Methods to Study the Brain - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... The Brain Tools of discovery 2. Manipulating the brain a. Lesions – purposely destroying a part of the brain and observing the results. b. Brain Stimulation ...
... The Brain Tools of discovery 2. Manipulating the brain a. Lesions – purposely destroying a part of the brain and observing the results. b. Brain Stimulation ...
Problems with Imbalance
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any r ...
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any r ...
NS Review
... 23. During a what**** potential the cell is negative outside & positive inside? 24. During depolarization the blank *** channels open. 25. The Na/K pump reestablishes the what *** potential. 26. A bruise to the brain which could be mild to severe is called what? 27. The substance released at axonal ...
... 23. During a what**** potential the cell is negative outside & positive inside? 24. During depolarization the blank *** channels open. 25. The Na/K pump reestablishes the what *** potential. 26. A bruise to the brain which could be mild to severe is called what? 27. The substance released at axonal ...
Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are
... 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? En ...
... 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? En ...
Biological Basis for Understanding Psychotropic Drugs
... psychosocial stress), and physical disease all can increase the probability of psychiatric disorders. Specific neurotransmitters also are associated with mental dysfunction. ...
... psychosocial stress), and physical disease all can increase the probability of psychiatric disorders. Specific neurotransmitters also are associated with mental dysfunction. ...
Chapter 03 - Jen Wright
... 15. How does studying people with brain damage help scientists to better understand the brain? As a classic example, what did the case of Phineas Gage teach us? 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, and an fMRI? How do these machines help us to better understand the brain? How do the ...
... 15. How does studying people with brain damage help scientists to better understand the brain? As a classic example, what did the case of Phineas Gage teach us? 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, and an fMRI? How do these machines help us to better understand the brain? How do the ...
An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology
... relative to general population (or biological parents ...
... relative to general population (or biological parents ...
jeopardy bio psych review
... sensory signals and sends them to correct brain area for processing ...
... sensory signals and sends them to correct brain area for processing ...
Reading the neural code in behaving animals, ~1000 neurons at a ,me
... The microscope also allows 3me-‐lapse imaging, for watching how individual cells' coding proper3es evolve over weeks. By using the integrated microscope to perform calcium-‐imaging in behaving mice as they rep ...
... The microscope also allows 3me-‐lapse imaging, for watching how individual cells' coding proper3es evolve over weeks. By using the integrated microscope to perform calcium-‐imaging in behaving mice as they rep ...
to-BBB receives Michael J. Fox Foundation funding for
... to-BBB, the Dutch brain drug delivery company, has been awarded funding by The Michael J. Fox Foundation (MJFF) to conduct preclinical research targeting neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease (PD) with its second product in development, 2B3-201. This is to-BBB’s first grant from MJFF. “We strongl ...
... to-BBB, the Dutch brain drug delivery company, has been awarded funding by The Michael J. Fox Foundation (MJFF) to conduct preclinical research targeting neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease (PD) with its second product in development, 2B3-201. This is to-BBB’s first grant from MJFF. “We strongl ...
Read the perspective by Temel and Jahanshahi here.
... to single-base-pair resolution, a much larger set of orthogonal interfaces could be constructed relative to a given bundle size. This would allow assembly of larger, more complex, and therefore more sophisticated devices. The authors note some challenges for including base-pairing interactions, inst ...
... to single-base-pair resolution, a much larger set of orthogonal interfaces could be constructed relative to a given bundle size. This would allow assembly of larger, more complex, and therefore more sophisticated devices. The authors note some challenges for including base-pairing interactions, inst ...
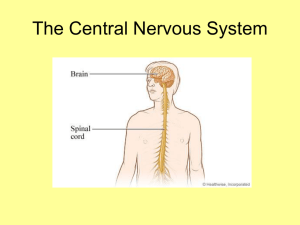
the central nervous system
... The brain carries out most of the functions for the body while the spinal cord acts more like a liaison between the body and the brain. Most information is brought to the brain by moving up the neurons of the spinal cord. The spinal cord does, however, perform many reflex reactions. Both the brain a ...
