HEARING
... frequency as the sound wave/oval window – The higher the frequency wave the faster the firing of hair cells – Theory used to explain how you hear low frequencies • Place theory—different frequencies cause larger vibrations at different locations along the basilar membrane – Different pitches stimula ...
... frequency as the sound wave/oval window – The higher the frequency wave the faster the firing of hair cells – Theory used to explain how you hear low frequencies • Place theory—different frequencies cause larger vibrations at different locations along the basilar membrane – Different pitches stimula ...
Audiometry practical
... that of the average person. The audiometer is calibrated to ISO (International Organization for Standardization) threshold levels for air conduction. According to this standard the absolute intensity of sound in watts/m2 produces by the audiometer at each frequency is set in such a way that when an ...
... that of the average person. The audiometer is calibrated to ISO (International Organization for Standardization) threshold levels for air conduction. According to this standard the absolute intensity of sound in watts/m2 produces by the audiometer at each frequency is set in such a way that when an ...
Module 20: Hearing
... Place Theory • Different frequencies cause larger vibrations at different locations along the basilar membrane ...
... Place Theory • Different frequencies cause larger vibrations at different locations along the basilar membrane ...
Lecture 11- Hearing
... Fibres end in the auditory area, where it is heard, then interpretation occurs in the auditory association areas (wernikes area) ...
... Fibres end in the auditory area, where it is heard, then interpretation occurs in the auditory association areas (wernikes area) ...
Response of Human Skull to Bone
... is largely the case with sound at less than 5 kHz (the range of most interest for perception of unmodified speech), there is great variability in both frequency response and attenuation across the skull in the higher frequencies . An understanding of this complex response to bone-conducted vibration ...
... is largely the case with sound at less than 5 kHz (the range of most interest for perception of unmodified speech), there is great variability in both frequency response and attenuation across the skull in the higher frequencies . An understanding of this complex response to bone-conducted vibration ...
10_Susan Scollie_non linear frequency
... Stelmachowicz, P.G., Pittman, A.L., Hoover, B.M., Lewis, D.E., and Moeller, M.P. (2004). The Importance of High-Frequency Audibility in the Speech and Language Development of Children with Hearing Loss. Archives of Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery, 130, 556-562. Wolfe, J., Caraway, T., John, A., ...
... Stelmachowicz, P.G., Pittman, A.L., Hoover, B.M., Lewis, D.E., and Moeller, M.P. (2004). The Importance of High-Frequency Audibility in the Speech and Language Development of Children with Hearing Loss. Archives of Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery, 130, 556-562. Wolfe, J., Caraway, T., John, A., ...
Introduction to Audiology Today
... A complete 360 degree course of a single sine wave from beginning to end Decrease in the amplitude of a vibrating body over time. A unit of pressure used in acoustic immittance measurements, such as tympanometry A unit of sound intensity level. A dB is the logarithm of the sound pressure of a sound ...
... A complete 360 degree course of a single sine wave from beginning to end Decrease in the amplitude of a vibrating body over time. A unit of pressure used in acoustic immittance measurements, such as tympanometry A unit of sound intensity level. A dB is the logarithm of the sound pressure of a sound ...
Chapter 11
... A given neuron can vary firing rate over about 40dB, but normal humans can hear loudness variations over 130dB. ...
... A given neuron can vary firing rate over about 40dB, but normal humans can hear loudness variations over 130dB. ...
Lecture 2 Hearing Loss Issues
... severe or profound hearing loss may not hear any speech sounds, unless they are shouted at close range. Hearing impaired people also have trouble understanding speech because essential parts of some phonemes are not audible. Sounds are recognized by noting which frequencies contain the most energy. ...
... severe or profound hearing loss may not hear any speech sounds, unless they are shouted at close range. Hearing impaired people also have trouble understanding speech because essential parts of some phonemes are not audible. Sounds are recognized by noting which frequencies contain the most energy. ...
17.4 Sound and Hearing
... Most people hear sounds between 20 hertz and 20,000 hertz. • Infrasound is sound at frequencies lower than most people can hear. • Ultrasound is sound at frequencies higher than ...
