Rotational Motion Practice Test Fill in symbol and units Linear
... a) Find the center of mass of the two objects. b) An additional mass mC = 5.0 kg would need to be located where in order to move the center of mass to the origin? 11) A 3.0 m-long bamboo fishing rod of negligible mass is pivoted at one end, and F = ? held in equilibrium by a 21 N-horizontal 21 N for ...
... a) Find the center of mass of the two objects. b) An additional mass mC = 5.0 kg would need to be located where in order to move the center of mass to the origin? 11) A 3.0 m-long bamboo fishing rod of negligible mass is pivoted at one end, and F = ? held in equilibrium by a 21 N-horizontal 21 N for ...
Electrostatics
... The Nature of Electric Charge Discovery of charge The Greeks first noticed electric charges by rubbing amber with fur. In Greek, “elektron” means amber, and “atomos” means indivisible. Charges are arbitrarily called positive and negative. In most cases, only the negative charge is mobile. Propertie ...
... The Nature of Electric Charge Discovery of charge The Greeks first noticed electric charges by rubbing amber with fur. In Greek, “elektron” means amber, and “atomos” means indivisible. Charges are arbitrarily called positive and negative. In most cases, only the negative charge is mobile. Propertie ...
charge
... The Nature of Electric Charge Discovery of charge The Greeks first noticed electric charges by rubbing amber with fur. In Greek, “elektron” means amber, and “atomos” means indivisible. Charges are arbitrarily called positive and negative. In most cases, only the negative charge is mobile. Propertie ...
... The Nature of Electric Charge Discovery of charge The Greeks first noticed electric charges by rubbing amber with fur. In Greek, “elektron” means amber, and “atomos” means indivisible. Charges are arbitrarily called positive and negative. In most cases, only the negative charge is mobile. Propertie ...
Chapter 23 – Electric Fields
... Electric Potential Energy describes how easy or difficult moving two charges together or apart is. If the electric potential energy is zero then that means there is no force acting on a charge at all. In each of the following situations describe if the potential energy is increased or decreased by t ...
... Electric Potential Energy describes how easy or difficult moving two charges together or apart is. If the electric potential energy is zero then that means there is no force acting on a charge at all. In each of the following situations describe if the potential energy is increased or decreased by t ...
relative - Purdue Physics
... into a particle of mass m0 • It is possible to convert a particle of mass m0 into an amount of energy (m0c2) • The principle of conservation of energy must be extended to include this type of energy ...
... into a particle of mass m0 • It is possible to convert a particle of mass m0 into an amount of energy (m0c2) • The principle of conservation of energy must be extended to include this type of energy ...
Phys 102 * Lecture 2
... Which configuration has a higher electric potential energy? A. Case A has a higher E.P.E. B. Case B has a higher E.P.E. C. Both have the same E.P.E. ...
... Which configuration has a higher electric potential energy? A. Case A has a higher E.P.E. B. Case B has a higher E.P.E. C. Both have the same E.P.E. ...
Work and Kinetic Energy
... Work and Kinetic Energy - Another Bridge between the World of Motion and the World of Forces - The Work-Energy Theorem - Work ...
... Work and Kinetic Energy - Another Bridge between the World of Motion and the World of Forces - The Work-Energy Theorem - Work ...
Chapter 20: Electric Potential and Capacitance
... 3. (i) In a certain region of space, the electric potential is zero everywhere along the x axis. From this information, we can conclude that the x component of the electric field in this region is (a) zero, (b) in the +x direction, or (c) in the −x direction. (ii) In a certain region of space, the e ...
... 3. (i) In a certain region of space, the electric potential is zero everywhere along the x axis. From this information, we can conclude that the x component of the electric field in this region is (a) zero, (b) in the +x direction, or (c) in the −x direction. (ii) In a certain region of space, the e ...
A STRAIGHTFORWARD SET UP OF
... which strikingly turns out to be the exact Dirac solution were (the second term at the RHS of Eq.(31) neglected, and) the spin-orbit interaction not taken into account [1]. We can right away estimate that, in this case the magnitude of E R is larger than that of the corresponding Schrodinger eigenv ...
... which strikingly turns out to be the exact Dirac solution were (the second term at the RHS of Eq.(31) neglected, and) the spin-orbit interaction not taken into account [1]. We can right away estimate that, in this case the magnitude of E R is larger than that of the corresponding Schrodinger eigenv ...
Force, Mass, and Acceleration
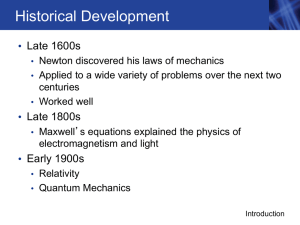
... of Natural Philosophy) in 1687. In his work, he described three ideas about motion that are now known as Newton’s Laws of Motion. First Law: Law of Inertia An object at rest will remain at rest until an unbalanced force causes it to move. An object in motion will continue moving at the same speed an ...
... of Natural Philosophy) in 1687. In his work, he described three ideas about motion that are now known as Newton’s Laws of Motion. First Law: Law of Inertia An object at rest will remain at rest until an unbalanced force causes it to move. An object in motion will continue moving at the same speed an ...
Document
... 4. Statement (1) is correct, because terminal voltage is V = E – Ir, now a resistor is added in parallel, so equivalent resistance decreases, so current increases, so terminal p.d. decreases. Statement (2) is correct as explained above. Statement (3) is incorrect because terminal p.d decreases, so c ...
... 4. Statement (1) is correct, because terminal voltage is V = E – Ir, now a resistor is added in parallel, so equivalent resistance decreases, so current increases, so terminal p.d. decreases. Statement (2) is correct as explained above. Statement (3) is incorrect because terminal p.d decreases, so c ...
File
... -explain why to change an object’s energy a force must be exerted parallel to the field -identify if potential energy increases or decreases when given a scenario -compare original energy to new energy (E : E’) 32. use the Law of Conservation of Energy to determine the conversion of electric potenti ...
... -explain why to change an object’s energy a force must be exerted parallel to the field -identify if potential energy increases or decreases when given a scenario -compare original energy to new energy (E : E’) 32. use the Law of Conservation of Energy to determine the conversion of electric potenti ...
Worked Example A Cylinder Rolling Down a Slope
... is not to say about a point moving down the slope – which would not be “safe” – but rather about a point fixed in the body on the circumference of the cylinder. At each time t we choose that point which will, instantaneously, be at the contact point (so we are considering different points in the bod ...
... is not to say about a point moving down the slope – which would not be “safe” – but rather about a point fixed in the body on the circumference of the cylinder. At each time t we choose that point which will, instantaneously, be at the contact point (so we are considering different points in the bod ...