Huffman PowerPoint Slides - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... – Barlow’s therapy includes a combination of breathing re-training, cognitive interventions, and exposure to the internal cues that elicit panic. Patient learns to relax and reinterpret these sensations as nonthreatening and controllable ...
... – Barlow’s therapy includes a combination of breathing re-training, cognitive interventions, and exposure to the internal cues that elicit panic. Patient learns to relax and reinterpret these sensations as nonthreatening and controllable ...
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY OF CHILDREN AND FAMILY
... Feeling of detachment or estrangement from others Losing interest in activities that used to give you pleasure Persistent symptoms of increased anxiety, such as difficulty falling or staying asleep, difficulty concentrating ...
... Feeling of detachment or estrangement from others Losing interest in activities that used to give you pleasure Persistent symptoms of increased anxiety, such as difficulty falling or staying asleep, difficulty concentrating ...
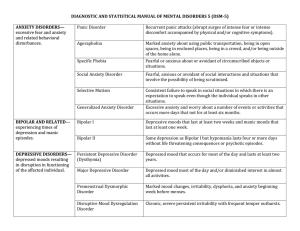
Major Disorders as Defined by DSM-5
... Multiple motor and one or more vocal tics. Deficits in general mental abilities such as reasoning, problem solving, planning, abstract thinking, judgment, academic learning, and learning ...
... Multiple motor and one or more vocal tics. Deficits in general mental abilities such as reasoning, problem solving, planning, abstract thinking, judgment, academic learning, and learning ...
Phobic disorders
... problems (difficulties in interactions with other students/oral presentations), or vocational problems (work in less demanding jobs, well below their abilities). Thoughts of suicide are relatively common. ...
... problems (difficulties in interactions with other students/oral presentations), or vocational problems (work in less demanding jobs, well below their abilities). Thoughts of suicide are relatively common. ...
Mental Disorders
... Ax murderer who goes from house to house chopping people up because of some early childhood experience shows little grasp of reality. ...
... Ax murderer who goes from house to house chopping people up because of some early childhood experience shows little grasp of reality. ...
Anxiety disorder
... possibly subjected to the critical eye of others. Social phobia can be subdivided into specific forms in which the fear is connected to a specific situation, such as stage fright, and in a general form in which the fear manifests in a variety of situations. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Recurrent a ...
... possibly subjected to the critical eye of others. Social phobia can be subdivided into specific forms in which the fear is connected to a specific situation, such as stage fright, and in a general form in which the fear manifests in a variety of situations. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Recurrent a ...
Understanding Anxiety Disorders
... biological and psychological factors, as well as exposure to challenging situations earlier in life. ...
... biological and psychological factors, as well as exposure to challenging situations earlier in life. ...
Anxiety Disorders
... Obsessions or compulsions or both defined by: Obsessions defined by: recurrent and persistent thoughts, impulses or images that are intrusive and unwanted that cause marked anxiety or distress The person attempts to ignore or suppress such thoughts, urges or images, or to neutralize them with ...
... Obsessions or compulsions or both defined by: Obsessions defined by: recurrent and persistent thoughts, impulses or images that are intrusive and unwanted that cause marked anxiety or distress The person attempts to ignore or suppress such thoughts, urges or images, or to neutralize them with ...
Impulse Control Disorders - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery
... (2) impaired personal, social, educational, and occupational functioning as consequence of gambling; (3) overly determined, out-of-control quality that drives, perpetuates, and escalates gambling despite derivative functional impairment and adverse consequences. patients often attempt unsuccessful ...
... (2) impaired personal, social, educational, and occupational functioning as consequence of gambling; (3) overly determined, out-of-control quality that drives, perpetuates, and escalates gambling despite derivative functional impairment and adverse consequences. patients often attempt unsuccessful ...
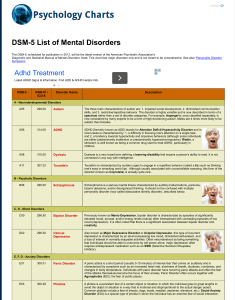
DSM-5 - KVCC Docs
... an awareness of the detachment. To someone experiencing depersonalization, the external world feels strange and unreal and a person can even get the sense that they are watching themselves from a third person perspective. However, unlike in psychosis, the individual remains very much aware of their ...
