Hearing and Sound - County Central High School
... When images are viewed up close, the pupil constricts to bring the object into focus. The Inuit people were aware of this principle when they made eyeglasses by drilling holes in whale bones. Light through narrow openings results in sharper ...
... When images are viewed up close, the pupil constricts to bring the object into focus. The Inuit people were aware of this principle when they made eyeglasses by drilling holes in whale bones. Light through narrow openings results in sharper ...
noise induced hearing loss - CT Technology Transfer Center
... of at least one type of ear plug and one type of earmuff must be provided, since individuals may be more comfortable in one type than another. The employer must ensure proper initial fitting and supervise the correct use of all hearing protectors. Hearing protectors must be replaced as necessary, an ...
... of at least one type of ear plug and one type of earmuff must be provided, since individuals may be more comfortable in one type than another. The employer must ensure proper initial fitting and supervise the correct use of all hearing protectors. Hearing protectors must be replaced as necessary, an ...
A Guide to Hearing Protection
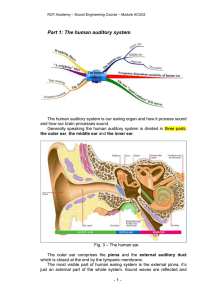
... As sound enters the outer ear, it is channeled down the ear canal until it reaches the ear drum. The ear drum, a thin membrane stretched over a tube, is moved by the sound waves. When the sound vibrations reach the coiled, liquid-filled tube called the cochlea, thousands of hair cells in the cochlea ...
... As sound enters the outer ear, it is channeled down the ear canal until it reaches the ear drum. The ear drum, a thin membrane stretched over a tube, is moved by the sound waves. When the sound vibrations reach the coiled, liquid-filled tube called the cochlea, thousands of hair cells in the cochlea ...
Periodicity and Pitch - Auditory Neuroscience
... The observed orientation of their periodotopic map (mediodorsal to latero-ventral for high to low) appears to differ from that described by Schreiner & Langner (1988) in the cat (predimonantly caudal to ...
... The observed orientation of their periodotopic map (mediodorsal to latero-ventral for high to low) appears to differ from that described by Schreiner & Langner (1988) in the cat (predimonantly caudal to ...
Chapter 6 Basics of Digital Audio
... Merits of dB • The decibel's logarithmic nature means that a very large range of ratios can be represented by a convenient number. This allows one to clearly visualize huge changes of some quantity. • The mathematical properties of logarithms mean that the overall decibel gain of a multi-component s ...
... Merits of dB • The decibel's logarithmic nature means that a very large range of ratios can be represented by a convenient number. This allows one to clearly visualize huge changes of some quantity. • The mathematical properties of logarithms mean that the overall decibel gain of a multi-component s ...
PERCEPTION OF MUSIC BY PATIENTS WITH COCHLEAR
... for post-lingual patients - the regeneration of the ability to perceive and to understand spoken language (the forming of connections between the distorted auditory information and previous internal patterns of speech and other sounds) for pre-lingual patients - the development of the foundation ...
... for post-lingual patients - the regeneration of the ability to perceive and to understand spoken language (the forming of connections between the distorted auditory information and previous internal patterns of speech and other sounds) for pre-lingual patients - the development of the foundation ...
Types of Hearing Loss
... • It occurs when sounds does not going through the ear canal, which causes you not to hear as loudly as before. • Conductive hearing loss is caused by ear wax, fluid in the middle ear, middle ear infections, and deformations. • The person with this condition may talk softly because they hear themsel ...
... • It occurs when sounds does not going through the ear canal, which causes you not to hear as loudly as before. • Conductive hearing loss is caused by ear wax, fluid in the middle ear, middle ear infections, and deformations. • The person with this condition may talk softly because they hear themsel ...
Exam 3 Sample 2003
... a. morphine-like substances that naturally produce analgesic effects. b. naturally-occurring chemicals whose effect is magnified by the drug naloxone. c. placebos which have a larger-than-normal analgesic effect. d. synthetically-produced addictive, opiates. The senses of taste and smell are conside ...
... a. morphine-like substances that naturally produce analgesic effects. b. naturally-occurring chemicals whose effect is magnified by the drug naloxone. c. placebos which have a larger-than-normal analgesic effect. d. synthetically-produced addictive, opiates. The senses of taste and smell are conside ...
spectral and temporal contribution of different signals to asw
... shows the response level of the auditory nerve model on a sinus signal of different levels for the static excitation and an excitation with a hard switched sinus signal (dynamic). Figure 2 shows the output of the complete hearing model on a hard switched noise signal of 70 dB which was binaurally r ...
... shows the response level of the auditory nerve model on a sinus signal of different levels for the static excitation and an excitation with a hard switched sinus signal (dynamic). Figure 2 shows the output of the complete hearing model on a hard switched noise signal of 70 dB which was binaurally r ...
Weighting curves
... forces the pointer to raise very quickly but it slows the falling, helping users in ...
... forces the pointer to raise very quickly but it slows the falling, helping users in ...
5 - Neurobiology of Hearing
... amplitude due to cholinergic medial efferent neurons inhibiting them in order to isolate the meaningful sound parts. We will be looking for relative differences in the change over time in the amplitude of the OAEs between the two subject groups. The sound stimulus will be played for 10 seconds so as ...
... amplitude due to cholinergic medial efferent neurons inhibiting them in order to isolate the meaningful sound parts. We will be looking for relative differences in the change over time in the amplitude of the OAEs between the two subject groups. The sound stimulus will be played for 10 seconds so as ...