... Most people hear sounds between 20 hertz and 20,000 hertz. • Infrasound is sound at frequencies lower than most people can hear. • Ultrasound is sound at frequencies higher than ...
Sounds under different topics
... record what they hear through the air. The same person will tap lightly again while the second person lays his or her ear on the desk. The students should compare the sounds and record what they hear through the solid. Have the students try the experiment one last time, tapping louder, and, again, r ...
... record what they hear through the air. The same person will tap lightly again while the second person lays his or her ear on the desk. The students should compare the sounds and record what they hear through the solid. Have the students try the experiment one last time, tapping louder, and, again, r ...
17.4 Sound and Hearing
... Most people hear sounds between 20 hertz and 20,000 hertz. • Infrasound is sound at frequencies lower than most people can hear. • Ultrasound is sound at frequencies higher than ...
... Most people hear sounds between 20 hertz and 20,000 hertz. • Infrasound is sound at frequencies lower than most people can hear. • Ultrasound is sound at frequencies higher than ...
Lesson 5 - WordPress.com
... about 60 dB and sounds above 85 dB can cause hearing loss. The decibel scale works logarithmically, meaning that when a sound increases by 10 decibels it is actually 10 times louder. On this scale 0 dB measures the sound of total science, a sound 10 times more powerful would be 10 dB, while a sound ...
... about 60 dB and sounds above 85 dB can cause hearing loss. The decibel scale works logarithmically, meaning that when a sound increases by 10 decibels it is actually 10 times louder. On this scale 0 dB measures the sound of total science, a sound 10 times more powerful would be 10 dB, while a sound ...
The Physiology of the Senses
... Loud sounds produce a larger amplitude vibration of the basilar membrane than soft sounds. The large vibration produces more displacement of the hair cells and a larger change in potential inside these cells. Thus loudness is encoded by the frequency of action potentials that travel down a particula ...
... Loud sounds produce a larger amplitude vibration of the basilar membrane than soft sounds. The large vibration produces more displacement of the hair cells and a larger change in potential inside these cells. Thus loudness is encoded by the frequency of action potentials that travel down a particula ...
Hearing Conservation and Noise Measuring Equipment
... to determine if hearing protector’s are adequate to forego noise control The OSHA method is described well on the OSHA Noise & Hearing Conservation e-Tool website http://www.osha.gov/dts/osta/otm/noise/hcp/attenuation ...
... to determine if hearing protector’s are adequate to forego noise control The OSHA method is described well on the OSHA Noise & Hearing Conservation e-Tool website http://www.osha.gov/dts/osta/otm/noise/hcp/attenuation ...
Auditory System - PROFESSOR AC BROWN
... a. ossicular function: sound transmission from tympanic membrane to oval window of the cochlea b. middle ear muscles (tensor tympani and stapedius): muscle contraction decreases efficiency of ossicular sound transmission function: protect against cochlear damage due to excess sound energy; tympanic ...
... a. ossicular function: sound transmission from tympanic membrane to oval window of the cochlea b. middle ear muscles (tensor tympani and stapedius): muscle contraction decreases efficiency of ossicular sound transmission function: protect against cochlear damage due to excess sound energy; tympanic ...
Auditory encoding of speech features: Effects of hearing impairment
... AI predicts intelligibility rather well for mild and moderate hearing losses. But not for severe and profound losses – here the effects of audibility are not enough to explain limits to speech recognition ...
... AI predicts intelligibility rather well for mild and moderate hearing losses. But not for severe and profound losses – here the effects of audibility are not enough to explain limits to speech recognition ...
Determining the Wavelength of Sound
... then they know that something is near. The frequencies of bats are different in many books. In one source it says that the frequency is 120 kHz, while in another it says 100 kHz. The truth is it ranges because when the bat makes a sound it isn't of the same frequency all the time. Sound and music ar ...
... then they know that something is near. The frequencies of bats are different in many books. In one source it says that the frequency is 120 kHz, while in another it says 100 kHz. The truth is it ranges because when the bat makes a sound it isn't of the same frequency all the time. Sound and music ar ...
