Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
... • To divide fractions: Invert the second fraction then multiply: 1/2 ÷ 3/5 = 1/2 x 5/3 = 5/6 • To divide mixed numbers, change to a fraction first • A prime number has only two unique factors, 1 and itself – Every composite number can be factored by primes – Primes are useful for simplifying fractio ...
... • To divide fractions: Invert the second fraction then multiply: 1/2 ÷ 3/5 = 1/2 x 5/3 = 5/6 • To divide mixed numbers, change to a fraction first • A prime number has only two unique factors, 1 and itself – Every composite number can be factored by primes – Primes are useful for simplifying fractio ...
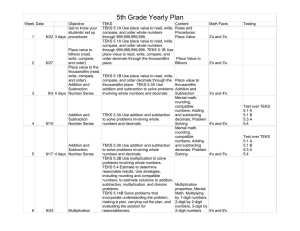
SpringBoard Math Unit- At-a-Glance– Course 1: Common Core
... standing for numbers. For example, express the calculation “Subtract y from 5” as 5 − y. 6.EE.A.2b Identify parts of an expression using mathematical terms (sum, term, product, factor, quotient, coefficient); view one or more parts of an expression as a single entity. For example, describe the expre ...
... standing for numbers. For example, express the calculation “Subtract y from 5” as 5 − y. 6.EE.A.2b Identify parts of an expression using mathematical terms (sum, term, product, factor, quotient, coefficient); view one or more parts of an expression as a single entity. For example, describe the expre ...
goa board of sec
... (C) Without performing the long division method, determine whether the rational number 17 has a terminating or non - terminating decimal ...
... (C) Without performing the long division method, determine whether the rational number 17 has a terminating or non - terminating decimal ...
Chapter`s 1 and 2 lecture handout
... a. Leading zeros are zeros that precede all the nonzero digits. These do not count as significant figures. b. Captive zeros are zeros between nonzero digits. These always count as significant figures. c. Trailing zeros are zeros at the right end of the number. They are significant only if the number ...
... a. Leading zeros are zeros that precede all the nonzero digits. These do not count as significant figures. b. Captive zeros are zeros between nonzero digits. These always count as significant figures. c. Trailing zeros are zeros at the right end of the number. They are significant only if the number ...
General Education Mathematics MAT 125 Daily Schedule F2014
... 1.1 Reasoning Activities; Write one list of numbers that has two patterns so that the next number in the list can be 15 and the next number in that same list can be 20. (p.12 #72) 1.1 Label each statement as inductive or deductive reasoning. (*Problem Solving Unit; Inductive and Deductive Reason ...
... 1.1 Reasoning Activities; Write one list of numbers that has two patterns so that the next number in the list can be 15 and the next number in that same list can be 20. (p.12 #72) 1.1 Label each statement as inductive or deductive reasoning. (*Problem Solving Unit; Inductive and Deductive Reason ...
Describe a scatter with a negative correlation
... the end of the cleaner, so beads do not fall off. Put 2 blue beads on other side and fold just the end of the cleaner, so beads do not fall off. ...
... the end of the cleaner, so beads do not fall off. Put 2 blue beads on other side and fold just the end of the cleaner, so beads do not fall off. ...
Fibonacci Numbers ANSWERS
... always work for picking the right Fibonacci numbers to add up to the numbers? Write one or two sentences to explain how you could find the numbers to add. One possible answer: Try to start with the largest possible Fibonacci number. Standards: Patterns, number theory, communication ...
... always work for picking the right Fibonacci numbers to add up to the numbers? Write one or two sentences to explain how you could find the numbers to add. One possible answer: Try to start with the largest possible Fibonacci number. Standards: Patterns, number theory, communication ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.