The Periodic Table
... • Not found pure in nature, but combined with other elements (as compounds). • Soft – can be cut with a knife. • Usually lustrous but will dull in contact with air. ...
... • Not found pure in nature, but combined with other elements (as compounds). • Soft – can be cut with a knife. • Usually lustrous but will dull in contact with air. ...
The Periodic Table
... • Not found pure in nature, but combined with other elements (as compounds). • Soft – can be cut with a knife. • Usually lustrous but will dull in contact with air. ...
... • Not found pure in nature, but combined with other elements (as compounds). • Soft – can be cut with a knife. • Usually lustrous but will dull in contact with air. ...
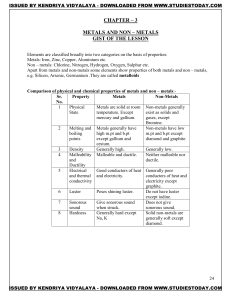
METALS AND NON – METALS Concepts
... Metals: Iron, Zinc, Copper, Aluminium etc. Non – metals: Chlorine, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulphur etc. Apart from metals and non-metals some elements show properties of both metals and non – metals, e.g. Silicon, Arsenic, Germanium .They are called metalloids Comparison of physical and chemical ...
... Metals: Iron, Zinc, Copper, Aluminium etc. Non – metals: Chlorine, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulphur etc. Apart from metals and non-metals some elements show properties of both metals and non – metals, e.g. Silicon, Arsenic, Germanium .They are called metalloids Comparison of physical and chemical ...
Module-2-s-and-d-elements - Львівський національний медичний
... Hydrogen has a lower boiling point and melting point than any other substance except helium; hydrogen melts at –259.2 °C and boils at –252.77° C. At 0 °C and 1 atmosphere pressure (STP), hydrogen is a gas with a density of 0.089 g/L. Liquid hydrogen, obtained firstly by the British chemist Sir James ...
... Hydrogen has a lower boiling point and melting point than any other substance except helium; hydrogen melts at –259.2 °C and boils at –252.77° C. At 0 °C and 1 atmosphere pressure (STP), hydrogen is a gas with a density of 0.089 g/L. Liquid hydrogen, obtained firstly by the British chemist Sir James ...
Periodic Trends & the Periodic Table
... Groups • The group tell you the number of valence electrons that the element has • Valence electrons are electrons in the outermost shell of the atom • All group 1A elements have 1 valence ...
... Groups • The group tell you the number of valence electrons that the element has • Valence electrons are electrons in the outermost shell of the atom • All group 1A elements have 1 valence ...
Periodictable - Trupia
... Only found in compounds in nature Have 7 valence electrons Gain 1 valence electron from a metal to form -1 ions Share 1 valence electron with another nonmetal atom to form one covalent bond. ...
... Only found in compounds in nature Have 7 valence electrons Gain 1 valence electron from a metal to form -1 ions Share 1 valence electron with another nonmetal atom to form one covalent bond. ...
Reactions of Main Group ...ith Nitrogen - Chemwiki
... and hydroxide ions. The heavier alkali metals are seen to be chemically inactive in regards to nitrogen upon heating or under ambient states. Due to this idleness, the notion that nitrides are unable to form through traditional chemical conditions has been formed. Since the nitride ion holds a hi ...
... and hydroxide ions. The heavier alkali metals are seen to be chemically inactive in regards to nitrogen upon heating or under ambient states. Due to this idleness, the notion that nitrides are unable to form through traditional chemical conditions has been formed. Since the nitride ion holds a hi ...
Unit 2 - Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding
... A. Metals are good conductors of heat and light B. Metals are shiny 1. Narrow range of energy differences between orbitals allows electrons to be easily excited, and emit light upon returning to a lower energy level C. Metals are Malleable 1. Can be hammered into thin sheets D. Metals are ductile 1 ...
... A. Metals are good conductors of heat and light B. Metals are shiny 1. Narrow range of energy differences between orbitals allows electrons to be easily excited, and emit light upon returning to a lower energy level C. Metals are Malleable 1. Can be hammered into thin sheets D. Metals are ductile 1 ...
10.2 – District 2: Periodic Table and Trends Key Points Notes The
... 10.2 – District 2: Periodic Table and Trends Notes ...
... 10.2 – District 2: Periodic Table and Trends Notes ...
Chapter Test A
... ______16. Which of the following elements have full outer energy levels when they are in the ground state? a. alkali metals b. noble gases c. halogens d. transition metals ______ 17. In which period is an element that has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p1 when it is in its ground ...
... ______16. Which of the following elements have full outer energy levels when they are in the ground state? a. alkali metals b. noble gases c. halogens d. transition metals ______ 17. In which period is an element that has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p1 when it is in its ground ...
helium
... They have two valence electrons. Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
... They have two valence electrons. Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
Activity 16 Elements and the Periodic Table
... and “bond” or move apart and never connect. Remember that chemical reactions involve the electrons. Electrons come and go and change the charge of the element. Some elements have all the electrons that they “need” and therefore are not “interested in” reacting. These elements are not reactive; often ...
