* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Telescope Light Effects
Arecibo Observatory wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Lovell Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Allen Telescope Array wikipedia , lookup
CfA 1.2 m Millimeter-Wave Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
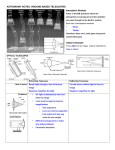
By Mitchell Round History of Telescopes The earliest evidence of working telescopes were the refracting telescopes that appeared in the Netherlands in 1608. Their development is credited to three individuals: Hans Lippershey and Zacharias Janssen, who were spectacle makers in Middelburg, and Jacob Metius of Alkmaar. Galileo greatly improved upon these designs the following year. What a telescope does A telescope is used to view things that are millions of kilometres away out in space. Refracting telescope uses a concave mirror, a plane mirror, and a convex lens to Magnify images. Telescopes use its lens to gather light and other electromagnetic radiation to bring that light or radiation to a focal point. The lens can make sure that the picture is not distorted on its way back. Development The 20th century also saw the development of telescopes that worked in a wide range of wavelengths from radio to gamma-rays. The first purpose built radio telescope went into operation in 1937. Since then, a tremendous variety of complex astronomical instruments have been developed. The maximum physical size limit for refracting telescopes is about 1 meter , Showing that the Most of the large optical researching telescopes built since the 20th century have been reflectors. Types of telescopes The largest reflecting telescopes currently have objectives larger then 10 m. The invention of the achromatic lens in 1733 partially corrected colour problems in the simple lens and enabled the construction of shorter, more functional refracting telescopes. Reflecting telescopes, though not limited by the colour problems seen in refractors, were hampered by the use of fast breaking metal mirrors employed during the 18th and early 19th century a problem fixed by the introduction of silver coated glass mirrors in 1857 and aluminized mirrors in 1932. There are optical telescopes, Radio telescopes and High energy particle telescopes. Lenses Telescopes can use concave lenses. They use concave lenses because they can see further and they can get a better image back instead of convex lenses which are used in microscopes. Concave lenses are used in telescopes and glasses. Concave lenses are thinner in the middle than at the edges. When light passes through concave lenses it always bend away from each other toward the edges of the lens. Diagram of how a telescope works Bibliography Info from : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telescope Pictures from : http://images.google.com.au/imghp?hl=e n&tab=wi Diagram from: http://www.math.ubc.ca/~cass/courses/ m309-01a/chu/Applications/apps.htm