... • One end of the electromagnet is a north pole and the other end is a south pole. • If placed in a magnetic field, an electromagnet will align itself along the magnetic field lines, just as a compass needle will. • An electromagnet also will attract magnetic materials and be attracted or repelled by ...
Magnetism - Iroquois Central School District / Home Page
... What we do know… The north magnetic pole and the geographic North Pole do not coincide. The magnetic pole is about 1500 km (930 mi) south of the geographic North Pole and it wanders. A compass actually indicates the direction of magnetic north, not true north. Therefore a navigator must need to kno ...
... What we do know… The north magnetic pole and the geographic North Pole do not coincide. The magnetic pole is about 1500 km (930 mi) south of the geographic North Pole and it wanders. A compass actually indicates the direction of magnetic north, not true north. Therefore a navigator must need to kno ...
Spin Conductivity in Two-Dimensional Non
... Spin currents have attracted considerable interest with the development of spintronics in recent years. Spin conductivity is well-studied theoretically in one-dimensional antiferromagnets by many methods including exact diagonalization.1, 2 It is also studied in twodimensional antiferromagnets.3–5 T ...
... Spin currents have attracted considerable interest with the development of spintronics in recent years. Spin conductivity is well-studied theoretically in one-dimensional antiferromagnets by many methods including exact diagonalization.1, 2 It is also studied in twodimensional antiferromagnets.3–5 T ...
Use of Rotating Coordinates in Magnetic Resonance Problems
... rota, ting field region than it did in the first. On the other hand, if the average value of Hs — a&/y in the intermediate region is zero the orientation of the nucleus relative to H, „ is the same in the second oscillating field region as in the first. This will be true regardless of the velocity o ...
... rota, ting field region than it did in the first. On the other hand, if the average value of Hs — a&/y in the intermediate region is zero the orientation of the nucleus relative to H, „ is the same in the second oscillating field region as in the first. This will be true regardless of the velocity o ...
Infrared Spectroscopy_03
... the transition from n to n+1 corresponds to the energy of the absorbed light quantum • The difference between two adjacent energy levels gets smaller with increasing n until dissociation of the molecule occurs (Dissociation energy ED ) Note: Weaker transitions called “overtones” are sometimes observ ...
... the transition from n to n+1 corresponds to the energy of the absorbed light quantum • The difference between two adjacent energy levels gets smaller with increasing n until dissociation of the molecule occurs (Dissociation energy ED ) Note: Weaker transitions called “overtones” are sometimes observ ...
Integrated X-ray L Absorption Spectra. Counting Holes in Ni
... to NiIV, the number of d holes increases; hence, the L edge resonance intensity should also increase. This is indeed observed, most dramatically for KNiIVIO6 (Figure 1). The qualitative trend for L edge intensities to increase with Ni oxidation states is not a surprise. However, it is gratifying to ...
... to NiIV, the number of d holes increases; hence, the L edge resonance intensity should also increase. This is indeed observed, most dramatically for KNiIVIO6 (Figure 1). The qualitative trend for L edge intensities to increase with Ni oxidation states is not a surprise. However, it is gratifying to ...
Electron paramagnetic resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a technique for studying materials with unpaired electrons. The basic concepts of EPR are analogous to those of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), but it is electron spins that are excited instead of the spins of atomic nuclei. EPR spectroscopy is particularly useful for studying metal complexes or organic radicals. EPR was first observed in Kazan State University by Soviet physicist Yevgeny Zavoisky in 1944, and was developed independently at the same time by Brebis Bleaney at the University of Oxford.