Gravitational Potential Energy and Work (Syllabus: 9.2.1.2.2
... This is the same as calculating the change in Gravitational Potential Energy as for a box falling off a shelf, only instead of defining ground level as the reference (zero level) we are defining infinity as the reference point. For a box falling off a shelf the change in the value of acceleration du ...
... This is the same as calculating the change in Gravitational Potential Energy as for a box falling off a shelf, only instead of defining ground level as the reference (zero level) we are defining infinity as the reference point. For a box falling off a shelf the change in the value of acceleration du ...
PYP001-122-Final Exam Solution [Choice A is the correct
... A) Thermal energy that is transferred from one substance to another is called heat. B) The temperature of the melting point is the same as the temperature of vaporization point for a substance. C) All changes of state involve a change in color. D) The change of state from a gas to a liquid is called ...
... A) Thermal energy that is transferred from one substance to another is called heat. B) The temperature of the melting point is the same as the temperature of vaporization point for a substance. C) All changes of state involve a change in color. D) The change of state from a gas to a liquid is called ...
Lab: Millikan`s Oil Drop Experiment and Elements of the Periodic Table
... In the early 1900’s (1908-1917) an American physicist named Robert Millikan devised a method of determining the charge on an electron. This experiment is known as Millikan’s oil drop experiment. Earlier, an English scientist named J.J. Thomson used a device known as a cathode ray tube to determine t ...
... In the early 1900’s (1908-1917) an American physicist named Robert Millikan devised a method of determining the charge on an electron. This experiment is known as Millikan’s oil drop experiment. Earlier, an English scientist named J.J. Thomson used a device known as a cathode ray tube to determine t ...
Answer Key Physics Study Guide A
... Know how color affects heat absorption Dark colors absorb more heat than light colors g. Analyze and measure power. P=W/t; the faster something does work, the more powerful it is. ...
... Know how color affects heat absorption Dark colors absorb more heat than light colors g. Analyze and measure power. P=W/t; the faster something does work, the more powerful it is. ...
02mc
... B. False. If the star is approaching the earth, wavelength should decrease and the observed spectra should shift toward the violet end. C. False. Same as A. D. True. Light sources on the spinning star are moving with different velocities, which depend on how far away the sources from the rotating ax ...
... B. False. If the star is approaching the earth, wavelength should decrease and the observed spectra should shift toward the violet end. C. False. Same as A. D. True. Light sources on the spinning star are moving with different velocities, which depend on how far away the sources from the rotating ax ...
Physics Lab Exam - La Salle University
... height 88 cm. One end of a string is attached to the block and the other end to hanger. A range of masses can be placed on the hanger without setting the system into motion. Draw all the forces acting on the block in each scenario. Draw the forces acting on the hanger. Fil in the table below. Normal ...
... height 88 cm. One end of a string is attached to the block and the other end to hanger. A range of masses can be placed on the hanger without setting the system into motion. Draw all the forces acting on the block in each scenario. Draw the forces acting on the hanger. Fil in the table below. Normal ...
Physics 103 Hour Exam #3 Solution Point values are given for each
... (a) How could Anderson tell that this particle was a positron rather than an electron? Give a brief answer. (Hint: another way to ask this question is: how would the track be different if it were due to an electron? Make a reasonable assumption about how the apparatus was set up.) If the particle w ...
... (a) How could Anderson tell that this particle was a positron rather than an electron? Give a brief answer. (Hint: another way to ask this question is: how would the track be different if it were due to an electron? Make a reasonable assumption about how the apparatus was set up.) If the particle w ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... a force that is equal in strength and opposite in direction they cancel each other out so the force = 0 Newtons results in no motion o What is an unbalanced force? a force that is unequal and moves towards the stronger force if the forces (arrows) are going in the same direction add the ...
... a force that is equal in strength and opposite in direction they cancel each other out so the force = 0 Newtons results in no motion o What is an unbalanced force? a force that is unequal and moves towards the stronger force if the forces (arrows) are going in the same direction add the ...
Document
... Friction is a term used to describe forces that result from the relative motion between objects. Simply defined, friction is a force that opposes motion. Friction is caused by two surfaces rubbing against one another. The amount of friction depends on the smoothness or roughness of the surfaces. Thi ...
... Friction is a term used to describe forces that result from the relative motion between objects. Simply defined, friction is a force that opposes motion. Friction is caused by two surfaces rubbing against one another. The amount of friction depends on the smoothness or roughness of the surfaces. Thi ...
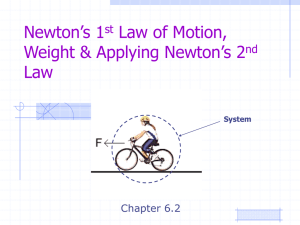
Newton`s Laws
... So, what happens if you are trying to see how fast a force can accelerate a particular mass?? The equation for acceleration is: a=F m But does the equation make sense?? What happens to the acceleration of a bicycle if the force is ...
... So, what happens if you are trying to see how fast a force can accelerate a particular mass?? The equation for acceleration is: a=F m But does the equation make sense?? What happens to the acceleration of a bicycle if the force is ...
Module 11 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... Note that the time of maximum jerk, the acceleration at this time, and the position at this time all depend on the mass of the electron and the force it experiences. The force depends on the electron’s charge and the size of electric field that does the accelerating. What is interesting is that the ...
... Note that the time of maximum jerk, the acceleration at this time, and the position at this time all depend on the mass of the electron and the force it experiences. The force depends on the electron’s charge and the size of electric field that does the accelerating. What is interesting is that the ...
Module 11
... Note that the time of maximum jerk, the acceleration at this time, and the position at this time all depend on the mass of the electron and the force it experiences. The force depends on the electron’s charge and the size of electric field that does the accelerating. What is interesting is that the ...
... Note that the time of maximum jerk, the acceleration at this time, and the position at this time all depend on the mass of the electron and the force it experiences. The force depends on the electron’s charge and the size of electric field that does the accelerating. What is interesting is that the ...
AP Physics B Content Outline
... multiply force * distance on each object and add all objects together on each side of meter stick You will be solving for distance to the object or the weight of the object Be careful whether you are solving for mass or weight and what the question is asking for Pulleys the larger weight will be m ...
... multiply force * distance on each object and add all objects together on each side of meter stick You will be solving for distance to the object or the weight of the object Be careful whether you are solving for mass or weight and what the question is asking for Pulleys the larger weight will be m ...
The Rocket Equation!!
... Space Shuttle Columbia’s engine ejects mass at a rate of 30 kg/s with an exhaust velocity of 3,100 m/s. The pressure at the nozzle exit is 5 kPa and the exit area is 0.7 m2. The mass of the shuttle solids (not including fuel) is about 500,000 kilograms. Find the acceleration of the rocket. ...
... Space Shuttle Columbia’s engine ejects mass at a rate of 30 kg/s with an exhaust velocity of 3,100 m/s. The pressure at the nozzle exit is 5 kPa and the exit area is 0.7 m2. The mass of the shuttle solids (not including fuel) is about 500,000 kilograms. Find the acceleration of the rocket. ...
SEPT 19 HPS
... The electric motor of a model train accelerates the train from rest to 0.620 m/s in 21.0 ms. The total mass of the train is 875 g. Find the average power delivered to the train during the acceleration. ...
... The electric motor of a model train accelerates the train from rest to 0.620 m/s in 21.0 ms. The total mass of the train is 875 g. Find the average power delivered to the train during the acceleration. ...