Colitis There are several different types of Colitis, all of which are
... Crohn’s disease (affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract) Ulcerative colitis (affects only the colon, also known as the large intestine) Ischemic colitis (lack of sufficient blood supply to the colon) Infectious enterocolitis CMV colitis (a viral infection of the colon) Q. How is Colitis trea ...
... Crohn’s disease (affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract) Ulcerative colitis (affects only the colon, also known as the large intestine) Ischemic colitis (lack of sufficient blood supply to the colon) Infectious enterocolitis CMV colitis (a viral infection of the colon) Q. How is Colitis trea ...
PowerPoint
... 4.cobblestone appearance, combination of mucosal edema and criss-crossing ulceration Radiological signs of late stage of the disease are: 1.deep ulcers penetrating muscular layer (rose-thorn ulcers or deep fissures) 2.more extensive deep ulceration produce fistulae and abscess formation 3.strictures ...
... 4.cobblestone appearance, combination of mucosal edema and criss-crossing ulceration Radiological signs of late stage of the disease are: 1.deep ulcers penetrating muscular layer (rose-thorn ulcers or deep fissures) 2.more extensive deep ulceration produce fistulae and abscess formation 3.strictures ...
Relationships
... muscle. It passes posterior to the testicular/ovarian vessels. The left ureter is also crossed by the inferior mesenteric artery and vein. Then, it courses anterior to the bifurcation of the common iliac artery. It makes a sharp bend over the pelvic brim and courses to the bladder in the floor of th ...
... muscle. It passes posterior to the testicular/ovarian vessels. The left ureter is also crossed by the inferior mesenteric artery and vein. Then, it courses anterior to the bifurcation of the common iliac artery. It makes a sharp bend over the pelvic brim and courses to the bladder in the floor of th ...
Colon Cancer - GutCare.com
... presence of blood. The physician could collect a stool sample during a routine examination or the patient could collect a sample off spontaneously voided stool using ...
... presence of blood. The physician could collect a stool sample during a routine examination or the patient could collect a sample off spontaneously voided stool using ...
Parts
... --- “H” shaped groove: 4 lobes the right and left lobes, the caudate lobe, the quadrate lobe the fissure for ligamentum teres hepatis the fissure for ligamentum venosum the fossa for gallbladder the fossa for vena cava (the secondary porta hepatis ) ...
... --- “H” shaped groove: 4 lobes the right and left lobes, the caudate lobe, the quadrate lobe the fissure for ligamentum teres hepatis the fissure for ligamentum venosum the fossa for gallbladder the fossa for vena cava (the secondary porta hepatis ) ...
digestive system
... peritoneum Serous membranes lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities and covers the related organs. It is attached to the stomach curves. Lesser omentum; attaches the liver to the lesser curvature. Greater omentum; attaches the greater curvature to the transverse colon, and then to the poste ...
... peritoneum Serous membranes lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities and covers the related organs. It is attached to the stomach curves. Lesser omentum; attaches the liver to the lesser curvature. Greater omentum; attaches the greater curvature to the transverse colon, and then to the poste ...
intestine rectum aorta vena cava
... • Is the longest part of the gastrointesAnal tract - length of 5 metres (3–7 metres) in the living adult • Consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum • Extends from the pyloric opening to the ileocecal juncAon • Is the locaAon of complete digesAon and absorpAon of most of the products of ...
... • Is the longest part of the gastrointesAnal tract - length of 5 metres (3–7 metres) in the living adult • Consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum • Extends from the pyloric opening to the ileocecal juncAon • Is the locaAon of complete digesAon and absorpAon of most of the products of ...
digestive sys 212 (M..
... peritoneum Serous membranes lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities and covers the related organs. It is attached to the stomach curves. Lesser omentum; attaches the liver to the lesser curvature. Greater omentum; attaches the greater curvature to the transverse colon, and then to the poste ...
... peritoneum Serous membranes lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities and covers the related organs. It is attached to the stomach curves. Lesser omentum; attaches the liver to the lesser curvature. Greater omentum; attaches the greater curvature to the transverse colon, and then to the poste ...
