Cardiovascular Physiology 2016
... the passage from the resting to active state is a function of the length of the fiber.” ...
... the passage from the resting to active state is a function of the length of the fiber.” ...
release hormones - Lone Star College
... Actions of Steroid Hormones • hormone crosses membranes • hormone combines with receptor in nucleus • synthesis of mRNA activated ...
... Actions of Steroid Hormones • hormone crosses membranes • hormone combines with receptor in nucleus • synthesis of mRNA activated ...
Physiologic changes of pregnancy lect 2
... By 38 weeks the cervix is taken up into the lower segment ...
... By 38 weeks the cervix is taken up into the lower segment ...
Respiratory Physio Detailed File
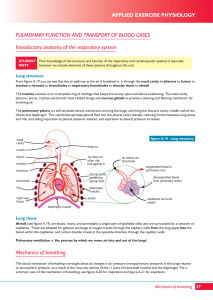
... • Pulmonary ventilation (breathing): movement of air into and out of the lungs • External respiration: O2 and CO2 exchange between the lungs and the blood • Transport: O2 and CO2 in the blood • Internal respiration: O2 and CO2 exchange between systemic blood vessels and tissues ...
... • Pulmonary ventilation (breathing): movement of air into and out of the lungs • External respiration: O2 and CO2 exchange between the lungs and the blood • Transport: O2 and CO2 in the blood • Internal respiration: O2 and CO2 exchange between systemic blood vessels and tissues ...
Diffusion, Blood O2, CO2 Content and Transport
... itself a greater blood perfusion during higher metabolic activity (active hyperemia). The cerebral and coronary vasculature also exploits the CO2 vascular resistancelowering actions in autoregulaton to maintain a relatively constant blood flow. The pulmonary circulation represents the entire cardiac ...
... itself a greater blood perfusion during higher metabolic activity (active hyperemia). The cerebral and coronary vasculature also exploits the CO2 vascular resistancelowering actions in autoregulaton to maintain a relatively constant blood flow. The pulmonary circulation represents the entire cardiac ...
Annelida By: Omar Abdulkader, Marcus Bray
... • Instead muscles work against the noncompressible fluid of the coelom. (hydrostatic skeleton) ...
... • Instead muscles work against the noncompressible fluid of the coelom. (hydrostatic skeleton) ...
colloid osmotic pressures
... • The greater the viscosity , the greater the resistance to flow. the thicker a liquid , the more viscous it is. viscosity of blood is determined by two factors: (1) the concentration of plasma proteins (2) the number of circulating red blood cells ...
... • The greater the viscosity , the greater the resistance to flow. the thicker a liquid , the more viscous it is. viscosity of blood is determined by two factors: (1) the concentration of plasma proteins (2) the number of circulating red blood cells ...
2. Physiology_Respiratory_System
... ♦ The pressure in the airway becomes slightly positive, and airflows out of the lungs ♦ Strong inspiratory efforts reduce intrapleural pressure to values as low as - 30mm Hg, producing correspondingly greater degrees of lung inflation Since in the question we are not dealing with normal inspiration ...
... ♦ The pressure in the airway becomes slightly positive, and airflows out of the lungs ♦ Strong inspiratory efforts reduce intrapleural pressure to values as low as - 30mm Hg, producing correspondingly greater degrees of lung inflation Since in the question we are not dealing with normal inspiration ...
Annelida 2010 - The Bronx High School of Science
... •parapodia are fleshy paddle-like extensions •highly vascularized for gas exchange •used as gills & for locomotion •reproduction •lack clitellum •free-swimming trochophore larva •mostly marine ...
... •parapodia are fleshy paddle-like extensions •highly vascularized for gas exchange •used as gills & for locomotion •reproduction •lack clitellum •free-swimming trochophore larva •mostly marine ...
chapter 21 electrolyte balance
... release sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, sulfate, phosphate, bicarbonate, and hydrogen ions • These ions are primarily obtained from foods, but some are from water and other beverages ...
... release sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, sulfate, phosphate, bicarbonate, and hydrogen ions • These ions are primarily obtained from foods, but some are from water and other beverages ...
Hypovolemic Shock
... myocardial function, and vascular stability are all determinants of effective systemic cardiovascular function. If any one of these factors is impaired by illness or injury, the body will attempt to compensate and normalize perfusion through modification of other physiologic components. This is refl ...
... myocardial function, and vascular stability are all determinants of effective systemic cardiovascular function. If any one of these factors is impaired by illness or injury, the body will attempt to compensate and normalize perfusion through modification of other physiologic components. This is refl ...
Embryonic Adaptations
... of the embryo. By 60 hours of incubation the heart begins to beat and blood circulates to and from the yolk. ...
