Need help with a new Telescope?
... to straighten them. This gives an inverted image, which is usually not a problem. ...
... to straighten them. This gives an inverted image, which is usually not a problem. ...
Skymax-180 Review by Sky At Night Magazine
... I call the scope my ‘planet killer’! The best single upgrade I have made to the telescope was to add a Moonlite focuser. This has made a great telescope into an amazing one, as I take high-resolution lunar images and the focuser makes this a breeze to achieve, critical focus is important. After 30 y ...
... I call the scope my ‘planet killer’! The best single upgrade I have made to the telescope was to add a Moonlite focuser. This has made a great telescope into an amazing one, as I take high-resolution lunar images and the focuser makes this a breeze to achieve, critical focus is important. After 30 y ...
Clinical Techniques for Prescribing Bioptic Telescope
... the bioptic which provides your customary distance vision. • Look directly at the object you want to magnify. • Drop your head slightly and look up into the eyepiece. • You should see a full, round magnified image. • You may have to focus it to get the image clear. • Practice switching between the c ...
... the bioptic which provides your customary distance vision. • Look directly at the object you want to magnify. • Drop your head slightly and look up into the eyepiece. • You should see a full, round magnified image. • You may have to focus it to get the image clear. • Practice switching between the c ...
Astro 10 Practice Test 1
... c. Because they’ve been launched far out into space, they are beyond the pull of the Earth’s gravity. d. There actually is some gravity from the Earth there, but it has gotten so weak (due to distance from the Earth), that the astronauts can hardly notice it. 21. Which of the following is NOT a reas ...
... c. Because they’ve been launched far out into space, they are beyond the pull of the Earth’s gravity. d. There actually is some gravity from the Earth there, but it has gotten so weak (due to distance from the Earth), that the astronauts can hardly notice it. 21. Which of the following is NOT a reas ...
SOAR Spartan Infrared Camera E. Loh, MSU, July 2014
... E. Loh, MSU, July 2014 The Spartan Infrared Camera operates in the 1–2.4μm wavelength range. It has two focal ratios, a wide-field (WF) configuration with 66 mas/pixel a high-res (HR) configuration with 40 mas/pixel, which has not proved to be useful. The detectors are four HAWAII-2 arrays, each wit ...
... E. Loh, MSU, July 2014 The Spartan Infrared Camera operates in the 1–2.4μm wavelength range. It has two focal ratios, a wide-field (WF) configuration with 66 mas/pixel a high-res (HR) configuration with 40 mas/pixel, which has not proved to be useful. The detectors are four HAWAII-2 arrays, each wit ...
Sky News – March 2015 The Realm of the Galaxies
... M49, 60, and 87. These main bodies are surrounded by clouds of lesser galaxies. The galaxy M87 is an extremely massive galaxy that contains 2.7 trillion stars with a supermassive black hole at the centre. Visible in large amateur telescopes is one of the plasma jets emanating from the black hole and ...
... M49, 60, and 87. These main bodies are surrounded by clouds of lesser galaxies. The galaxy M87 is an extremely massive galaxy that contains 2.7 trillion stars with a supermassive black hole at the centre. Visible in large amateur telescopes is one of the plasma jets emanating from the black hole and ...
Sirius Astronomer - Orange County Astronomers
... Herschel (far infrared space telescope) has observed a dark spot in the sky next to the nebula NGC 1999, thought to be dust or gas obscuring any stars, but instead found it was empty. Dust would have appeared bright in infrared. Astronomers think that the hole must have been created when the narrow ...
... Herschel (far infrared space telescope) has observed a dark spot in the sky next to the nebula NGC 1999, thought to be dust or gas obscuring any stars, but instead found it was empty. Dust would have appeared bright in infrared. Astronomers think that the hole must have been created when the narrow ...
October - Sonoma County Astronomical Society
... Capodimonte in Naples, Italy. This newly discovered extrasolar planet is more than 3 times as large as Jupiter. It used to orbit its star, called V391 Pegasi, at about the same distance that Earth is from the sun. V391 Pegasi belongs to a rare class of stars, called B-type subdwarfs. It started out ...
... Capodimonte in Naples, Italy. This newly discovered extrasolar planet is more than 3 times as large as Jupiter. It used to orbit its star, called V391 Pegasi, at about the same distance that Earth is from the sun. V391 Pegasi belongs to a rare class of stars, called B-type subdwarfs. It started out ...
July - Westchester Amateur Astronomers
... “wobbles”—the gravitational tugs they exert on their central stars. Some are found when they transit the ...
... “wobbles”—the gravitational tugs they exert on their central stars. Some are found when they transit the ...
