Here - Math-Boise State
... my minimal assumptions; you may assume standard algebra rules. You may also do inductions that start at 0, and reason in contexts involving integers and rational numbers, as usual. 3. State the definition of what it means for a natural number n to be the smallest element of a set A of natural number ...
... my minimal assumptions; you may assume standard algebra rules. You may also do inductions that start at 0, and reason in contexts involving integers and rational numbers, as usual. 3. State the definition of what it means for a natural number n to be the smallest element of a set A of natural number ...
Chapter 2: Integers - Independent School District 196
... the x-coordinate represents how far to move right or left and the y-coordinate represents how far to move up or down. What exhibit is located at (6, 5)? ...
... the x-coordinate represents how far to move right or left and the y-coordinate represents how far to move up or down. What exhibit is located at (6, 5)? ...
equivalent fractions
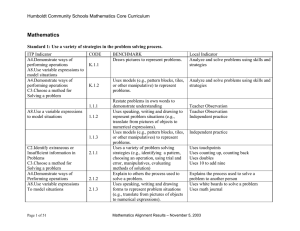
... NS2.4 Determine the least common multiple and the greatest common divisor of whole numbers; use them to solve problems with fractions (e.g. to find a common denominator to add two fractions or to find the reduced form of a fraction). Also covered: NS1.1 ...
... NS2.4 Determine the least common multiple and the greatest common divisor of whole numbers; use them to solve problems with fractions (e.g. to find a common denominator to add two fractions or to find the reduced form of a fraction). Also covered: NS1.1 ...
Document
... MA.912.A.3.4 Solve and graph simple…inequalities in one variable and be able to justify each step in a solution. Also MA.912.A.3.5, MA.912.A.10.2. ...
... MA.912.A.3.4 Solve and graph simple…inequalities in one variable and be able to justify each step in a solution. Also MA.912.A.3.5, MA.912.A.10.2. ...
EE332 Lecture 2 PowerPoint Slides
... sign of result depends on sign of number with the larger magnitude. This is what we do in base 10. ...
... sign of result depends on sign of number with the larger magnitude. This is what we do in base 10. ...
Document
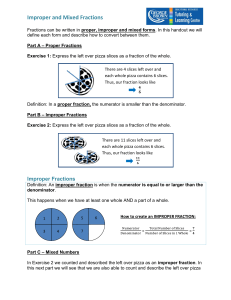
... Multiply Fractions and Whole Numbers When multiplying a fraction by a whole number, the order of the factors does not change the product. This is true for any numbers and is an example of the ...
... Multiply Fractions and Whole Numbers When multiplying a fraction by a whole number, the order of the factors does not change the product. This is true for any numbers and is an example of the ...
Rational Numbers
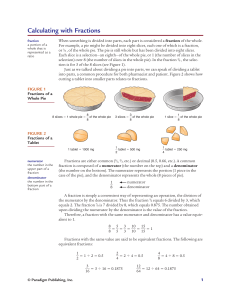
... where the numerator is either 0 or a positive integer and the denominator, a positive integer. You compared two fractions, found their equivalent forms and studied all the four basic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division on them. In this Chapter, we shall extend the number ...
... where the numerator is either 0 or a positive integer and the denominator, a positive integer. You compared two fractions, found their equivalent forms and studied all the four basic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division on them. In this Chapter, we shall extend the number ...
Comparing Fractions and Decimals by: April
... Comparing Fractions and Decimals In order to compare fractions and decimals, you have to use all of the skills you have learned and reviewed in this session. You can not compare fractions and decimals. You have to convert them all to either fractions or all to decimals. ...
... Comparing Fractions and Decimals In order to compare fractions and decimals, you have to use all of the skills you have learned and reviewed in this session. You can not compare fractions and decimals. You have to convert them all to either fractions or all to decimals. ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.