Intestinal Obstruction
... • Mixed OR Incomplete rotation :2nd common rotational abnormalities . Chch. By arrest of normal rotational process or at near 180 degree Prearterial segment has failed to complete its rotation post. & Lt. of the SMA . Cecum resides in the upper abdomen (usually Lt. to the SMApertoneal band ) . ...
... • Mixed OR Incomplete rotation :2nd common rotational abnormalities . Chch. By arrest of normal rotational process or at near 180 degree Prearterial segment has failed to complete its rotation post. & Lt. of the SMA . Cecum resides in the upper abdomen (usually Lt. to the SMApertoneal band ) . ...
Abdominal Viscera Basics - Page 1 of 10 Learning Modules
... cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon. The cecum receives the contents of the ileum at the ileocecal junction, and the vermiform appendix is attached to the cecum posteroinferiorly. The ascending colon bends to the left at the hepatic or right colic flexure to ...
... cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon. The cecum receives the contents of the ileum at the ileocecal junction, and the vermiform appendix is attached to the cecum posteroinferiorly. The ascending colon bends to the left at the hepatic or right colic flexure to ...
File
... mesentery of small intestine by a short mesentery (mesoappendix) that contains appendicular vessels and nerves. Arteries: appendicular artery (branch of ...
... mesentery of small intestine by a short mesentery (mesoappendix) that contains appendicular vessels and nerves. Arteries: appendicular artery (branch of ...
large - Radiology - University of South Carolina
... Pyloric Stenosis is seen in newborns within the first months. There is a 4:1 male ratio and is due to hypertrophied musculature at the pylorus. ...
... Pyloric Stenosis is seen in newborns within the first months. There is a 4:1 male ratio and is due to hypertrophied musculature at the pylorus. ...
******* 1
... are chronic inflammatory bowel disease which have relapsing and limiting course. The major types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC). ...
... are chronic inflammatory bowel disease which have relapsing and limiting course. The major types of IBD are Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC). ...
What is Colorectal Cancer
... world it is the third most common cancer type. Usually it originates from adenomatous polyps in colon. It creates 10-15% of all cancers and it is the most common type among gastrointestinal system (digestive system) cancers. It is the second common cause of death among men following lung cancer and ...
... world it is the third most common cancer type. Usually it originates from adenomatous polyps in colon. It creates 10-15% of all cancers and it is the most common type among gastrointestinal system (digestive system) cancers. It is the second common cause of death among men following lung cancer and ...
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis
... intestine. This is the long, thin segment of bowel that begins at the stomach and ends in the right lower abdomen. After the digestive process is complete, the liquid waste enters the 5 feet of large intestine, or colon, which ends in the rectum. Just above the rectum is the sigmoid (s-shaped) part ...
... intestine. This is the long, thin segment of bowel that begins at the stomach and ends in the right lower abdomen. After the digestive process is complete, the liquid waste enters the 5 feet of large intestine, or colon, which ends in the rectum. Just above the rectum is the sigmoid (s-shaped) part ...
The digestive system
... Formation of the rectum and the separation of urogenital sinus from the cloaca; Rotation gastric to horizontal position; Intestinal elongation and turning it counterclockwise. ...
... Formation of the rectum and the separation of urogenital sinus from the cloaca; Rotation gastric to horizontal position; Intestinal elongation and turning it counterclockwise. ...
Total Mesorectal Excision: Tips and Techniques.
... mobilized by lateral to medial approach, begin at 2 mm anterior to the white line of Toldt. The left side colon was mobilized by lateral to medial approach, begin at 2 mm. above the white line of Toldt. By extending this plane upwardly, the splenic flexure was mobilized as in laparoscopic surgery. M ...
... mobilized by lateral to medial approach, begin at 2 mm anterior to the white line of Toldt. The left side colon was mobilized by lateral to medial approach, begin at 2 mm. above the white line of Toldt. By extending this plane upwardly, the splenic flexure was mobilized as in laparoscopic surgery. M ...
529773.FEBS_abstract__Ana_Savic
... investigated by quantitative real-time PCR (TaqMan). The outcome of the first treatment course was studied in one patient after 3 months. Results: There is regional variation of ABC transporters in gastrointestinal tract, but in general localization did not differ between IBD patients and controls. ...
