Kepler`s Search for Exoplanets
... [VE - Go to sunrise; stars fade off] Here we’ve marked stars with confirmed exoplanets. There are over nearly 2000 confirmed exoplanets [update as needed], and we’re still just getting started! Results from Kepler indicate that it’s likely every star we see in the night sky has planets. And it’s jus ...
... [VE - Go to sunrise; stars fade off] Here we’ve marked stars with confirmed exoplanets. There are over nearly 2000 confirmed exoplanets [update as needed], and we’re still just getting started! Results from Kepler indicate that it’s likely every star we see in the night sky has planets. And it’s jus ...
Observing the Night Sky - Constellations
... binoculars available to assist you in seeing the fainter stars. 3. Determine Limiting Magnitude - Your instructor will point out a constellation with a large variety of stellar magnitudes. The constellation should be located high above the horizon, where Earth's atmosphere cannot dim the star's brig ...
... binoculars available to assist you in seeing the fainter stars. 3. Determine Limiting Magnitude - Your instructor will point out a constellation with a large variety of stellar magnitudes. The constellation should be located high above the horizon, where Earth's atmosphere cannot dim the star's brig ...
Venus is the Roman goddess of love and beauty. She is known as
... Most of Venus' surface consists of gently rolling plains. You won't find many mountains or hills. Data from the Magellan spacecraft shows that much of Venus' surface is covered by lava flows. There are many large volcanoes (like the ones in Hawaii) such as Sif Mons. Scientists have recently found th ...
... Most of Venus' surface consists of gently rolling plains. You won't find many mountains or hills. Data from the Magellan spacecraft shows that much of Venus' surface is covered by lava flows. There are many large volcanoes (like the ones in Hawaii) such as Sif Mons. Scientists have recently found th ...
Goal: To understand how to find the brightness of stars and what
... to be first magnitude. • The next brightest was 2nd magnitude. • And so on – and we can see down to about 6 or 7th magnitude in a “dark” sky with our naked eye. ...
... to be first magnitude. • The next brightest was 2nd magnitude. • And so on – and we can see down to about 6 or 7th magnitude in a “dark” sky with our naked eye. ...
PSF - ESO
... Each program has its own method - sometimes several methods – of performing this, but the basic idea is to produce an initial list of approximate centroid positions for all stars that can be distinguished in the two dimensional data array. The star finder must have at least some ability to tell the ...
... Each program has its own method - sometimes several methods – of performing this, but the basic idea is to produce an initial list of approximate centroid positions for all stars that can be distinguished in the two dimensional data array. The star finder must have at least some ability to tell the ...
Packet 3
... 4. Is the relationship of brightness to temperature for these stars puzzling, or does it make sense? Explain Group 3 Questions: 1. Compare the areas of the graph where the Group 2 and Group 3 stars are plotted. How are they different? 2. Overall, are the stars in Group 3 very bright or very dim? 3. ...
... 4. Is the relationship of brightness to temperature for these stars puzzling, or does it make sense? Explain Group 3 Questions: 1. Compare the areas of the graph where the Group 2 and Group 3 stars are plotted. How are they different? 2. Overall, are the stars in Group 3 very bright or very dim? 3. ...
PLANETS
... was the first transiting extrasolar planet discovered, the first extrasolar planet known to have an atmosphere, the first extrasolar planet observed to have an evaporating hydrogen atmosphere, the first extrasolar planet found to have an atmosphere containing oxygen and carbon, and one of the first ...
... was the first transiting extrasolar planet discovered, the first extrasolar planet known to have an atmosphere, the first extrasolar planet observed to have an evaporating hydrogen atmosphere, the first extrasolar planet found to have an atmosphere containing oxygen and carbon, and one of the first ...
The star formation histories of two northern LMC fields
... burst of star formation activity began some 3±5 Gyr ago, with a star formation rate as high as ten times the rate at older ages. These results confirm the expectations from the cluster studies. Recently, however, HST results have brought this seemingly firm picture into question. Holtzman et al. (19 ...
... burst of star formation activity began some 3±5 Gyr ago, with a star formation rate as high as ten times the rate at older ages. These results confirm the expectations from the cluster studies. Recently, however, HST results have brought this seemingly firm picture into question. Holtzman et al. (19 ...
Heliacal Rising of Canopus in Indian Astronomy
... In the present paper we discuss briefly the phenomenon of heliacal rising and setting of stars in general and of Canopus in particular. The importance of star Agastya (Canopus), apart from its religious significance, lies in its becoming circumpolar for different latitudes during different periods, ...