... The brain carries out most of the functions for the body while the spinal cord acts more like a liaison between the body and the brain. Most information is brought to the brain by moving up the neurons of the spinal cord. The spinal cord does, however, perform many reflex reactions. Both the brain a ...
Time Zones
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
Day2AM-exome-variant
... • Exomes more cost effective: Sequence patient DNA and filter common SNPs; compare parents child trios; compare paired normal cancer ...
... • Exomes more cost effective: Sequence patient DNA and filter common SNPs; compare parents child trios; compare paired normal cancer ...
The Teenage Brain
... Arnsten AF. (2010) Stress signaling pathways that impair prefrontal cortex structure and function ...
... Arnsten AF. (2010) Stress signaling pathways that impair prefrontal cortex structure and function ...
Biology 30 – Notes Neurotransmitters and the Brain, September 15
... areas of the hindbrain and forebrain. It also plays an important role in eye movement and control of ...
... areas of the hindbrain and forebrain. It also plays an important role in eye movement and control of ...
Brain Muscle Interface
... bleeds into the brain. A spinal cord injury (SCI) on the other hand is damage to the spinal cord that causes changes in its function, either temporary or permanent. These changes translate into loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in parts of the body served by the spinal cord b ...
... bleeds into the brain. A spinal cord injury (SCI) on the other hand is damage to the spinal cord that causes changes in its function, either temporary or permanent. These changes translate into loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in parts of the body served by the spinal cord b ...
Study Guide
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho
... Motor cortex: an area at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary movements Somatosensory cortex: registers and processes body touch and movement sensations (in the front of the parietal lobes) Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex involving the higher mental functions, such as lea ...
... Motor cortex: an area at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary movements Somatosensory cortex: registers and processes body touch and movement sensations (in the front of the parietal lobes) Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex involving the higher mental functions, such as lea ...
Brain Anatomy and Function p. 95
... Controls feeling pleasure, feeding and drinking behavior, the fight or flight response, aggression, submission, memory, body temperature, sexual behavior, emotions, and motivation for behavior. It is responsible for physical reactions to emotions. Limbic system also interprets olfactory sensations. ...
... Controls feeling pleasure, feeding and drinking behavior, the fight or flight response, aggression, submission, memory, body temperature, sexual behavior, emotions, and motivation for behavior. It is responsible for physical reactions to emotions. Limbic system also interprets olfactory sensations. ...
A New Source for New Neurons : TheologyPlus : http://www
... networks.” In other words, they do what neurons normally do. They process signals from one end of the cell to another. They form synaptic connections with other neurons. And they integrate into larger networks. Will this become a new strategy for treating diseases or injuries to brain cells? That is ...
... networks.” In other words, they do what neurons normally do. They process signals from one end of the cell to another. They form synaptic connections with other neurons. And they integrate into larger networks. Will this become a new strategy for treating diseases or injuries to brain cells? That is ...
the brain - Cloudfront.net
... 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a non-musician. ...
... 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a non-musician. ...
The Brain for Not-So
... Infants greatly preferred the “cloth mother” Retreated to the soft mother when anxious Were more outgoing, adventurous, able to meet new monkeys in presence of “cloth mother” Touch (e.g., “skin to skin”) now an important part of ...
... Infants greatly preferred the “cloth mother” Retreated to the soft mother when anxious Were more outgoing, adventurous, able to meet new monkeys in presence of “cloth mother” Touch (e.g., “skin to skin”) now an important part of ...
Clinical Day
... • Average onset age 33 • Progressive loss of function interspersed with remission periods ...
... • Average onset age 33 • Progressive loss of function interspersed with remission periods ...
The Brain and Nervous System
... other parts of the brain that influence our motives. This includes release of pleasure hormones, rats that could stimulate their HT electrically would do so 7000 times an hour. ...
... other parts of the brain that influence our motives. This includes release of pleasure hormones, rats that could stimulate their HT electrically would do so 7000 times an hour. ...