1 - KopyKitab.com
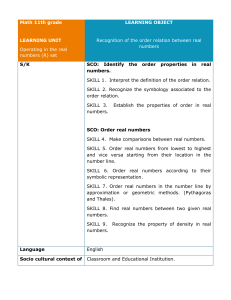
... 2. Examples of non-recurring/non-terminating decimals. Existence of non-rational numbers (irrational numbers) such as 2, 3 and their representation on the number line. Explaining that every real number is represented by a unique point on the number line and conversely, viz. every point on the number ...
... 2. Examples of non-recurring/non-terminating decimals. Existence of non-rational numbers (irrational numbers) such as 2, 3 and their representation on the number line. Explaining that every real number is represented by a unique point on the number line and conversely, viz. every point on the number ...
1-2 - Plain Local Schools
... First substitute –14 for x. To subtract –12, add 12. When the signs of the numbers are different, find the difference of the absolute values: 14 – 12 = 2. ...
... First substitute –14 for x. To subtract –12, add 12. When the signs of the numbers are different, find the difference of the absolute values: 14 – 12 = 2. ...
Problem Solving
... Can You Just Tell Me How Old Your Children Are! 11. A student asked his math teacher, “How many children do you have, and how old are they?” “I have 3 girls,” replied the teacher. “The product of their ages is 72, and the sum of their ages is the same as the room number of this classroom.” Knowing ...
... Can You Just Tell Me How Old Your Children Are! 11. A student asked his math teacher, “How many children do you have, and how old are they?” “I have 3 girls,” replied the teacher. “The product of their ages is 72, and the sum of their ages is the same as the room number of this classroom.” Knowing ...