... investigated by quantitative real-time PCR (TaqMan). The outcome of the first treatment course was studied in one patient after 3 months. Results: There is regional variation of ABC transporters in gastrointestinal tract, but in general localization did not differ between IBD patients and controls. ...
Abdomen
... Largest vein in the body Carries blood to the heart from the lower limbs, pelvic organs and abdomen L5- is formed by the common iliac veins Ascends superiorly through the retroperitoneum along the anterior verterbal column to the RT of the AO. Renal veins- empty into IVC @ L2 Lt renal vein- poster ...
... Largest vein in the body Carries blood to the heart from the lower limbs, pelvic organs and abdomen L5- is formed by the common iliac veins Ascends superiorly through the retroperitoneum along the anterior verterbal column to the RT of the AO. Renal veins- empty into IVC @ L2 Lt renal vein- poster ...
Human Digestive System Anatomy
... in the walls of the passage way are responsible for peristalsis. You will view the regions along this tube that are specialized for various activities of the digestive system. Path of Air Since the paths of air and food are closely associated, let's also trace the path of air through the head and ne ...
... in the walls of the passage way are responsible for peristalsis. You will view the regions along this tube that are specialized for various activities of the digestive system. Path of Air Since the paths of air and food are closely associated, let's also trace the path of air through the head and ne ...
MBS 101-B
... Rectus abdominis muscle plays an important role in each of following Except: a) Parturition b) Defecation c) Micturition d) Extension of trunk ...
... Rectus abdominis muscle plays an important role in each of following Except: a) Parturition b) Defecation c) Micturition d) Extension of trunk ...
25 The peritoneum
... !1 The superior wall of the abdominal cavity, separating it from the thoracic cavity, is: the diaphragm #the transverse colon the lesser omentum the liver ! The anterior wall of the abdominal cavity is formed by: the tendinous expansions of the three broad abdominal muscles and the rectus abdominis ...
... !1 The superior wall of the abdominal cavity, separating it from the thoracic cavity, is: the diaphragm #the transverse colon the lesser omentum the liver ! The anterior wall of the abdominal cavity is formed by: the tendinous expansions of the three broad abdominal muscles and the rectus abdominis ...
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis
... Diverticula seem to occur when the pressure inside the colon is too high. There are several ways this pressure may become high. The main cause of high pressure appears to be too little fiber in the diet. Fiber helps keep digested food bulky and soft as it passes through the colon. This makes it easi ...
... Diverticula seem to occur when the pressure inside the colon is too high. There are several ways this pressure may become high. The main cause of high pressure appears to be too little fiber in the diet. Fiber helps keep digested food bulky and soft as it passes through the colon. This makes it easi ...
Abdominal Assessment
... Gallbladder: aids in fat digestion and concentrates/stores bile produced by the liver. Pancreas: produces digestive enzymes, secretes insulin/glucagon/somatostatin to control blood sugar levels Spleen: stores and produces lymphocytes ...
... Gallbladder: aids in fat digestion and concentrates/stores bile produced by the liver. Pancreas: produces digestive enzymes, secretes insulin/glucagon/somatostatin to control blood sugar levels Spleen: stores and produces lymphocytes ...
Anatomy Abdomen Forum 2012
... Patient A – 42 yearold male presenting after trying to move his dishwasher ...
... Patient A – 42 yearold male presenting after trying to move his dishwasher ...
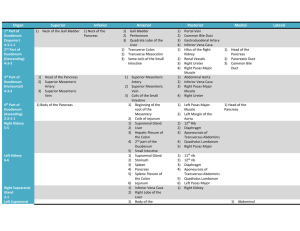
Large intestine
The large intestine, also called the colon or the large bowel, is the last part of the digestive system in vertebrates. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored as feces before being removed by defecation.Terminologia Anatomica, Medscape, and Gray's Anatomy define the large intestine as the combination of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. Other sources, such as Mosby's Medical Dictionary and the Oxford Dictionaries of Medicine and Biology exclude the anal canal. In humans, it begins in the right iliac region of the pelvis, just at or below the waist, where it is joined to the end of the small intestine. It then continues up the abdomen, across the width of the abdominal cavity, and then down to its endpoint at the anus. Overall, in humans, the large intestine is about 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) long, which is about one-fifth of the whole length of the gastrointestinal tract