... an awareness of the detachment. To someone experiencing depersonalization, the external world feels strange and unreal and a person can even get the sense that they are watching themselves from a third person perspective. However, unlike in psychosis, the individual remains very much aware of their ...
Working with youth who have ED/BD diagnoses
... public transportation, being in open spaces, enclosed spaces, being in a crowd, standing in line, being outside of home alone (fear escape might be difficult) ...
... public transportation, being in open spaces, enclosed spaces, being in a crowd, standing in line, being outside of home alone (fear escape might be difficult) ...
SYSTEMATIC ASSESSMENT OF CO
... M – Medical – including iron deficiency, poor nutrition, hearing/vision impairment, seizure disorder, head injury, drug/alcohol abuse, iatrogenic D – Depression – including depression, mood disorder For some children, the comorbid condition may be equally or more impairing than the ADHD. For example ...
... M – Medical – including iron deficiency, poor nutrition, hearing/vision impairment, seizure disorder, head injury, drug/alcohol abuse, iatrogenic D – Depression – including depression, mood disorder For some children, the comorbid condition may be equally or more impairing than the ADHD. For example ...
Factors associated with poor response in cognitive
... response (56%, 53%, and 39%, respectively). Others have also shown that the presence of a comorbid tic disorder negatively impacts pharmacotherapy response but not CBT response (Grados & Riddle, 2008; March et al., 2007; McDougle et al., 1993). Symptom Presentation OCD varies from other anxiety diso ...
... response (56%, 53%, and 39%, respectively). Others have also shown that the presence of a comorbid tic disorder negatively impacts pharmacotherapy response but not CBT response (Grados & Riddle, 2008; March et al., 2007; McDougle et al., 1993). Symptom Presentation OCD varies from other anxiety diso ...
Anorexia Nervosa
... - Provides link between perceptive and cognitive brain regions 2. Bridge between left and right hemispheres 3. Social emotion and the sense of self. -Sensory homunculi - Every person has somatotopic representation of a body map in their mind. This is called a sensory homunculi. Sensory homunculi hav ...
... - Provides link between perceptive and cognitive brain regions 2. Bridge between left and right hemispheres 3. Social emotion and the sense of self. -Sensory homunculi - Every person has somatotopic representation of a body map in their mind. This is called a sensory homunculi. Sensory homunculi hav ...
10:30 AM Anxiety - Vanderbilt University Medical Center
... • Tolerance to the antianxiety effects is low • Rates of dependency are high with chronic use ...
... • Tolerance to the antianxiety effects is low • Rates of dependency are high with chronic use ...
Panic Disorder - Cloudfront.net
... situations), Specific Phobia (e.g., on exposure to a specific phobic situation), Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (e.g., on exposure to dirt in someone with an obsession about contamination), Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (e.g., in response to stimuli associated with a severe stressor), or Separation A ...
... situations), Specific Phobia (e.g., on exposure to a specific phobic situation), Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (e.g., on exposure to dirt in someone with an obsession about contamination), Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (e.g., in response to stimuli associated with a severe stressor), or Separation A ...
SEPTA Anxiety Mental Health Concerns_March 2016
... Anxiety Disorders: Symptoms ● Excessive anxiety, worry, or fear that markedly exceeds the level for the student’s stage of development. ● High level of motor tension such as restlessness, tiredness, shakiness, or muscle tension. ● Autonomic hyperactivity such as rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath ...
... Anxiety Disorders: Symptoms ● Excessive anxiety, worry, or fear that markedly exceeds the level for the student’s stage of development. ● High level of motor tension such as restlessness, tiredness, shakiness, or muscle tension. ● Autonomic hyperactivity such as rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath ...
Abnormal and treatment
... other twin has one. Drops to 15% for fraternal twins (Also known as concordance rate) Kagan studies temperament – found roughly 15-20% of infants display an inhibited temperament, characterized by shyness, timidity, and wariness. This temperament is a risk factor for anxiety disorders. Especially fo ...
