Chapter 9 Geometry: Transformations, Congruence and Similarity
... A mapping (or transformation T of the plane is a correspondence that has the property that different points go to different points; that is, for two points P , Q we must also have T (P) , T (Q). This is in fact just what a map does: it takes a piece of the surface of the earth and represents it, poi ...
... A mapping (or transformation T of the plane is a correspondence that has the property that different points go to different points; that is, for two points P , Q we must also have T (P) , T (Q). This is in fact just what a map does: it takes a piece of the surface of the earth and represents it, poi ...
Geometry III/IV
... impossible since the sum of angles of a triangle should be smaller than π. If l3 does not intersect l4 then l1 , l2 , l3 , l4 bound a quadrilateral with four right angles, which is also impossible (the sum of angles of a quadrilateral should be smaller than 2π). This implies that at least one of the ...
... impossible since the sum of angles of a triangle should be smaller than π. If l3 does not intersect l4 then l1 , l2 , l3 , l4 bound a quadrilateral with four right angles, which is also impossible (the sum of angles of a quadrilateral should be smaller than 2π). This implies that at least one of the ...
GEOMETRY Advanced Constructions OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.13
... Endpoint: A point marking either end of a line segment. Equidistant: Two points that are the same distance from a given point. Hexagon: A polygon with six sides. Line: An undefined term that extends in one dimension, which is usually represented by a straight line with two arrowheads. Line ...
... Endpoint: A point marking either end of a line segment. Equidistant: Two points that are the same distance from a given point. Hexagon: A polygon with six sides. Line: An undefined term that extends in one dimension, which is usually represented by a straight line with two arrowheads. Line ...
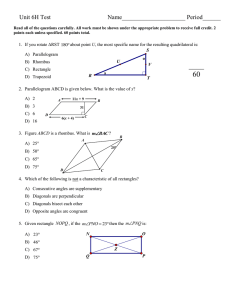
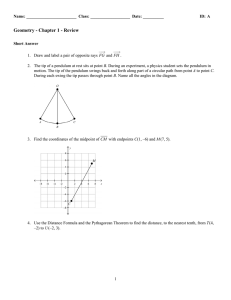
Unit 1 Review
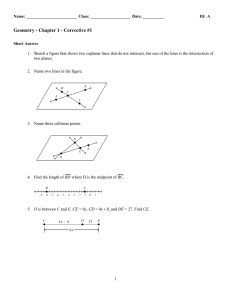
... ____ 25. a method of creating a figure that is considered to be mathematically precise ____ 26. given three points A, B, and C, B is between A and C if and only if all three of the points lie on the same line, and AB + BC = AC ____ 27. a plane that is divided into four regions by a horizontal line c ...
... ____ 25. a method of creating a figure that is considered to be mathematically precise ____ 26. given three points A, B, and C, B is between A and C if and only if all three of the points lie on the same line, and AB + BC = AC ____ 27. a plane that is divided into four regions by a horizontal line c ...