The Kunlun Infrared Sky Survey
... Race is now on to distinguish Einstein vacuum energy from other possible equations of state. Requires accumulation of hundreds of accurate SNIa measurements. SkyMapper (Schmidt et al. 2005) is devoted to this. ...
... Race is now on to distinguish Einstein vacuum energy from other possible equations of state. Requires accumulation of hundreds of accurate SNIa measurements. SkyMapper (Schmidt et al. 2005) is devoted to this. ...
8_StarGalaxiesUniversePP
... Star Clusters larger groupings stars belong to All stars in a cluster formed from the SAME nebula at about the SAME time and are about the SAME distance from Earth Open cluster loose, disorganized, only a few thousand stars Globular cluster large groupings of older stars ...
... Star Clusters larger groupings stars belong to All stars in a cluster formed from the SAME nebula at about the SAME time and are about the SAME distance from Earth Open cluster loose, disorganized, only a few thousand stars Globular cluster large groupings of older stars ...
December 2010 Clear Skies Newsletter PDF
... temperature, which characterizes its thermal emission to space, started to warm up or cool down as a change of season approached. Because Saturn’s weather is variable and the atmosphere tends to retain heat (called heat inertia), the temperature changes in complicated ways throughout the atmosphere. ...
... temperature, which characterizes its thermal emission to space, started to warm up or cool down as a change of season approached. Because Saturn’s weather is variable and the atmosphere tends to retain heat (called heat inertia), the temperature changes in complicated ways throughout the atmosphere. ...
Telescope Light Effects
... millions of kilometres away out in space. Refracting telescope uses a concave mirror, a plane mirror, and a convex lens to Magnify images. Telescopes use its lens to gather light and other electromagnetic radiation to bring that light or radiation to a focal point. The lens can make sure that the pi ...
... millions of kilometres away out in space. Refracting telescope uses a concave mirror, a plane mirror, and a convex lens to Magnify images. Telescopes use its lens to gather light and other electromagnetic radiation to bring that light or radiation to a focal point. The lens can make sure that the pi ...
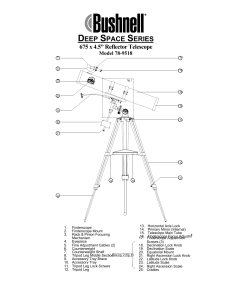
Deep Space
... will be UPSIDE DOWN and REVERSED, this is acceptable for viewing celestial bodies. Selecting an Eyepiece: 1. You should always start viewing with the lowest power eyepiece, which in this case is the 20 mm lens. Note: the base power of each eyepiece is determined by the focal length of the telescope ...
... will be UPSIDE DOWN and REVERSED, this is acceptable for viewing celestial bodies. Selecting an Eyepiece: 1. You should always start viewing with the lowest power eyepiece, which in this case is the 20 mm lens. Note: the base power of each eyepiece is determined by the focal length of the telescope ...
Herschel`s Telescopes
... Herschel’s two “workhorse” telescopes – those used for all his later various reviews of the heavens – were his 20-foot reflectors. The earlier and smaller of these in terms of aperture (referred to as the “Small 20-Foot”) used 12-inch mirrors, while the larger and later instrument (called the “Large ...
... Herschel’s two “workhorse” telescopes – those used for all his later various reviews of the heavens – were his 20-foot reflectors. The earlier and smaller of these in terms of aperture (referred to as the “Small 20-Foot”) used 12-inch mirrors, while the larger and later instrument (called the “Large ...
Astronomy - Bemidji State University
... The idea of a segmented mirror dated back to the 19th century, but experiments with it had been few and small, and many astronomers doubted its viability. It remained for the Keck Telescope to push the technology forward and bring into reality this innovative design. A binocular is a optical instrum ...
... The idea of a segmented mirror dated back to the 19th century, but experiments with it had been few and small, and many astronomers doubted its viability. It remained for the Keck Telescope to push the technology forward and bring into reality this innovative design. A binocular is a optical instrum ...
GEARS Workshop Monday - Georgia Southern University
... The Chandra data shows bright X-ray sources in this field, most of which are young stars. In this image, red, green, and blue represent low, medium, and high energy X-rays. The Chandra data have been overlaid on the Hubble Space Telescope image to show the context of these X-ray data. Very few X-ray ...
... The Chandra data shows bright X-ray sources in this field, most of which are young stars. In this image, red, green, and blue represent low, medium, and high energy X-rays. The Chandra data have been overlaid on the Hubble Space Telescope image to show the context of these X-ray data. Very few X-ray ...
