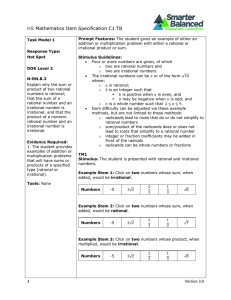
Sequences, Series, and the Binomial Theorem
... One interesting example is the Fibonacci sequence. The first two numbers in the Fibonacci sequence are 1, and each successive term is the sum of the previous two. Therefore, the general term is expressed in terms of the previous two as follows: ...
... One interesting example is the Fibonacci sequence. The first two numbers in the Fibonacci sequence are 1, and each successive term is the sum of the previous two. Therefore, the general term is expressed in terms of the previous two as follows: ...
NS8-1 Factors and Multiples
... Two numbers are called consecutive if one number is the next number after the other. Example: 13 and 14 are consecutive because 14 is the next number after 13. ...
... Two numbers are called consecutive if one number is the next number after the other. Example: 13 and 14 are consecutive because 14 is the next number after 13. ...
Rational Numbers.pmd
... • If the numerator and denominator of a rational number are multiplied or divided by a non-zero integer, we get a rational number which is said to be equivalent to the given rational number. • Rational numbers are classified as positive, zero or negative rational numbers. When the numerator and deno ...
... • If the numerator and denominator of a rational number are multiplied or divided by a non-zero integer, we get a rational number which is said to be equivalent to the given rational number. • Rational numbers are classified as positive, zero or negative rational numbers. When the numerator and deno ...
ppt
... • Not So Simple Case: If denominator is not an exponent of 2. • Then we can’t represent number precisely, but that’s why we have so many bits in significand: for precision • Once we have significand, normalizing a number to get the exponent is easy. • So how do we get the significand of a never-endi ...
... • Not So Simple Case: If denominator is not an exponent of 2. • Then we can’t represent number precisely, but that’s why we have so many bits in significand: for precision • Once we have significand, normalizing a number to get the exponent is easy. • So how do we get the significand of a never-endi ...
Complexity of Mergesort
... • Since the sum is stored in a finite memory space, at some point the terms to be added will be much smaller than the sum itself. • If the sum is stored in a float, which has about 7 significant digits, a term of about 1x10-8 would not be significant. So, i would be about 108 - that’s a lot of itera ...
... • Since the sum is stored in a finite memory space, at some point the terms to be added will be much smaller than the sum itself. • If the sum is stored in a float, which has about 7 significant digits, a term of about 1x10-8 would not be significant. So, i would be about 108 - that’s a lot of itera ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.