Audio Fundamentals
... as air. Sound energy travels through all phases of matter; i.e. gases, solids, or liquids. This molecular disturbance propagates through the given medium at a rate related to the close proximity of its own molecule structure, or density. The molecular disturbance is a type of kinetic energy known as ...
... as air. Sound energy travels through all phases of matter; i.e. gases, solids, or liquids. This molecular disturbance propagates through the given medium at a rate related to the close proximity of its own molecule structure, or density. The molecular disturbance is a type of kinetic energy known as ...
Lecture_34_2014_noquiz
... larger amplitude= louder sound -larger amplitude results in stronger pressure on the hair cells, more rapid firing of action potentials 2. Pitch - basilar membrane varies in thickness and flexibility -base= narrow and stiff; stimulated by higher frequencies -tip (apex)= wider and more flexible; stim ...
... larger amplitude= louder sound -larger amplitude results in stronger pressure on the hair cells, more rapid firing of action potentials 2. Pitch - basilar membrane varies in thickness and flexibility -base= narrow and stiff; stimulated by higher frequencies -tip (apex)= wider and more flexible; stim ...
open Gail Gudmunssen`s description of the ER20
... needs to hear clearly in noise. This applies to musicians and others who need to perform their job, enjoy a concert, or participate in recreational and sporting activities where hearing protection is needed, but sound quality cannot be compromised. Etymotic ETYPlugs® earplugs allow people to hear th ...
... needs to hear clearly in noise. This applies to musicians and others who need to perform their job, enjoy a concert, or participate in recreational and sporting activities where hearing protection is needed, but sound quality cannot be compromised. Etymotic ETYPlugs® earplugs allow people to hear th ...
Speech Sound Lesson Plan - DeafEd-Course
... going to go. Let’s practice touching your tongue on the top of your mouth. Good! Now open your lips just a little like this (teacher demonstrates opening their mouth slightly, looking in the mirror to model for the student). Okay now it is your turn. Here is the mirror. Look in the mirror to make su ...
... going to go. Let’s practice touching your tongue on the top of your mouth. Good! Now open your lips just a little like this (teacher demonstrates opening their mouth slightly, looking in the mirror to model for the student). Okay now it is your turn. Here is the mirror. Look in the mirror to make su ...
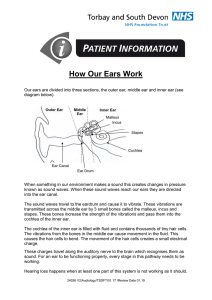
How our ears work information leaflet
... into the ear canal. The sound waves travel to the eardrum and cause it to vibrate. These vibrations are transmitted across the middle ear by 3 small bones called the malleus, incus and stapes. These bones increase the strength of the vibrations and pass them into the cochlea of the inner ear. The co ...
... into the ear canal. The sound waves travel to the eardrum and cause it to vibrate. These vibrations are transmitted across the middle ear by 3 small bones called the malleus, incus and stapes. These bones increase the strength of the vibrations and pass them into the cochlea of the inner ear. The co ...
Studio Magic Student Guide
... Waves are a powerful model for explaining the properties of light, including reflection, changing direction in different materials (refraction) and spreading out around obstacles (diffraction). A ...
... Waves are a powerful model for explaining the properties of light, including reflection, changing direction in different materials (refraction) and spreading out around obstacles (diffraction). A ...
The Ear and Hearing
... The vestibular and tympanic canals contain perilymph - a liquid almost identical with spinal fluid. The cochlea duct contains endolymph - a liquid similar to the fluid within cells. The canals are separated by thin membranes: Reissner's membrane between the vestibular canal and the cochlea duct is t ...
... The vestibular and tympanic canals contain perilymph - a liquid almost identical with spinal fluid. The cochlea duct contains endolymph - a liquid similar to the fluid within cells. The canals are separated by thin membranes: Reissner's membrane between the vestibular canal and the cochlea duct is t ...