... In the present paper we discuss briefly the phenomenon of heliacal rising and setting of stars in general and of Canopus in particular. The importance of star Agastya (Canopus), apart from its religious significance, lies in its becoming circumpolar for different latitudes during different periods, ...
X-ray output should be time variable
... •O star X-ray emission comes from shock-heated gas present in their stellar winds; for B stars, the situation is more uncertain, and their Xrays may be related to magnetic fields, at least in some cases. The same may be true for certain O stars too. • Unstable mass flow driven by the radiation field ...
... •O star X-ray emission comes from shock-heated gas present in their stellar winds; for B stars, the situation is more uncertain, and their Xrays may be related to magnetic fields, at least in some cases. The same may be true for certain O stars too. • Unstable mass flow driven by the radiation field ...
Characteristics of Stars
... they imagined that groups of stars formed pictures of people or animals. Today, we call these imaginary patterns of stars constellations. Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and ...
... they imagined that groups of stars formed pictures of people or animals. Today, we call these imaginary patterns of stars constellations. Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and ...
AUI CA science talk - National Radio Astronomy Observatory
... • Science priorities expressed in various venues are generally consistent with the Key Science Projects proposed by the SKA science working group in 2004. • [Even SKA project office admits full SKA is not realizable in next decade.] • Near term: Narrow focus to quantify how NRAO facilities will make ...
... • Science priorities expressed in various venues are generally consistent with the Key Science Projects proposed by the SKA science working group in 2004. • [Even SKA project office admits full SKA is not realizable in next decade.] • Near term: Narrow focus to quantify how NRAO facilities will make ...
02-StarryStarryNight.. - Saptarishis Astrology
... was very unusual at the time, and is forever associated with him, coming from him cutting a reed pen and using this to draw with directly, inspired by the approach of the Japanese print artists that he admired so much and then translating that into brushwork when painting. His third house is ruled b ...
... was very unusual at the time, and is forever associated with him, coming from him cutting a reed pen and using this to draw with directly, inspired by the approach of the Japanese print artists that he admired so much and then translating that into brushwork when painting. His third house is ruled b ...
Deep Space Mystery Note Form 3
... Stars up to eight times the mass of our sun usually evolve into white dwarfs. A star that is condensed to this size has a very strong gravitational pull. With that gravity, if the second star is close enough, it can pull material from there. White dwarf gets a lot of mass ...
... Stars up to eight times the mass of our sun usually evolve into white dwarfs. A star that is condensed to this size has a very strong gravitational pull. With that gravity, if the second star is close enough, it can pull material from there. White dwarf gets a lot of mass ...
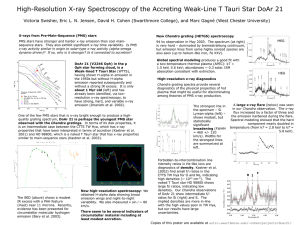
DoAr21_AAS2005 - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... having shown H-alpha in emission in the 1950s but without H-alpha emission reported subsequently and without a strong IR excess. It is only about 1 Myr old (left) and has already been identified, via lowresolution x-ray spectroscopy, to have strong, hard, and variable x-ray emission (Imanishi et al. ...
... having shown H-alpha in emission in the 1950s but without H-alpha emission reported subsequently and without a strong IR excess. It is only about 1 Myr old (left) and has already been identified, via lowresolution x-ray spectroscopy, to have strong, hard, and variable x-ray emission (Imanishi et al. ...
ABSOLUTE AND APPARENT MAGNITUDES
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
Star of Bethlehem

In Christian tradition, the Star of Bethlehem, also called the Christmas Star, revealed the birth of Jesus to the Biblical Magi, and later led them to Bethlehem. The star appears only in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew, where astrologers from the east are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask where the king of the Jews had been born. Herod, following a verse from the Book of Micah interpreted as a prophecy, directs them to Bethlehem, to the south of Jerusalem. The star leads them to Jesus' home in the town, where they worship him and give him gifts. The wise men are then given a divine warning not to return to Herod so they return home by a different route.Many Christians see the star as a miraculous sign to mark the birth of the Christ (or messiah). Some theologians claimed that the star fulfilled a prophecy, known as the Star Prophecy. Astronomers have made several attempts to link the star to unusual astronomical events, such as a conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn, a comet or a supernova.Many modern scholars do not consider the story to be describing a historical event but a pious fiction created by the author of the Gospel of Matthew.The subject is a favorite at planetarium shows during the Christmas season, although the Biblical account describes Jesus with a broader Greek word, which can mean either ""infant"" or ""child"" (paidon), rather than the more specific word for infant (brephos), possibly implying that some time has passed since the birth. The visit is traditionally celebrated on Epiphany (January 6) in Western Christianity.