... and “bond” or move apart and never connect. Remember that chemical reactions involve the electrons. Electrons come and go and change the charge of the element. Some elements have all the electrons that they “need” and therefore are not “interested in” reacting. These elements are not reactive; often ...
HERE
... 2) One difference between mixtures and pure substances is that A) mixtures can be physically separated. B) mixtures are made of one type of atom. C) pure substances have no chemical bonds. D) pure substances can be physically separated. 3) When two or more substances combine, but each keeps its own ...
... 2) One difference between mixtures and pure substances is that A) mixtures can be physically separated. B) mixtures are made of one type of atom. C) pure substances have no chemical bonds. D) pure substances can be physically separated. 3) When two or more substances combine, but each keeps its own ...
Periodic Trends Student
... • It doesn’t take much energy to pull electrons from alkali metals, since they want to give them away. And it takes lots of energy to pull electrons from noble gases, since they are so happy with their full outer shell. ...
... • It doesn’t take much energy to pull electrons from alkali metals, since they want to give them away. And it takes lots of energy to pull electrons from noble gases, since they are so happy with their full outer shell. ...
Chapter 5 Organizing The Elements
... Ex. Sodium chloride (table salt) Group 1A Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr Their reactivity increases from TOP TO BOTTOM ...
... Ex. Sodium chloride (table salt) Group 1A Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr Their reactivity increases from TOP TO BOTTOM ...
Section 15.1
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
Define the following: Electronegativity
... 17. The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the nucleus? Protons and also electrons if electrically neutral 18. What is the electron configuration of the noble gases? End with s2p6 19. Which subatomic particle plays the greatest part in determining the properties of ...
... 17. The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the nucleus? Protons and also electrons if electrically neutral 18. What is the electron configuration of the noble gases? End with s2p6 19. Which subatomic particle plays the greatest part in determining the properties of ...
E/F Physical Science Learning Targets ALL Name: Date: Hour
... 2. Elements within a group have the ___________________ number of valence electrons. 3. The reactivity of alkali metals ____________________ from the top of Group 1A to the bottom. 4. Sodium is stored under oil because it _________________________________. 5. Differences in reactivity among alkaline ...
... 2. Elements within a group have the ___________________ number of valence electrons. 3. The reactivity of alkali metals ____________________ from the top of Group 1A to the bottom. 4. Sodium is stored under oil because it _________________________________. 5. Differences in reactivity among alkaline ...
Properties of Elements
... familiar: copper, tin, zinc, iron, nickel, gold, and silver. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
... familiar: copper, tin, zinc, iron, nickel, gold, and silver. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
BOOKLETColoring-the-Periodic-Table-Families
... Arrangements of elements in order of increasing ...
... Arrangements of elements in order of increasing ...
The Periodic Table of Elements Mendeleev
... • Ionization Energy (required!) – Left Æ right within the period: increase – Top Æ bottom within the group: decrease – Trends opposite that of atomic radius (why?) ...
... • Ionization Energy (required!) – Left Æ right within the period: increase – Top Æ bottom within the group: decrease – Trends opposite that of atomic radius (why?) ...
Ch. 9
... • The more electronegative element is written last and w/ ide • Use prefixes to tell you the subscript in each • Mono is not written w/ the 1st word of a compound’s name (Ex: CO2) • Prefixes are sometimes shortened to make a name easier to say (Ex: CO is carbon monoxide not mono oxide) • Sometimes u ...
... • The more electronegative element is written last and w/ ide • Use prefixes to tell you the subscript in each • Mono is not written w/ the 1st word of a compound’s name (Ex: CO2) • Prefixes are sometimes shortened to make a name easier to say (Ex: CO is carbon monoxide not mono oxide) • Sometimes u ...
g - Santa Rosa Junior College
... – The inorganic cycle involves slow weathering of phosphatecontaining rocks, which causes PO43- to leach into the rivers and seas. – The land-based biological cycle involves incorporation of PO43- into organisms and its release through excretion and ...
... – The inorganic cycle involves slow weathering of phosphatecontaining rocks, which causes PO43- to leach into the rivers and seas. – The land-based biological cycle involves incorporation of PO43- into organisms and its release through excretion and ...
Name: Date: _____ Pd: _____ Chemistry, PERIODIC TABLE Spring
... when it comes in contact with hydrogen sulfide, , which is found in the air and in some foods. However, stainless steel does not tarnish when it comes in contact with hydrogen sulfide. 14. Draw a Lewis electron-dot diagram for the compound that tarnishes silver. 15. In the ground state, an atom of w ...
... when it comes in contact with hydrogen sulfide, , which is found in the air and in some foods. However, stainless steel does not tarnish when it comes in contact with hydrogen sulfide. 14. Draw a Lewis electron-dot diagram for the compound that tarnishes silver. 15. In the ground state, an atom of w ...
elements in a family have the same number of
... One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, ...
... One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, ...