Wave theory of positive and negative electrons - Neo
... Proca – On the undulatory theory of positive and negative electrons ...
... Proca – On the undulatory theory of positive and negative electrons ...
Indian National Physics Olympiad – 2014 - HBCSE
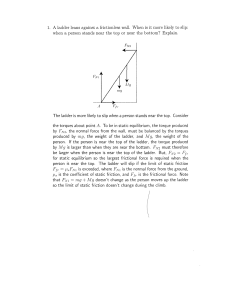
... (d) In the figure below mark the approximate locations of the equilibrium point(s) for this system. Justify your answer. Solution: For small δ force on the test charge is upwards while for large δ (eg. at D) force is downwards. So there is a neutral point between O and D. By symmetry there will be n ...
... (d) In the figure below mark the approximate locations of the equilibrium point(s) for this system. Justify your answer. Solution: For small δ force on the test charge is upwards while for large δ (eg. at D) force is downwards. So there is a neutral point between O and D. By symmetry there will be n ...
Torque and Motion Relationships
... What is the COM and why is it important? • What is COM (or COG) and why is it important? – It simplifies mechanical analysis of a complicated system – It is the point at which all of the mass of the system may be considered to be located – It is the only point that represents movement of the total ...
... What is the COM and why is it important? • What is COM (or COG) and why is it important? – It simplifies mechanical analysis of a complicated system – It is the point at which all of the mass of the system may be considered to be located – It is the only point that represents movement of the total ...
Document
... The atomic weight of an element is the weighted average of the masses of its stable isotopes Example 5-2: Naturally occurring Cu consists of 2 isotopes. It is 69.1% 63Cu with a mass of 62.9 amu, and 30.9% 65Cu, which has a mass of 64.9 amu. Calculate the atomic weight of Cu to one ...
... The atomic weight of an element is the weighted average of the masses of its stable isotopes Example 5-2: Naturally occurring Cu consists of 2 isotopes. It is 69.1% 63Cu with a mass of 62.9 amu, and 30.9% 65Cu, which has a mass of 64.9 amu. Calculate the atomic weight of Cu to one ...
A2 Force and Momentum
... A golf club undergoes an inelastic collision with a golf ball and gives it an initial velocity of 60 m s–1. The ball is in contact with the club for 15 ms and the mass of the ball is 4.5 × 10–2 kg. (a) ...
... A golf club undergoes an inelastic collision with a golf ball and gives it an initial velocity of 60 m s–1. The ball is in contact with the club for 15 ms and the mass of the ball is 4.5 × 10–2 kg. (a) ...
10 Mass Spectrometry
... The superposition of U0 and −U0 at positive and negative eclectrodes, respectively, creates a hyperbolic field symmetric with respect to the z-direction (this is not axial symmetry; the z axis is a four fold symmetry axis for a rotary reflection). The equation of motion is described by the Mattieu d ...
... The superposition of U0 and −U0 at positive and negative eclectrodes, respectively, creates a hyperbolic field symmetric with respect to the z-direction (this is not axial symmetry; the z axis is a four fold symmetry axis for a rotary reflection). The equation of motion is described by the Mattieu d ...
Subtle is the Gravity - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... it can be removed locally as demonstrated by Galileo’s famous experiment of the leaning tower of Pisa. All particles share the two properties, one inertia and other linkage to gravity (gravitational charge). The only one universal parameter available is mass (energy) for all particles. Thus the meas ...
... it can be removed locally as demonstrated by Galileo’s famous experiment of the leaning tower of Pisa. All particles share the two properties, one inertia and other linkage to gravity (gravitational charge). The only one universal parameter available is mass (energy) for all particles. Thus the meas ...