Telescopes: More Than Meets the Eye
... concentrate it together and therefore make faint objects appear brighter. The larger the aperature of a telescope the greater the light gathering capabilities it has. Light Year: A light year is the distance that a beam of light will travel in one years time. Light travels at 186,000 miles per secon ...
... concentrate it together and therefore make faint objects appear brighter. The larger the aperature of a telescope the greater the light gathering capabilities it has. Light Year: A light year is the distance that a beam of light will travel in one years time. Light travels at 186,000 miles per secon ...
Ch 5 notes on telescopes
... 1. Can be used in tandem 2. Interferometry – a technique that makes it possible to produce radio images of angular resolution higher than the best optical telescopes v. Advantages: ...
... 1. Can be used in tandem 2. Interferometry – a technique that makes it possible to produce radio images of angular resolution higher than the best optical telescopes v. Advantages: ...
Exploring Chile, the Astronomy Capital of the World
... This panoramic view of the Chajnantor Plateau shows the site of the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), taken from near the peak of Cerro Chico [ESO/B. Tafreshi (twanight.org)] astronomy as we know it. Its mirror will be only a little larger than Gemini’s 8 meters, but the LSST is ...
... This panoramic view of the Chajnantor Plateau shows the site of the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), taken from near the peak of Cerro Chico [ESO/B. Tafreshi (twanight.org)] astronomy as we know it. Its mirror will be only a little larger than Gemini’s 8 meters, but the LSST is ...
TWINKLE – A Low Earth Orbit Visible and Infrared Exoplanet
... highly stable instrument will allow the photometric and spectroscopic observation of a wide range of planetary classes around different types of stars, with a focus on bright sources close to the ecliptic. The planets will be observed through transit and eclipse photometry and spectroscopy, as well ...
... highly stable instrument will allow the photometric and spectroscopic observation of a wide range of planetary classes around different types of stars, with a focus on bright sources close to the ecliptic. The planets will be observed through transit and eclipse photometry and spectroscopy, as well ...
Overview of Technologies for Direct Optical Imaging of Exoplanets
... pursued a vigorous technology program and funded studies to evaluate concepts using direct optical imaging and mid-infra red interferometry, which together, provide definitive characterization of planets. Designs operating at visible wavelengths offer several advantages. At shorter wavelengths, a sm ...
... pursued a vigorous technology program and funded studies to evaluate concepts using direct optical imaging and mid-infra red interferometry, which together, provide definitive characterization of planets. Designs operating at visible wavelengths offer several advantages. At shorter wavelengths, a sm ...
Eyles, Bunker, Ellis et al. astro-ph/0607306 Eyles, Bunker, Ellis et al
... -- In Stark, Bunker, Ellis et al. (2007) we look at vdrops (z~5) in the GOODS-South -- In Eyles, Bunker, Ellis et al. (2007) we survey all the ...
... -- In Stark, Bunker, Ellis et al. (2007) we look at vdrops (z~5) in the GOODS-South -- In Eyles, Bunker, Ellis et al. (2007) we survey all the ...
James Webb Space Telescope

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), previously known as Next Generation Space Telescope (NGST), is a space observatory under construction and scheduled to launch in October 2018. The JWST will offer unprecedented resolution and sensitivity from long-wavelength visible to the mid-infrared, and is a successor instrument to the Hubble Space Telescope and the Spitzer Space Telescope. The telescope features a segmented 6.5-meter (21 ft) diameter primary mirror and will be located near the Earth–Sun L2 point. A large sunshield will keep its mirror and four science instruments below 50 K (−220 °C; −370 °F).JWST's capabilities will enable a broad range of investigations across the fields of astronomy and cosmology. One particular goal involves observing some of the most distant objects in the Universe, beyond the reach of current ground and space based instruments. This includes the very first stars, the epoch of reionization, and the formation of the first galaxies. Another goal is understanding the formation of stars and planets. This will include imaging molecular clouds and star-forming clusters, studying the debris disks around stars, direct imaging of planets, and spectroscopic examination of planetary transits.In gestation since 1996, the project represents an international collaboration of about 17 countries led by NASA, and with significant contributions from the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. It is named after James E. Webb, the second administrator of NASA, who played an integral role in the Apollo program.The JWST has a history of major cost overruns and delays. The first realistic budget estimates were that the observatory would cost $1.6 billion and launch in 2011. NASA has now scheduled the telescope for a 2018 launch. In 2011, the United States House of Representatives voted to terminate funding, after about $3 billion had been spent and 75 percent of its hardware was in production. Funding was restored in compromise legislation with the US Senate, and spending on the program was capped at $8 billion. As of December 2014, the telescope remained on schedule and within budget, but at risk of further delays.