Acidification of Urine
... • When a strong acid is added to the blood, the major buffer reactions are driven to the left. • The blood levels of the three "buffer anions" Hb– (hemoglobin), Prot– (protein), and HCO3– consequently drop. • The anions of the added acid are filtered into the renal tubules. • They are accompanied (" ...
... • When a strong acid is added to the blood, the major buffer reactions are driven to the left. • The blood levels of the three "buffer anions" Hb– (hemoglobin), Prot– (protein), and HCO3– consequently drop. • The anions of the added acid are filtered into the renal tubules. • They are accompanied (" ...
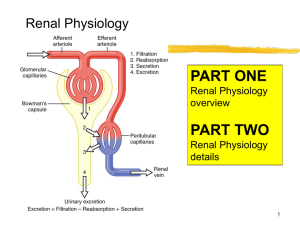
13 Renal Clearance overview
... (PCT), down the loop of Henle and back up, then into the distal convoluted tubule (DCT), and into the collecting duct. In the PCT, the nutrients are reabsorbed. If there are more nutrients than can be reabsorbed (such as excess sugar), it will be excreted in the urine. When the nutrients in the ...
... (PCT), down the loop of Henle and back up, then into the distal convoluted tubule (DCT), and into the collecting duct. In the PCT, the nutrients are reabsorbed. If there are more nutrients than can be reabsorbed (such as excess sugar), it will be excreted in the urine. When the nutrients in the ...
The Laws of Thermodynamics
... Temperature and the Zeroth law of Thermodynamics We all know that a glass of ice water (ice and water) will eventually warm to room temperature if left out, melting the ice in the process. And a cup of hot tea will eventually cool to room temperature. But what is this thing we call "temperature"? I' ...
... Temperature and the Zeroth law of Thermodynamics We all know that a glass of ice water (ice and water) will eventually warm to room temperature if left out, melting the ice in the process. And a cup of hot tea will eventually cool to room temperature. But what is this thing we call "temperature"? I' ...
Student worksheet
... 1. Chose one of the liquids and measure 2 mL into the 10 mL graduated cylinder. Chose a second liquid and carefully pour 2 mL of this liquid into the same cylinder. Observe what happens. Carefully pour 2mL of the third liquid in on top of the other two and observe what happens. Sketch, label, and co ...
... 1. Chose one of the liquids and measure 2 mL into the 10 mL graduated cylinder. Chose a second liquid and carefully pour 2 mL of this liquid into the same cylinder. Observe what happens. Carefully pour 2mL of the third liquid in on top of the other two and observe what happens. Sketch, label, and co ...
Secretion
... Descending Limb LH • Deeper regions of medulla reach 1400 mOsm/L. • Impermeable to passive diffusion of NaCl. • Permeable to H20. • Hypertonic interstitial fluid causes H20 movement out of the descending limb via osmosis, and H20 enters capillaries. • Fluid volume decreases in tubule, causing highe ...
... Descending Limb LH • Deeper regions of medulla reach 1400 mOsm/L. • Impermeable to passive diffusion of NaCl. • Permeable to H20. • Hypertonic interstitial fluid causes H20 movement out of the descending limb via osmosis, and H20 enters capillaries. • Fluid volume decreases in tubule, causing highe ...
Physics 2
... 11. Compressed air in the tube of a wheel of a cycle at normal temperature suddenly starts coming out from a puncture. The air inside. [NCERT 1970] Starts becoming hotter ...
... 11. Compressed air in the tube of a wheel of a cycle at normal temperature suddenly starts coming out from a puncture. The air inside. [NCERT 1970] Starts becoming hotter ...
Integrative Sciences: Biological Systems B
... calculate the filtered load, tubular transport, and excretion rate of a given compound. Given the appropriate plasma and urine concentrations and the urine flow, calculate the clearance of inulin, creatinine, para-amino hippuric acid (PAH), and glucose. Predict how changes in filtration, reabsorptio ...
... calculate the filtered load, tubular transport, and excretion rate of a given compound. Given the appropriate plasma and urine concentrations and the urine flow, calculate the clearance of inulin, creatinine, para-amino hippuric acid (PAH), and glucose. Predict how changes in filtration, reabsorptio ...
Countercurrent exchange

Countercurrent exchange is a mechanism occurring in nature and mimicked in industry and engineering, in which there is a crossover of some property, usually heat or some component, between two flowing bodies flowing in opposite directions to each other. The flowing bodies can be liquids, gases, or even solid powders, or any combination of those. For example, in a distillation column, the vapors bubble up through the downward flowing liquid while exchanging both heat and mass.The maximum amount of heat or mass transfer that can be obtained is higher with countercurrent than co-current (parallel) exchange because countercurrent maintains a slowly declining difference or gradient (usually temperature or concentration difference). In cocurrent exchange the initial gradient is higher but falls off quickly, leading to wasted potential. For example, in the diagram at the right, the fluid being heated (exiting top) has a higher exiting temperature than the cooled fluid (exiting bottom) that was used for heating. With cocurrent or parallel exchange the heated and cooled fluids can only approach one another. The result is that countercurrent exchange can achieve a greater amount of heat or mass transfer than parallel under otherwise similar conditions. See: flow arrangement.Countercurrent exchange when set up in a circuit or loop can be used for building up concentrations, heat, or other properties of flowing liquids. Specifically when set up in a loop with a buffering liquid between the incoming and outgoing fluid running in a circuit, and with active transport pumps on the outgoing fluid's tubes, the system is called a Countercurrent multiplier, enabling a multiplied effect of many small pumps to gradually build up a large concentration in the buffer liquid.Other countercurrent exchange circuits where the incoming and outgoing fluids touch each other are used for retaining a high concentration of a dissolved substance or for retaining heat, or for allowing the external buildup of the heat or concentration at one point in the system.Countercurrent exchange circuits or loops are found extensively in nature, specifically in biologic systems. In vertebrates, they are called a Rete mirabile, originally the name of an organ in fish gills for absorbing oxygen from the water. It is mimicked in industrial systems. Countercurrent exchange is a key concept in chemical engineering thermodynamics and manufacturing processes, for example in extracting sucrose from sugar beet roots.Countercurrent multiplication is a similar but different concept where liquid moves in a loop followed by a long length of movement in opposite directions with an intermediate zone. The tube leading to the loop passively building up a gradient of heat (or cooling) or solvent concentration while the returning tube has a constant small pumping action all along it, so that a gradual intensification of the heat or concentration is created towards the loop. Countercurrent multiplication has been found in the kidneys as well as in many other biological organs.