Homework due 5-10
... difference V = 1,500 volts is applied across the parallel plates L and K, which are separated by a distance d = 0.012 meter and which act as a velocity selector. a. In which direction, relative to the coordinate system shown above on the right, should the magnetic field point in order for positive i ...
... difference V = 1,500 volts is applied across the parallel plates L and K, which are separated by a distance d = 0.012 meter and which act as a velocity selector. a. In which direction, relative to the coordinate system shown above on the right, should the magnetic field point in order for positive i ...
AP Physics I - Southern Regional School District
... Vectors can be used to describe the motion of an object. The value for acceleration due to gravity near the surface of the Earth is approximately 9.8 m/s . The orthogonal components of an object’s velocity are completely independent. ...
... Vectors can be used to describe the motion of an object. The value for acceleration due to gravity near the surface of the Earth is approximately 9.8 m/s . The orthogonal components of an object’s velocity are completely independent. ...
Mass of an Electromagnetic Wave
... of light, since it would require an infinite amount of energy to accelerate to this speed [2]. Thus it has been argued that electromagnetic waves or photons must be massless, as these by definition travel at the speed of light when in a vacuum. In this paper we will use some relativity equations to ...
... of light, since it would require an infinite amount of energy to accelerate to this speed [2]. Thus it has been argued that electromagnetic waves or photons must be massless, as these by definition travel at the speed of light when in a vacuum. In this paper we will use some relativity equations to ...
doc - Seth Baum
... 8) The magnitude of the electric field halfway between two equally charge particles a. What is zero 9) The difference between a sine wave and a cosine wave in radians a. What is pi/2 10) The two equations needed to find the object’s wavelength just before hitting the ground, given the object’s mass ...
... 8) The magnitude of the electric field halfway between two equally charge particles a. What is zero 9) The difference between a sine wave and a cosine wave in radians a. What is pi/2 10) The two equations needed to find the object’s wavelength just before hitting the ground, given the object’s mass ...
Physics Final Review Problems 2014 *Note: the following problems
... 15. A meter stick (100 cm) is supported at the 50 cm mark. A 20 g mass sits on the 20 cm mark, a 40 g mass sits on the 40 cm mark, a 60 g mass sits on the 60 cm mark, and an 80 g mass sits on the 80 cm mark. Where would a 150 g mass need to be located in order to balance the system? (cm) 16. Fred (9 ...
... 15. A meter stick (100 cm) is supported at the 50 cm mark. A 20 g mass sits on the 20 cm mark, a 40 g mass sits on the 40 cm mark, a 60 g mass sits on the 60 cm mark, and an 80 g mass sits on the 80 cm mark. Where would a 150 g mass need to be located in order to balance the system? (cm) 16. Fred (9 ...
Physics Final Review Problems 2013 *Note: the following problems
... 15. A meter stick (100 cm) is supported at the 50 cm mark. A 20 g mass sits on the 20 cm mark, a 40 g mass sits on the 40 cm mark, a 60 g mass sits on the 60 cm mark, and an 80 g mass sits on the 80 cm mark. Where would a 150 g mass need to be located in order to balance the system? (cm) 16. Fred (9 ...
... 15. A meter stick (100 cm) is supported at the 50 cm mark. A 20 g mass sits on the 20 cm mark, a 40 g mass sits on the 40 cm mark, a 60 g mass sits on the 60 cm mark, and an 80 g mass sits on the 80 cm mark. Where would a 150 g mass need to be located in order to balance the system? (cm) 16. Fred (9 ...
Physical Science Vocabulary 2016
... magnet, spread out from the N pole, curve around the magnet and return to the S pole forming loops Line close together=stronger magnetic field Lines far apart=weaker magnetic field 12.Electric charges= basic property of matter, charges can be positive (more protons in an atom) or negative (more ...
... magnet, spread out from the N pole, curve around the magnet and return to the S pole forming loops Line close together=stronger magnetic field Lines far apart=weaker magnetic field 12.Electric charges= basic property of matter, charges can be positive (more protons in an atom) or negative (more ...
Mass Spectrometer
... •These high energy electrons knock an e- from a sample atom. Producing a positive ion. •X(g) X+(g) + e- ...
... •These high energy electrons knock an e- from a sample atom. Producing a positive ion. •X(g) X+(g) + e- ...
lesson homework Tuesday may 1st
... (b) A proton is placed at point P shown above and released. Describe its motion for a long time after its release. (c) An electron of charge magnitude e is now placed at point P. which is a distance r from the center of the sphere, and released. Determine the kinetic energy of the electron as a func ...
... (b) A proton is placed at point P shown above and released. Describe its motion for a long time after its release. (c) An electron of charge magnitude e is now placed at point P. which is a distance r from the center of the sphere, and released. Determine the kinetic energy of the electron as a func ...
