Energy Level diagram for a spin-1/2 nucleus as a function of
... The z-component of the nuclear angular momentum is related to the z-component of the nuclear spin. Recall in quantum mechanics that a total angular momentum of L has 2(L+1) components. The same is true for nuclear angular momentum and hence spin. (this gives rise to the different orbital structures) ...
... The z-component of the nuclear angular momentum is related to the z-component of the nuclear spin. Recall in quantum mechanics that a total angular momentum of L has 2(L+1) components. The same is true for nuclear angular momentum and hence spin. (this gives rise to the different orbital structures) ...
Dark matter
... dark matter, it doesn’t “clump up”). Since its energy density is so low everywhere, how do we know the dark energy’s there? ...
... dark matter, it doesn’t “clump up”). Since its energy density is so low everywhere, how do we know the dark energy’s there? ...
5 Elements of nuclear physics 5.1 Strong interaction and structure of atomic nuclei
... (6.27) is written as 32/3 π 4/3 a0 (5/3)~2 −1/3 ...
... (6.27) is written as 32/3 π 4/3 a0 (5/3)~2 −1/3 ...
PWE 19-2: Measuring Isotopes with a Mass Spectrometer
... recall from Chapter 17 that 1 V = 1 J>C = 1 N # m>C. So we can write the speed as ...
... recall from Chapter 17 that 1 V = 1 J>C = 1 N # m>C. So we can write the speed as ...
Midterm Review
... 13. Newton’s Third Law of Motion describes a. Why forces act in pairs b. All aspects of an object’s motion c. Motion when a balanced force acts on an object. d. Motion when an unbalanced force acts on an object. 14. A force a. Can cause an object to change its motion c. Is a push or pull b. Gives e ...
... 13. Newton’s Third Law of Motion describes a. Why forces act in pairs b. All aspects of an object’s motion c. Motion when a balanced force acts on an object. d. Motion when an unbalanced force acts on an object. 14. A force a. Can cause an object to change its motion c. Is a push or pull b. Gives e ...
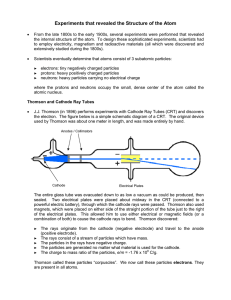
Experiments that revealed the Structure of the Atom
... Rutherford and his team (Geiger and Marsden) bombarded a number of different thin metal foils with alpha (α) particles from a radioactive source. Alpha particles are tiny, heavy particles with a positive charge. Particles passing through the foil would strike a screen coated with zinc sulfide, and a ...
... Rutherford and his team (Geiger and Marsden) bombarded a number of different thin metal foils with alpha (α) particles from a radioactive source. Alpha particles are tiny, heavy particles with a positive charge. Particles passing through the foil would strike a screen coated with zinc sulfide, and a ...
Life of a star
... mechanics come to help us. However one must not be surprised by the leap from one scientific discipline to another. The different scientific branches support each other and more and more often their discoveries overlap to give a single more complete picture of the situation. So, quantum mechanics sa ...
... mechanics come to help us. However one must not be surprised by the leap from one scientific discipline to another. The different scientific branches support each other and more and more often their discoveries overlap to give a single more complete picture of the situation. So, quantum mechanics sa ...
PP Mass spectrometer and atoms
... The first mass spectrometer was built in 1918 by Francis W Aston, a student of J J Thomson, the man who discovered the electron. Aston used the instrument to show that there were different forms of the same element. We now call these isotopes. In a mass spectrometer, particles are turned into positi ...
... The first mass spectrometer was built in 1918 by Francis W Aston, a student of J J Thomson, the man who discovered the electron. Aston used the instrument to show that there were different forms of the same element. We now call these isotopes. In a mass spectrometer, particles are turned into positi ...