Chapter 12 – Auditory Localization and Organization
... Sounds in front of us If a sound strikes both L and R at the same time, L’s action potential will arrive at the end of its axon, followed by R’s. That’s because the action potential has further to travel in R than it does in L. Thus, the total release of neurotransmitter substance at MSO will be lon ...
... Sounds in front of us If a sound strikes both L and R at the same time, L’s action potential will arrive at the end of its axon, followed by R’s. That’s because the action potential has further to travel in R than it does in L. Thus, the total release of neurotransmitter substance at MSO will be lon ...
Handout 8
... Rule 3: Loudness is strongly affected by the frequency of the signal. If intensity is held constant, a mid-frequency signal (in the range from ~1000-4000 Hz) will be louder than lower or higher frequency signals. ...
... Rule 3: Loudness is strongly affected by the frequency of the signal. If intensity is held constant, a mid-frequency signal (in the range from ~1000-4000 Hz) will be louder than lower or higher frequency signals. ...
The Auditory and Vestibular Systems
... The receptors of the cochlea are contained in a structure called the organ of Corti. The receptors are called hair cells. The hair cells have 100 or more stereocilia extending from their apical surface and are contacted at their basal end by the sensory afferents of the eighth nerve (vestibulocochle ...
... The receptors of the cochlea are contained in a structure called the organ of Corti. The receptors are called hair cells. The hair cells have 100 or more stereocilia extending from their apical surface and are contacted at their basal end by the sensory afferents of the eighth nerve (vestibulocochle ...
Perception Chapter 11: Hearing and Listening
... How widespread is activity on BM? Louder sounds will activate Lower spontaneous activity fibers; and will involve more fibers in total along BM Discriminatory power: usually 1-2dB change in intensity is ...
... How widespread is activity on BM? Louder sounds will activate Lower spontaneous activity fibers; and will involve more fibers in total along BM Discriminatory power: usually 1-2dB change in intensity is ...
Sound Sound is very important for our life. It is the sound that helps
... Ans. Because the sound of the train travels much faster through solid railway track made up of steel than through air. Q10. Define the following terms for a vibrating object: (a) Amplitude (b) Time-period (c) Frequency Ans. (a) Amplitude: The maximum displacement of vibrating object from its mean po ...
... Ans. Because the sound of the train travels much faster through solid railway track made up of steel than through air. Q10. Define the following terms for a vibrating object: (a) Amplitude (b) Time-period (c) Frequency Ans. (a) Amplitude: The maximum displacement of vibrating object from its mean po ...
Auditory Perception P1
... Waves can occupy the same part of a medium at the same time without interacting. Waves don’t collide like particles. Two waves (with the same amplitude, frequency, and wavelength) are traveling in opposite directions. ...
... Waves can occupy the same part of a medium at the same time without interacting. Waves don’t collide like particles. Two waves (with the same amplitude, frequency, and wavelength) are traveling in opposite directions. ...
HEARING CONSERVATION & NOISE EXPOSURE
... to one another – Filled with fluid and tiny hair cells – Depending on which way your head is tilted, the fluid moves the hair cells, an they send a signal to your brain ...
... to one another – Filled with fluid and tiny hair cells – Depending on which way your head is tilted, the fluid moves the hair cells, an they send a signal to your brain ...
Lesson Plan Hearing K-2
... Ears do more than hear. They keep you balanced, too. In the inner ear, there are three small loops above the cochlea called semicircular canals. Like the cochlea, they are also filled with liquid and have thousands of microscopic hairs. When you move your head, the liquid in the semicircular canals ...
... Ears do more than hear. They keep you balanced, too. In the inner ear, there are three small loops above the cochlea called semicircular canals. Like the cochlea, they are also filled with liquid and have thousands of microscopic hairs. When you move your head, the liquid in the semicircular canals ...
09 Sound And The Ear
... frequency - with harmonics added the fundamental frequency is the dominant pure tone ...
... frequency - with harmonics added the fundamental frequency is the dominant pure tone ...
Chapter 11
... changes, with the lowest intensity required for a given loudness always around 2000-3000 Hz. Tones of extremely low or extremely high frequencies are not perceived as loud as middle-frequency tones of the same intensity. 2. The curves are flatter at higher intensities – near the top of the graph. Th ...
... changes, with the lowest intensity required for a given loudness always around 2000-3000 Hz. Tones of extremely low or extremely high frequencies are not perceived as loud as middle-frequency tones of the same intensity. 2. The curves are flatter at higher intensities – near the top of the graph. Th ...
Physiology of auditory system (PDF Available)
... squared values over the wave form. The RMS value is very useful because ...
... squared values over the wave form. The RMS value is very useful because ...
What is Cochlear Damage?
... sounds are now missing. More powerful hearing aids may be appropriate in this case of cochlear damage. However, even when sound is made loud enough, the sounds may be distorted, because so much cochlear ...
... sounds are now missing. More powerful hearing aids may be appropriate in this case of cochlear damage. However, even when sound is made loud enough, the sounds may be distorted, because so much cochlear ...
Pitch - Auditory Neuroscience
... The observed orientation of their periodotopic map (mediodorsal to latero-ventral for high to low) appears to differ from that described by Schreiner & Langner (1988) in the cat (predimonantly caudal to ...
... The observed orientation of their periodotopic map (mediodorsal to latero-ventral for high to low) appears to differ from that described by Schreiner & Langner (1988) in the cat (predimonantly caudal to ...
Sound

In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as a typically audible mechanical wave of pressure and displacement, through a medium such as air or water. In physiology and psychology, sound is the reception of such waves and their perception by the brain.