Exam #: Printed Name: Signature: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT
... In the Einstein model for a solid, atoms are treated as one-dimensional quantum mechanical oscillators that can each accept an arbitrary number of energy units above the ground state. Recall that the multiplicity Ω(N, q) = (q + N − 1)!/(q!(N − 1)!) gives the number of states available to a system co ...
... In the Einstein model for a solid, atoms are treated as one-dimensional quantum mechanical oscillators that can each accept an arbitrary number of energy units above the ground state. Recall that the multiplicity Ω(N, q) = (q + N − 1)!/(q!(N − 1)!) gives the number of states available to a system co ...
The effective mass tensor in the General Relativity
... material, the force between other atoms will affect its movement and it will not be described by Newton's law. So we introduce the concept of effective mass to describe the movement of electron in Newton's law. The effective mass can be negative or different due to circumstances. Generally, in the a ...
... material, the force between other atoms will affect its movement and it will not be described by Newton's law. So we introduce the concept of effective mass to describe the movement of electron in Newton's law. The effective mass can be negative or different due to circumstances. Generally, in the a ...
Physics Qualifying Examination – Part I 7-Minute Questions February 7, 2015
... A cold sodium atom (23Na), at rest, is isolated in a vacuum system on the Earth's surface. A laser, with λ = 589 nm (i.e., D-line or the 3s to 3p transition) shines on this atom from directly below. The atom absorbs photons and then reradiates that energy uniformly in all directions. Gravity, with a ...
... A cold sodium atom (23Na), at rest, is isolated in a vacuum system on the Earth's surface. A laser, with λ = 589 nm (i.e., D-line or the 3s to 3p transition) shines on this atom from directly below. The atom absorbs photons and then reradiates that energy uniformly in all directions. Gravity, with a ...
2 Communications satellites are usually placed in a geo
... The mass of the nucleus of an isolated copper atom is 63 u and it carries a charge of +29 e. The diameter of the atom is 2.3 × 10-10 m. P is a point at the outer edge of the atom. ...
... The mass of the nucleus of an isolated copper atom is 63 u and it carries a charge of +29 e. The diameter of the atom is 2.3 × 10-10 m. P is a point at the outer edge of the atom. ...
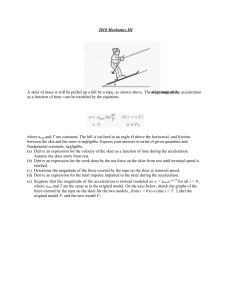
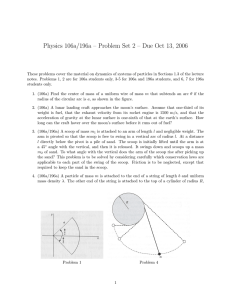
Physics 106a/196a – Problem Set 2 – Due Oct 13,...
... 1. (106a) Find the center of mass of a uniform wire of mass m that subtends an arc θ if the radius of the circular arc is a, as shown in the figure. 2. (106a) A lunar landing craft approaches the moon’s surface. Assume that one-third of its weight is fuel, that the exhaust velocity from its rocket e ...
... 1. (106a) Find the center of mass of a uniform wire of mass m that subtends an arc θ if the radius of the circular arc is a, as shown in the figure. 2. (106a) A lunar landing craft approaches the moon’s surface. Assume that one-third of its weight is fuel, that the exhaust velocity from its rocket e ...
Topic 6 Fields and Forces Name: The directives after the numbered
... 6.1 Gravitational force and field 6.1.1 State Newton’s universal law of gravitation Point mass Equation(s) – Know the relationship between the various variables in the equation. ...
... 6.1 Gravitational force and field 6.1.1 State Newton’s universal law of gravitation Point mass Equation(s) – Know the relationship between the various variables in the equation. ...
PHY2020 Test 2 November 5, 2014 Name: sin(30) = 1/2 cos(30
... const acceleration const acceleration Centripetal force pointing toward the center of circular motion Centripetal force pointing toward the center of circular motion T is the period of rotational motion. a is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration. Newton’s Law of gravity Newton’s Gravitation ...
... const acceleration const acceleration Centripetal force pointing toward the center of circular motion Centripetal force pointing toward the center of circular motion T is the period of rotational motion. a is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration. Newton’s Law of gravity Newton’s Gravitation ...
ap physics multiple choice medley
... across a frozen pond at speed vo. Two objects are dropped vertically into the sled one at a time: first an object of mass M and then an object of mass 2M. Afterward the sled moves with speed vf . What would be the final speed of the sled if only the 2M object was dropped in? a. 4vf /3 b. 3vf /2 c. v ...
... across a frozen pond at speed vo. Two objects are dropped vertically into the sled one at a time: first an object of mass M and then an object of mass 2M. Afterward the sled moves with speed vf . What would be the final speed of the sled if only the 2M object was dropped in? a. 4vf /3 b. 3vf /2 c. v ...