Why Synthetic Peptide Vaccines?
... • Antibodies are a critical component of the body’s immune defense against viruses and other infectious agents. • Vaccines stimulate the body to produce antibodies that will recognize a particular virus. ...
... • Antibodies are a critical component of the body’s immune defense against viruses and other infectious agents. • Vaccines stimulate the body to produce antibodies that will recognize a particular virus. ...
14.3 Vaccination
... • Killed vaccines often require repeated boosters to maintain the immune status of host. • Killed vaccines induce a predominantly humoral immune response; they are less effective than attenuated vaccines in inducing cell-mediated immunity and in eliciting IgA response. ...
... • Killed vaccines often require repeated boosters to maintain the immune status of host. • Killed vaccines induce a predominantly humoral immune response; they are less effective than attenuated vaccines in inducing cell-mediated immunity and in eliciting IgA response. ...
84. Which of the following describes an adjuvant correctly? A An
... 87. In which of the following situations might a fetus be at risk from Rhesus antibodies produced by the mother? ...
... 87. In which of the following situations might a fetus be at risk from Rhesus antibodies produced by the mother? ...
Lecture 26. Prevention and Control -
... • Gamma globulin – Ig’s from pooled blood of at least 1,000 human donors • variable content • non-specific ...
... • Gamma globulin – Ig’s from pooled blood of at least 1,000 human donors • variable content • non-specific ...
BeefIQ12
... – Contain no live or killed microorganisms – Are used to treat a variety of health related conditions – Almost every pharmaceutical has a withdrawal period – Example: Antibiotics such as LA-200 ...
... – Contain no live or killed microorganisms – Are used to treat a variety of health related conditions – Almost every pharmaceutical has a withdrawal period – Example: Antibiotics such as LA-200 ...
Laboratory Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment of Bacte rial Infection
... microbial antigens. Genetic probes identify genus- or species-specific DNA or RNA sequences. ...
... microbial antigens. Genetic probes identify genus- or species-specific DNA or RNA sequences. ...
Preparation of Vaccines
... – Harder to make this type for bacteria – usu. viruses – Example: MMR, Varicella zoster ...
... – Harder to make this type for bacteria – usu. viruses – Example: MMR, Varicella zoster ...
2.11.15 - WordPress.com
... duration of acquired immune responses are dictated by early innate signals triggered by live attenuated vaccines [6, 12–14]. ...
... duration of acquired immune responses are dictated by early innate signals triggered by live attenuated vaccines [6, 12–14]. ...
Vaccination
... mouth. Very new vaccines are available as nasal sprays. • Vaccines contain antigens to a disease which are inactivated or attenuated, and which stimulate an individual’s immune system to produce antibodies. ...
... mouth. Very new vaccines are available as nasal sprays. • Vaccines contain antigens to a disease which are inactivated or attenuated, and which stimulate an individual’s immune system to produce antibodies. ...
MALARIAL VACCINES
... Modification of Glucose-6phosphate dehydrogenase Ovalocytosis Duffy Ag–protects against P.vivax infection ...
... Modification of Glucose-6phosphate dehydrogenase Ovalocytosis Duffy Ag–protects against P.vivax infection ...
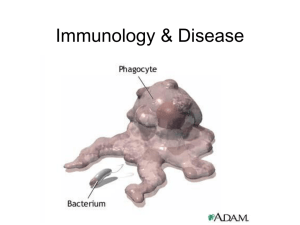
I. Immunity
... blood cells and antibodies 1. White blood cells: two types-T cells and B cells 2. Antibody—protein that disables antigens 3. B cells—makes antibodies 4. T cells—helps make antibodies, kills infected cells 5. Memory B cells—used if attacked again by same antigen -Draw Fig 39.12 p 1037 ...
... blood cells and antibodies 1. White blood cells: two types-T cells and B cells 2. Antibody—protein that disables antigens 3. B cells—makes antibodies 4. T cells—helps make antibodies, kills infected cells 5. Memory B cells—used if attacked again by same antigen -Draw Fig 39.12 p 1037 ...
Vaccines
... Vaccines • Protect our body from contracting viruses and certain types of bacteria • Allow body to become immune to a specific pathogens – Example: Flu vaccine ...
... Vaccines • Protect our body from contracting viruses and certain types of bacteria • Allow body to become immune to a specific pathogens – Example: Flu vaccine ...
Immune Memory and Vaccines
... produces antibodies to trigger a quick secondary response) – Naturally acquired active immunity: example— common cold viruses – “Artificially” acquired active immunity: Vaccines… *Passive immunity: Antibodies come from outside source—body does not produce them from activated B-cells. Source can be “ ...
... produces antibodies to trigger a quick secondary response) – Naturally acquired active immunity: example— common cold viruses – “Artificially” acquired active immunity: Vaccines… *Passive immunity: Antibodies come from outside source—body does not produce them from activated B-cells. Source can be “ ...
Basic Immunology - Pipestone Veterinary Services
... diseases lend themselves to control by vaccination. In the next few paragraphs we will take a look at the components in the little plastic bottle and how they work to prevent disease. ...
... diseases lend themselves to control by vaccination. In the next few paragraphs we will take a look at the components in the little plastic bottle and how they work to prevent disease. ...
AIDS vaccines
... SOME good news about AIDS. After more than two decades of research those laboring to find a vaccine against HIV, the virus that causes the disease, have found a method that might actually work. This method, known as “prime-boost”, has been tested on more than 16,000 volunteers in Thailand. The volun ...
... SOME good news about AIDS. After more than two decades of research those laboring to find a vaccine against HIV, the virus that causes the disease, have found a method that might actually work. This method, known as “prime-boost”, has been tested on more than 16,000 volunteers in Thailand. The volun ...
11.8.11 seminar_Lehrer (PDF)
... and dosing are adjusted to be sufficiently immunogenic to prevent viral infection or at least prevent the onset of clinical disease. As an example, there are currently no licensed vaccines to prevent the hemorrhagic fevers resulting from Ebola or Marburg virus infection. Classical approaches such as ...
... and dosing are adjusted to be sufficiently immunogenic to prevent viral infection or at least prevent the onset of clinical disease. As an example, there are currently no licensed vaccines to prevent the hemorrhagic fevers resulting from Ebola or Marburg virus infection. Classical approaches such as ...
Immune Memory and Vaccines
... immunity (active because the body actively produces antibodies to trigger a quick secondary response) – Naturally acquired active immunity: example— common cold viruses – “Artificially” acquired active immunity: Vaccines… Passive immunity: Antibodies come from outside source—body does not produce th ...
... immunity (active because the body actively produces antibodies to trigger a quick secondary response) – Naturally acquired active immunity: example— common cold viruses – “Artificially” acquired active immunity: Vaccines… Passive immunity: Antibodies come from outside source—body does not produce th ...