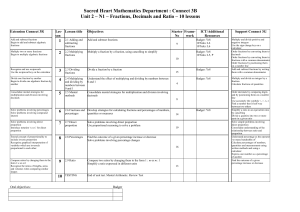
Middletown Public Schools Mathematics Unit Planning Organizer
... a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step “how many more” and “how many less” problems using information presented in scaled bar graphs. For example, draw a bar graph in which each square in the bar graph might represent 5 pets. Grade 3 Unit 1 Understanding Multiplication and Divis ...
... a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step “how many more” and “how many less” problems using information presented in scaled bar graphs. For example, draw a bar graph in which each square in the bar graph might represent 5 pets. Grade 3 Unit 1 Understanding Multiplication and Divis ...
Patterns Lesson - Gordon State College
... Gauss was given as a young student. In late 18th-century Germany, a teacher gave a class the following arithmetic problem: 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + . . . + 98 + 99 + 100. The student who first got the answer was to lay his slate on the table. The teacher had barely announced the problem when Karl laid his sl ...
... Gauss was given as a young student. In late 18th-century Germany, a teacher gave a class the following arithmetic problem: 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + . . . + 98 + 99 + 100. The student who first got the answer was to lay his slate on the table. The teacher had barely announced the problem when Karl laid his sl ...
Unit 2 - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... Calculate fractions of quantities Order decimals by comparing digits and by positioning them on a number line Use accurately the symbols <, >, , Find a number that is half way between two others Simplify a ratio to an equivalent ratio by cancelling Divide a quantity into two or more parts in a gi ...
... Calculate fractions of quantities Order decimals by comparing digits and by positioning them on a number line Use accurately the symbols <, >, , Find a number that is half way between two others Simplify a ratio to an equivalent ratio by cancelling Divide a quantity into two or more parts in a gi ...
review material
... The 1’s-complement of a binary number is found by simply inverting each bit. Finding the 2’s-complement is important since it allows us to negate a number and is the method used by most Arithmetic and Logic Units (ALUs) for subtracting. There are two easy ways to find the 2’s-complement: 1. Find the ...
... The 1’s-complement of a binary number is found by simply inverting each bit. Finding the 2’s-complement is important since it allows us to negate a number and is the method used by most Arithmetic and Logic Units (ALUs) for subtracting. There are two easy ways to find the 2’s-complement: 1. Find the ...
Notes 9 - wellsclass
... When the difference between successive terms of a sequence is always the same number, the sequence is called arithmetic. An Arithmetic sequence may be defined recursively as a1 =a, an-an-1 = d or as a1 =a, an= an-1 +d where a=a1 and d are real numbers. The number a is the first term and the number d ...
... When the difference between successive terms of a sequence is always the same number, the sequence is called arithmetic. An Arithmetic sequence may be defined recursively as a1 =a, an-an-1 = d or as a1 =a, an= an-1 +d where a=a1 and d are real numbers. The number a is the first term and the number d ...
Edited to include ordering 5 numbers: Ordering Numbers
... them one of the Ordering Numbers Cards. Have them write their numbers on their whiteboards and convert the numbers to decimal form, if they are not already in that form. Then, direct the five students to line up in the order of their numbers from smallest to largest, displaying their numbers. 2. Hol ...
... them one of the Ordering Numbers Cards. Have them write their numbers on their whiteboards and convert the numbers to decimal form, if they are not already in that form. Then, direct the five students to line up in the order of their numbers from smallest to largest, displaying their numbers. 2. Hol ...
Math 2
... Fluency Recommendations Functions: Fluency in graphing functions (including linear, quadratic, and exponential) and interpreting key features of the graphs in terms of their function rules and a table of value, as well as recognizing a relationship (including a relationship within a data set), fits ...
... Fluency Recommendations Functions: Fluency in graphing functions (including linear, quadratic, and exponential) and interpreting key features of the graphs in terms of their function rules and a table of value, as well as recognizing a relationship (including a relationship within a data set), fits ...
Guided notes: Scientific notation
... 1) First, move the decimal after the first whole number: 3 2 5 8. (use arrows to show how you move the decimal) 2) Second, add your multiplication sign and your base (10). 3 . 2 5 8 x 10 3) Count how many spaces the decimal moved and this is the exponent. 3 . 2 5 8 x 10 (add the correct exponent) Tr ...
... 1) First, move the decimal after the first whole number: 3 2 5 8. (use arrows to show how you move the decimal) 2) Second, add your multiplication sign and your base (10). 3 . 2 5 8 x 10 3) Count how many spaces the decimal moved and this is the exponent. 3 . 2 5 8 x 10 (add the correct exponent) Tr ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.