... of the embryo. By 60 hours of incubation the heart begins to beat and blood circulates to and from the yolk. ...
HYPOXIA (Dombrovský P., Rácz O.
... concentration of oxygen in blood. However, there can exist also hypoxia without hypoxemia. Hypercapnia (elevated concentration of CO2 in blood) is frequently found in hypoxic state, but not in every case. Sometimes hypoxia even can be accomapnied by hypocapnia (Tabs. 12.1 and 12.2) The consequences ...
... concentration of oxygen in blood. However, there can exist also hypoxia without hypoxemia. Hypercapnia (elevated concentration of CO2 in blood) is frequently found in hypoxic state, but not in every case. Sometimes hypoxia even can be accomapnied by hypocapnia (Tabs. 12.1 and 12.2) The consequences ...
Blood Pressure and Pulse BIOL 204, Section 550 Lab Report By
... DISCUSSION The experiments proved to be quite informative when the data is compared to the various hypotheses. To analyze this further, several pathways based on the Mean Arterial Pressure, or MAP, can explain the blood pressure and pulse changes during the experiments. MAP, as stated in the introdu ...
... DISCUSSION The experiments proved to be quite informative when the data is compared to the various hypotheses. To analyze this further, several pathways based on the Mean Arterial Pressure, or MAP, can explain the blood pressure and pulse changes during the experiments. MAP, as stated in the introdu ...
Respiratory Physiology
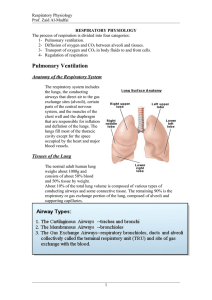
... conducting airways, alveoli, and blood supply. • Conducting airways enable air to reach alveoli and warm and humidify the air. • Alveoli are blind sacs where gases in the inspired air exchange with the blood. • Blood supply provides the heat and moisture to warm and humidify the inspired air and the ...
... conducting airways, alveoli, and blood supply. • Conducting airways enable air to reach alveoli and warm and humidify the air. • Alveoli are blind sacs where gases in the inspired air exchange with the blood. • Blood supply provides the heat and moisture to warm and humidify the inspired air and the ...
Respiratory physiology
... The blood volume of the lungs is about 450 milliliters, about 9 per cent of the total blood volume of the entire circulatory system. Approximately 70 milliliters of this pulmonary blood volume is in the pulmonary capillaries, and the remainder is divided about equally between the pulmonary arteries ...
... The blood volume of the lungs is about 450 milliliters, about 9 per cent of the total blood volume of the entire circulatory system. Approximately 70 milliliters of this pulmonary blood volume is in the pulmonary capillaries, and the remainder is divided about equally between the pulmonary arteries ...
Ch 27: Molluscs and Annelids
... Clam – How it eats Incurrent siphon pulls water across gills Food particles stick to gills Coordinated cilia move food to mouth Food is stored/digested in stomach and intestines Solid wastes exit via the anus ...
... Clam – How it eats Incurrent siphon pulls water across gills Food particles stick to gills Coordinated cilia move food to mouth Food is stored/digested in stomach and intestines Solid wastes exit via the anus ...
Document
... Homeostasis is so important that most disease can be regarded as a result of its disturbance, a condition called homeostatic imbalance. As we age, our body’s control systems become less efficient, and our internal environment becomes less and less stable. These events increase our risk for illness a ...
... Homeostasis is so important that most disease can be regarded as a result of its disturbance, a condition called homeostatic imbalance. As we age, our body’s control systems become less efficient, and our internal environment becomes less and less stable. These events increase our risk for illness a ...
Internal transport
... •Acoelomates have mesoderm but no body cavity. •Movement squeezes & distorts the body, restricting the flow of nutrients and other materials •Have no circulatory system. Must rely either on diffusion or on muscle contractions for the transport of nutrients, respiratory gases, and waste products aro ...
... •Acoelomates have mesoderm but no body cavity. •Movement squeezes & distorts the body, restricting the flow of nutrients and other materials •Have no circulatory system. Must rely either on diffusion or on muscle contractions for the transport of nutrients, respiratory gases, and waste products aro ...
Inotropes - GEOCITIES.ws
... • Arginine vasopressin is a synthetic analogue of ADH, which is produced by posterior pituitary • AVP causes vasoconstriction by direct stimulation of smooth muscle V1 receptors • No increase in myocardial oxygen consumption as no beta effects • Rapid onset with duration of action of 10-20 ...
... • Arginine vasopressin is a synthetic analogue of ADH, which is produced by posterior pituitary • AVP causes vasoconstriction by direct stimulation of smooth muscle V1 receptors • No increase in myocardial oxygen consumption as no beta effects • Rapid onset with duration of action of 10-20 ...