... other twin has one. Drops to 15% for fraternal twins (Also known as concordance rate) Kagan studies temperament – found roughly 15-20% of infants display an inhibited temperament, characterized by shyness, timidity, and wariness. This temperament is a risk factor for anxiety disorders. Especially fo ...
PsychAP Notes pt 11
... Thoughts on disorders: PTSD and GAD have similarities. They are both hyper-vigilant but one literally lives through an event. For PTSD there is an exaggerated startled response. There are no panic attacks in GAD, only excessive worrying, with no previous trauma. With OCD the acts and thoughts reduce ...
... Thoughts on disorders: PTSD and GAD have similarities. They are both hyper-vigilant but one literally lives through an event. For PTSD there is an exaggerated startled response. There are no panic attacks in GAD, only excessive worrying, with no previous trauma. With OCD the acts and thoughts reduce ...
CBT - ETSU.edu
... pediatric population for several reasons. For one thing, fears and worries are common in healthy children. Normal, developmentally appropriate worries, fears, and shyness can be difficult to distinguish from anxiety disorders. For diagnosis, worries and fears must persist and must lead to impaired f ...
... pediatric population for several reasons. For one thing, fears and worries are common in healthy children. Normal, developmentally appropriate worries, fears, and shyness can be difficult to distinguish from anxiety disorders. For diagnosis, worries and fears must persist and must lead to impaired f ...
Psychological Disorders
... - person cannot identify its cause; the anxiety is “free-floating” B. Panic Disorder - a disorder marked by a minutes-long episode of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations. Sufferers often report they feel like they a ...
... - person cannot identify its cause; the anxiety is “free-floating” B. Panic Disorder - a disorder marked by a minutes-long episode of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations. Sufferers often report they feel like they a ...
Psych Disorder Notes
... - person cannot identify its cause; the anxiety is “free-floating” B. Panic Disorder - a disorder marked by a minutes-long episode of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations. Sufferers often report they feel like they a ...
... - person cannot identify its cause; the anxiety is “free-floating” B. Panic Disorder - a disorder marked by a minutes-long episode of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations. Sufferers often report they feel like they a ...
Chapter 14- Abnormal Behavior
... Dissociative Amnesia: sudden loss of memory for personal information that is not due to normal forgetfulness • Fugue: forming a new identity ...
... Dissociative Amnesia: sudden loss of memory for personal information that is not due to normal forgetfulness • Fugue: forming a new identity ...
Obsessive–compulsive disorder

Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental disorder where people feel the need to check things repeatedly, have certain thoughts repeatedly, or feel they need to perform certain routines repeatedly. People are unable to control either the thoughts or the activities. Common activities include hand washing, counting of things, and checking to see if a door is locked. Some may have difficulty throwing things out. These activities occur to such a degree that the person's daily life is negatively affected. Often they take up more than an hour a day. Most adults realize that the behaviors do not make sense. The condition is associated with tics, anxiety disorder, and an increased risk of suicide.The cause is unknown. There appears to be some genetic components with identical twins more often affected than non-identical twins. Risk factors include a history of child abuse or other stress inducing event. Some cases have been documented to occur following infections. The diagnosis is based on the symptoms and requires ruling out other drug related or medical causes. Rating scales such as Yale–Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale can be used to assess the severity. Other disorders with similar symptoms include: anxiety disorder, major depressive disorder, eating disorders, tic disorders, and obsessive–compulsive personality disorder.Treatment for OCD involves the use of behavioral therapy and sometimes selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). The type of behavior therapy used involves increasing exposure to what causes the problems while not allowing the repetitive behavior to occur. Atypical antipsychotics such as quetiapine may be useful when used in addition to an SSRI in treatment-resistant cases but are associated with an increased risk of side effects. Without treament the condition often lasts decades.Obsessive–compulsive disorder affects about 2.3% of people at some point in their life. Rates during a given year are about 1.2% and it occurs worldwide. It is unusual for symptoms to begin after the age of thirty-five and half of people develop problems before twenty. Males and females are affected about equally. In English the phrase obsessive–compulsive is often used in an informal manner unrelated to OCD to describe someone who is excessively meticulous, perfectionistic, absorbed, or otherwise fixated.